
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological species. A series of Regional Red Lists, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit, are also produced by countries and organizations.

Babcary Meadows is a 13.6 hectares biological Site of Special Scientific Interest north of Babcary in Somerset, notified in 1988.

Pulicaria aromatica is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only on the island of Socotra in Yemen. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and rocky areas.

Pulicaria is a genus of flowering plant in the sunflower family, native to Europe, Asia, and Africa. In North America Pulicaria is known by the common name false fleabane.
Pulicaria dioscorides is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only on the island of Socotra in Yemen. Its natural habitat is rocky areas.
Pulicaria diversifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae.It is found only on the islands of Socotra and Samhah in Yemen. Its natural habitat is rocky areas.
Pulicaria elegans is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only on the island of Socotra in Yemen. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and subtropical or tropical dry shrubland.
Pulicaria lanata is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only on the island of Socotra in Yemen. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry shrubland.

Pulicaria stephanocarpa is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is endemic to Yemen's Socotra archipelago, where it is native to the islands of Socotra, Samhah, and Abd al Kuri. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland and rocky areas.

Hypericum scopulorum is a species of flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae. It is endemic to Socotra, an island archipelago that is part of Yemen. It is a common plant in shrubland habitat, and it is a dominant species in some areas along with Cephalocroton and another local endemic, Libinhania rosulata.

Helicia is a genus of 110 species of trees and shrubs, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. They grow naturally in rainforests throughout tropical South and Southeast Asia, including India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to New Guinea and as far south as New South Wales.

An epibiont is an organism that lives on the surface of another living organism, called the basibiont. The interaction between the two organisms is called epibiosis. An epibiont is, by definition, harmless to its host. In this sense, the interaction between the two organisms can be considered neutralistic or commensalistic; as opposed to being, for example, parasitic, in which case one organism benefits at the expense of the other, or mutualistic, in which both organisms obtain some explicit benefit from their coexistence. These organisms have evolved various adaptations to exploit their hosts for protection, transportation, or access to resources. Examples of common epibionts are bacteria, barnacles, remoras, and algae, many of which live on the surfaces of larger marine organisms such as whales, sharks, sea turtles, and mangrove trees.

Pulicaria dysenterica, the common fleabane, or, in North America, meadow false fleabane, is a species of fleabane in the family Asteraceae. It is native to Europe and western Asia where it grows in a variety of habitats ranging from semi-arid Mediterranean woodlands to wetter situations. Pulicaria dysenterica is perennial and can form dense clusters of plants, spreading by its roots. It flowers at its maximum height of about 60 centimetres (2.0 ft). Leaves are alternately arranged and clasp the stem, which itself contains a salty-astringent liquid. The yellow inflorescences are typically composed of a prominent centre of 40–100 disc florets surrounded by 20–30 narrow, pistillate ray florets. When setting seed the flower heads reflex.

Coleophora follicularis is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. The species was first described in 1802 by Jean Nicolas Vallot, a French entomologist. It is found in all of Europe.

Cissus subaphylla is a low shrub in the grape family Vitaceae. It is endemic to the Yemeni island of Socotra. The plant grows mainly in dry, low-lying areas on alluvial fans or on limestone slopes, and is rarely found above elevations of 300 metres (980 ft), where it is replaced by C. hamaderohensis. It does not have the climbing habit of other Cissus species, and its stems are flattened and gray-green in colour, with relatively small leaves and flowers. The tangled mats of C. subaphylla stems act as a protective covering for plants regularly eaten by goats and other browsing animals; the plant is thus important in the rehabilitation of species such as Dendrosicyos, Maerua and Commiphora.

Chaetocnema pulicaria, also known as the corn flea beetle and clover flea beetle, is a species of flea beetle from Chrysomelidae family, found in Texas, USA and Canada.

Pulicaria odora, also known as Mediterranean fleabane, is a species of plant from family Asteraceae. The plant can be found in pine woods and bushy places, and it also grows on sandy grounds. The leaves of the plant are cooked, and could be edible after it.
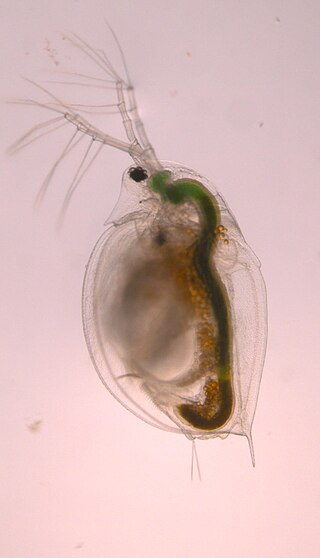
Daphnia pulicaria is a species of freshwater crustaceans found within the genus of Daphnia, which are often called "water fleas," and they are commonly used as model organisms for scientific research. Like other species of Daphnia, they reproduce via cyclic parthenogenesis. D. pulicaria are filter-feeders with a diet primarily consisting of algae, including Ankistrodesmus falcatus, and they can be found in deep lakes located in temperate climates. Furthermore, D. pulicaria are ecologically important herbivorous zooplankton, which help control algal populations and are a source of food for some fish. D. pulicaria are closely related to Daphnia pulex, and numerous studies have investigated the nature and strength of this relationship because these species can produce Daphnia pulex-pulicaria hybrids. In recent years, D. pulicaria along with other Daphnia species have been negatively affected by invasive predators, such as Bythotrephes longimanus.

Pulicaria microcephala is a species of flowering plant of the family Asteraceae endemic to the Berlengas archipelago in Portugal. It is a small and ramified plant occurring in clearings of scrubs in coastal cliffs. Its flowers are yellow, flowering between March and July. It is an endangered plant species, mainly threatened by the excessive nitrification of soils and invasive plant species, namely the ice plant.

Pulicaria vulgaris is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Asteraceae.

















