
The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica.
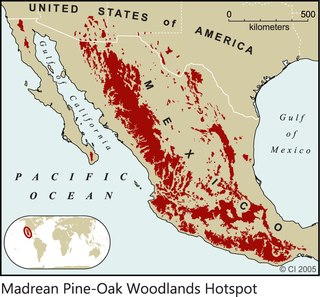
The Madrean pine–oak woodlands are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States. They are a biogeographic region of the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes, located in North America.

The Sierra Madre Occidental pine–oak forests are a Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range from the southwest USA region to the western part of Mexico. They are home to a large number of endemic plants and important habitat for wildlife.

California mixed evergreen forest is a plant community found in the mountain ranges of California and southwestern Oregon.

Quercus conzattii is an oak endemic to Mexico. It is placed in Quercus section Lobatae.

The Sierra Madre del Sur pine–oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion in the Sierra Madre del Sur mountain range of southern Mexico.

Quercus tarahumara is a species of tree in the beech family. It grows in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the Mexican States of Chihuahua, Sonora, Durango, and Sinaloa. Some of the populations lie within the territory occupied by the Tarahumara people, after whom the species is named. It is placed in Quercus section Lobatae.

Quercus castanea is a species of oak tree. It is widespread across much of Mexico, from Sonora to Chiapas, and in Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras.

Quercus urbani, also known as Quercus urbanii, is a species of oak. It is native to western and central Mexico from Sinaloa, Durango, and Zacatecas to Oaxaca. It was previously synonymized with Quercus pennivenia, but this was restored as an independent species in 2020.

Quercus iltisii is a species of oak tree native to western Mexico, where it is found in a small portion of Jalisco and Colima states.
Quercus tuberculata is a species of oak tree which is native to mountains of northeastern and northwestern Mexico. It is placed in Quercus section Quercus.
Quercus affinis is a species of oak native only to Mexico, mostly to the Sierra Madre Oriental pine-oak forests.
Magnolia tarahumara is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to Mexico, where it occurs in scattered locations in the Sierra Madre Occidental of southeastern Sonora, southwestern Chihuahua, Sinaloa, and northwestern Durango.
Papigochic Flora and Fauna Protection Area is a protected area in Chihuahua state of Mexico. It covers an area of 2227.64 km2 in the eastern Sierra Madre Occidental. To the northwest it adjoins Tutuaca Flora and Fauna Protection Area.
Quercus radiata is an endangered species of oak native to Mexico.
Quercus mcvaughii is a species of oak tree native to Mexico.

Quercus jonesii is a species of oak tree native to Mexico. It is commonly known as palo manzano. It is placed in Quercus section Lobatae.
Quercus striatula is a species of oak native to Mexico.

The Cuenca Alimentadora del Distrito Nacional de Riego 043 Estado de Nayarit is a protected natural area in west-central Mexico. It extends across portions of southern Sierra Madre Occidental and the westernmost Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. It has an area of 23290.27 km2, covering portions of southern Durango, northern Jalisco, eastern Nayarit, southern Zacatecas, and western Aguascalientes states.

The Espinazo del Diablo is a region of the Sierra Madre Occidental in the states of Sinaloa and Durango in northwestern Mexico. The region is known its natural beauty and biodiversity, including rare cloud forests, and for a stretch tortuous mountain highway also called the Espinazo del Diablo.














