Related Research Articles
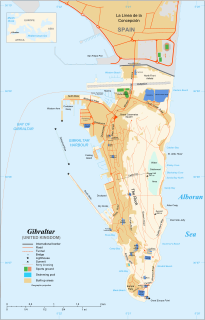
The Rock of Gibraltar, also known as the Jabel-al-Tariq, is a monolithic limestone promontory located in the territory of Gibraltar, near the southwestern tip of Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. It is 426 m (1,398 ft) high. Most of the Rock's upper area is covered by a nature reserve, which is home to around 300 Barbary macaques. These macaques, as well as a labyrinthine network of tunnels, attract many tourists each year.

Gorham's Cave is a sea-level cave in the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. Though not a sea cave, it is often mistaken for one. Considered to be one of the last known habitations of the Neanderthals in Europe, the cave gives its name to the Gorham's Cave complex, which is a combination of four distinct caves of such importance that they are combined into a UNESCO World Heritage site, the only one in Gibraltar. The three other caves are Vanguard Cave, Hyaena Cave, and Bennett's Cave.

St. Michael's Cave or Old St. Michael's Cave is the name given to a network of limestone caves located within the Upper Rock Nature Reserve in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar, at a height of over 300 metres (980 ft) above sea level. According to Alonso Hernández del Portillo, the first historian of Gibraltar, its name is derived from a similar grotto in Monte Gargano near the Sanctuary of Monte Sant'Angelo in Apulia, Italy, where the archangel Michael is said to have appeared.

Vanguard Cave is a natural sea cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar which is part of the Gorham's Cave complex. This complex of four caves has been nominated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site status in 2016. The cave complex is one of the last known habitations of the Neanderthals, with a period of inhabitation from 55,000 to 28,000 years ago. It is located on the southeast face of the Rock of Gibraltar.

Lord Airey's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located near the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just north of O'Hara's Battery. It was named after the Governor of Gibraltar, General Sir Richard Airey. Construction of the battery was completed in 1891. The first gun mounted on the battery was a 6-inch breech loading gun, which was replaced with a 9.2-inch Mark X BL gun by 1900. The gun at the battery was last fired in the 1970s. In 1997, it was discovered that Lord Airey's Shelter, adjacent to Lord Airey's Battery, was the site chosen for a covert World War II operation that entailed construction of a cave complex in the Rock of Gibraltar, to serve as an observation post. The battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Martin's Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It opens on the eastern cliffs of the Rock of Gibraltar, below its summit at O'Hara's Battery. It is an ancient sea cave, though it is now located over 700 feet (210 m) above the shore of the Mediterranean Sea. It is only accessible because Martin's Path was constructed.

Poca Roca Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Coptic Cave is a sea cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The cave was intended to be used as a decoy to protect Operation Tracer. This was a plan to leave behind spies should the British lose control of the Rock of Gibraltar in World War II.
Beefsteak Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located in the south of the Rock, between Europa Point and Windmill Hill.
Cave S is a limestone cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on the eastern side of the Rock of Gibraltar, near Holy Boy's Cave. Human remains were found in the cave in 1910 that did not appear to be of a modern man.
Fig Tree Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on the eastern cliffs of the Rock of Gibraltar, not far from Martin's Cave within the Upper Rock Nature Reserve.

The Goat's Hair Twin Caves are in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.
Devil's Tower Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Archaeologist Dorothy Garrod found a Neanderthal skull in the cave which, together with other evidence found in this cave, shows it was used as a rock shelter by the Neanderthals of Gibraltar.
Boathoist Cave, also known as Bulman's Cave, is a huge sea cave on the south eastern flank of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Douglas Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Wilson's Cave is a cave in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was named after Major W. H. Wilson, Royal Engineers, Company Commander.

Hayne's Cave Battery is the remains of two gun positions that made up an artillery battery on the west side of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar at Hayne's Cave. Gun emplacements can still be visited at this cave.

The Neanderthals in Gibraltar were among the first to be discovered by modern scientists and have been among the most well studied of their species according to a number of extinction studies which emphasize regional differences, usually claiming the Iberian Peninsula partially acted as a “refuge” for the shrinking Neanderthal populations and the Gibraltar community of Neanderthals as having been one of many dwindling communities of archaic human populations, existing just until around 42,000 years ago. Many other Neanderthal communities went extinct around the same time.

The Caves of Hercules is an archaeological cave complex located in Cape Spartel, Morocco. Situated 14 kilometres (9 mi) west of Tangier, the popular tourist attraction is adjacent to the summer palace of the King of Morocco.
References
- ↑ "Location of Caves - Gibraltar". Scribd . Retrieved 17 February 2013.
| | This Gibraltar location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |