The history of Trinidad and Tobago begins with the settlements of the islands by Indigenous First Peoples. Trinidad was visited by Christopher Columbus on his third voyage in 1498,, and claimed in the name of Spain. Trinidad was administered by Spanish hands until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists. Tobago changed hands between the British, French, Dutch, and Courlanders, but eventually ended up in British hands following the second Treaty of Paris (1814). In 1889, the two islands were incorporated into a single political entity. Trinidad and Tobago obtained its independence from the British Empire in 1962 and became a republic in 1976.

Port of Spain, officially the City of Port of Spain, is the capital of Trinidad and Tobago and the third largest municipality, after Chaguanas and San Fernando. The city has a municipal population of 37,074 (2011), an urban population of 81,142 and a transient daily population of 250,000. It is located on the Gulf of Paria, on the northwest coast of the island of Trinidad and is part of a larger conurbation stretching from Chaguaramas in the west to Arima in the east with an estimated population of 600,000.

Tobago is an island and ward within the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located 35 kilometres (22 mi) northeast of the larger island of Trinidad and about 160 kilometres (99 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela. It lies to the southeast of Grenada.

Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 4,768 km2 (1,841 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.
The Trinidad and Tobago national football team, nicknamed the "Soca Warriors", represents the twin-island Republic of Trinidad and Tobago in international football. It is controlled by the Trinidad and Tobago Football Association, which is a member of CONCACAF, the Caribbean Football Union (CFU), and the global jurisdiction of FIFA.

The Trinidad and Tobago dollar is the currency of Trinidad and Tobago. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively TT$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is subdivided into 100 cents. Cents are abbreviated with the cent sign ¢, or TT¢ to distinguish from other currencies that use cents. Its predecessor currencies are the Trinidadian dollar and the Tobagonian dollar.

Trinidad and Tobago are continental islands with a geologically very recent history of direct land bridge connection to South America. As a result, unlike most of the Caribbean Islands, Trinidad and Tobago supports a primarily South American flora and fauna and has greater diversity of plant and animal species than the Antilles. However, rates of endemism are lower than in the rest of the Caribbean because there has been less time for genetic isolation from mainland populations because of the history of land bridge connections and hence fewer opportunities for speciation, and so a greater proportion of the species in Trinidad and Tobago are also found on the South American mainland. Trinidad is nearer to mainland South America and has been directly connected to the mainland via land bridges more often and for longer periods than Tobago. This, as well as Trinidad's larger size and more varied topography and hydrology compared to that of Tobago allow greater species and ecosystem diversity on the former compared to that on the later of the islands.

Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated 11 kilometres off the coast of northeastern Venezuela and 130 kilometres south of Grenada. It shares maritime boundaries with Barbados to the east, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous municipality is Chaguanas.
Radiodiscus amdenus is a species of small air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Charopidae. This species is endemic to Brazil.
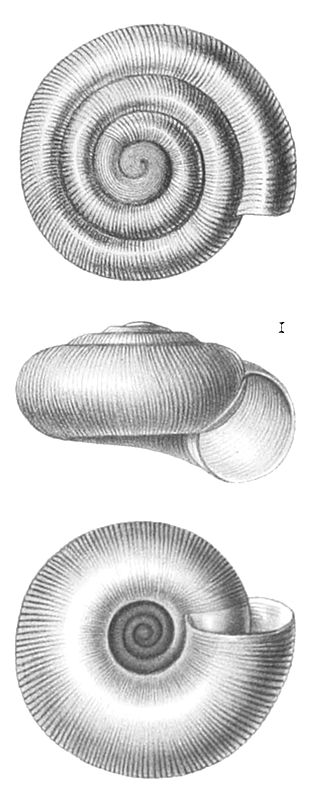
Radiodiscus is a genus of small air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Charopidae.
Radiodiscus compactus is a species of small air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Charopidae. This species is endemic to Brazil.
Radiodiscus coppingeri is a species of small air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Charopidae. This species is found in Brazil, Argentina, and Chile.
Radiodiscus iheringi is a species of small air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Charopidae.

Helicodiscidae is a family of small air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Punctoidea.

Charopidae is a taxonomic family of small air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Punctoidea.

Radiodiscus patagonicus is a minute species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Charopidae.

The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion covers most of Trinidad Island and Tobago Island near the coast of South America where the southeastern Caribbean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. Small portions of the islands around river estuaries and coastal lowlands are mangroves or dry forests. Species diversity is very high, in particular for plants and birds. Tobago, being much smaller, has fewer species.










