
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country comprising the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's fourth largest island, the second-largest island country and the 46th largest country in the world. Its capital and largest city is Antananarivo.

Elephant birds are extinct flightless birds belonging to the order Aepyornithiformes that were native to the island of Madagascar. They are thought to have become extinct around 1000 AD, likely as a result of human activity. Elephant birds comprised three species, one in the genus Mullerornis, and two in Aepyornis.Aepyornis maximus is possibly the largest bird to have ever lived, with their eggs being the largest known for any amniote. Elephant birds are palaeognaths, and their closest living relatives are kiwi, suggesting that ratites did not diversify by vicariance during the breakup of Gondwana but instead convergently evolved flightlessness from ancestors that dispersed more recently by flying.

Euphorbia milii, the crown of thorns, Christ plant, or Christ's thorn, is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family Euphorbiaceae, native to Madagascar. The species name commemorates Baron Milius, once Governor of Réunion, who introduced the species to France in 1821.
Ormocarpopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It includes eight species of shrubs or small trees endemic to Madagascar. They inhabit seasonally-dry tropical forest, woodland, and xerophytic shrubland, sometimes on rocky outcrops of sandstone or limestone. They are found throughout the island except in the eastern lowland rain forest. The genus was recently assigned to the informal monophyletic Dalbergia clade of the Dalbergieae. It contains the following species:
Ormocarpopsis tulearensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Madagascar.

Melhania is a genus of small shrubs or herbaceous plants. Traditionally included in the family Sterculiaceae, it is included in the expanded Malvaceae in the APG and most subsequent systematics. The genus is named for Mount Melhan in Yemen.
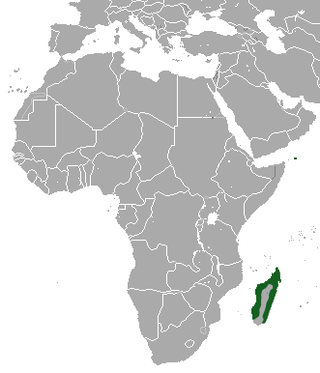
The Madagascan pygmy shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is the only known Malagasy shrew.

The brown-tailed mongoose, brown-tailed vontsira, Malagasy brown-tailed mongoose, or salano is a species of mammal in the family Eupleridae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is moist lowland tropical forest. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Euphorbia tulearensis is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is rocky areas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Pyrostria is a genus of dioecious flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. Most of the species are endemic to Madagascar, others occur on islands in the western Indian Ocean, a few are found in continental Africa, and only six species occur in tropical Southeast Asia. The formerly recognized genus Leroya, containing two species endemic to Madagascar, L. madagascariensis and L. richardiae, was sunk into synonymy with Pyrostria.

Kalidos is a genus of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the subfamily Helicarioninae of the family Helicarionidae.
Lyria tulearensis is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Volutidae, the volutes.

Hypogeomys australis is an extinct rodent from central and southeastern Madagascar. First described in 1903, it is larger than its close relative, the living Hypogeomys antimena, which occurs further west, but otherwise similar. Average length of the femur is 72.1 mm, compared to 63.8 mm in H. antimena. One of the few extinct rodents of Madagascar, it survived to at least around 1536 BP based on radiocarbon dating. Little is known of its ecology, but it may have lived in burrows like its living relative and eaten some arid-adapted plants.

The Central Highlands, Central High Plateau, or Hauts-Plateaux are a mountainous biogeographical region in central Madagascar. They include the contiguous part of the island's interior above 800 m (2,600 ft) elevation. The Central Highlands are separated from the Northern Highlands of the northern tip of Madagascar by a low-lying valley, the Mandritsara Window, which has apparently acted as a barrier to dispersal for species in the highlands, leading to species pairs such as Voalavo gymnocaudus and Voalavo antsahabensis in the Northern and Central Highlands. Species restricted to the Central Highlands include the bats Miniopterus manavi and Miniopterus sororculus; the rodents Brachyuromys betsileoensis and Voalavo antsahabensis; the tenrecs Hemicentetes nigriceps and Oryzorictes tetradactylus; and the lemur Cheirogaleus sibreei. Because of the continuous habitat of the Central Highlands, there is little local endemism, unlike the Northern Highlands.
Alexey Nikolaievich Diakonoff, also transliterated as Alexej Nikolajewitsch Diakonoff, was a Russian–Dutch entomologist who specialised in Microlepidoptera.

Xerophyta is a genus of flowering plants in the family Velloziaceae. It was named in 1789 by de Jussieu. It is native to Africa, Madagascar, and the Arabian Peninsula.
Eulima tulearensis is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Eulimidae. The species is one of a number within the genus Eulima.
Phisalixella is a genus of pseudoxyrhophiid snakes endemic to the island of Madagascar. They are harmless to humans.
Tephraciura tulearensis is a species of tephritid or fruit flies in the genus Tephraciura of the family Tephritidae.
Microsteira is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Malpighiaceae.












