
Acadia was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River.

Penobscot Indian Island Reservation is an Indian reservation for the Penobscot Tribe of Maine, a federally recognized tribe of the Penobscot in Penobscot County, Maine, United States, near Old Town. The population was 758 at the 2020 census. The reservation extends for many miles alongside 15 towns and two unorganized territories in a thin string along the Penobscot River, from its base at Indian Island, near Old Town and Milford, northward to the vicinity of East Millinocket, almost entirely in Penobscot County. A small, uninhabited part of the reservation used as a game preserve and hunting and gathering ground is in South Aroostook, Aroostook County, by which it passes along its way northward.

King William's War was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg. It was the first of six colonial wars fought between New France and New England along with their respective Native allies before France ceded its remaining mainland territories in North America east of the Mississippi River in 1763.
The Isthmus of Chignecto is an isthmus bordering the Maritime provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia that connects the Nova Scotia peninsula with North America.
Beaubassin was an important Acadian village and trading centre on the Isthmus of Chignecto in what is now Nova Scotia, Canada. The area was a significant place in the geopolitical struggle between the British and French empires. It was established in the 1670s on an upland close to an extensive area of saltwater marsh. Settlers reclaimed the land to engage in cattle ranching and trade.

Colonel Benjamin Church was a New England military officer and politician who is best known for his role in innovative military tactics notably developing Unconventional warfare. He is also known for commanding the first ranger units in North America. Born in the Plymouth Colony, Church was commissioned by Governor Josiah Winslow to establish a company of Rangers called after the outbreak of King Philip's War. Church participated in numerous conflicts which involved the New England Colonies. A force of New Englanders led by him was responsible for tracking down and killing Wampanoag sachem Metacomet, which played a major role in ending the conflict.

The Battle of Port Royal occurred at Port Royal, the capital of Acadia, during King William's War. A large force of New England provincial militia arrived before Port Royal. The Governor of Acadia Louis-Alexandre des Friches de Menneval had only 70 soldiers; the unfinished enceinte remained open and its 18 cannon had not been brought into firing positions; 42 young men of Port-Royal were absent. Any resistance therefore appeared useless. Meneval surrendered without resistance not long after the New Englanders arrived. The New Englanders, led by Sir William Phips, after alleging Acadian violations of the terms of surrender, plundered the town and the fort.
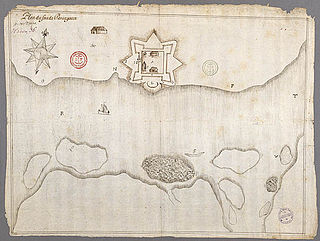
Fort Pentagouët was a French fort established in present-day Castine, Maine, which was the capital of Acadia (1670–1674). It is the oldest permanent settlement in New England.
Jean Baudoin (1662–1698) was a French Sulpician priest who served as a missionary in Acadia, and later as a chaplain during military expeditions carried on by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville.
Claude-Sébastien de Villieu was a French military officer best known for his service in New France. In addition to service during King William's War, he served for a time as military governor of Acadia.
Pierre Maisonnat dit Baptiste was a French privateer famous for the success he had against New England merchant shipping and fishing interests during King William's War and Queen Anne's War. Baptiste's crew members were primarily Acadians.

The Raid on Grand Pré was the major action of a raiding expedition conducted by the New England militia Colonel Benjamin Church against French Acadia in June 1704, during Queen Anne's War. The expedition was allegedly in retaliation for a French and Indian raid against the Massachusetts frontier community of Deerfield earlier that year.

Fort William Henry is located in the village of New Harbor in the town of Bristol, Maine. The fort was, in its time, the largest in New England. The fort was originally built in 1692 but destroyed four years later by New France in the Siege of Pemaquid (1696). A reconstruction was built in 1908. The fort was added to the National Register of Historic Places on December 1, 1969. Fort William Henry is now operated as a museum about the fort's history.

The siege of Pemaquid occurred during King William's War when French and Native forces from New France attacked the English settlement at Pemaquid, a community on the border with Acadia. The siege was led by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville and Baron de St Castin between August 14–15, 1696. Commander of Fort William Henry, Captain Pasco Chubb, surrendered the fort. Iberville killed three of the soldiers and sent the other 92 back to Boston.

The Battle of Chedabucto occurred against Fort St. Louis in Chedabucto on June 3, 1690 during King William's War (1689–97). The battle was part of Sir William Phips and New England's military campaign against Acadia. New England sent an overwhelming force to conquer Acadia by capturing the capital Port Royal, Chedabucto, and attacking other villages. The aftermath of these battles was unlike any of the previous military campaigns against Acadia. The violence of the attacks alienated many of the Acadians from the New Englanders, broke their trust, and made it difficult for them to deal amicably with the English-speakers.

The Battle at Chignecto happened during Father Le Loutre's War when Charles Lawrence, in command of the 45th Regiment of Foot and the 47th Regiment, John Gorham in command of the Rangers and Captain John Rous in command of the navy, fought against the French monarchists at Chignecto. This battle was the first attempt by the British to occupy the head of the Bay of Fundy since the disastrous Battle of Grand Pré three years earlier. They fought against a militia made up of Mi'kmaq and Acadians led by Jean-Louis Le Loutre and Joseph Broussard (Beausoliel). The battle happened at Isthmus of Chignecto, Nova Scotia on 3 September 1750.

The siege of Fort Nashwaak occurred during King William's War when New England forces from Boston attacked the capital of Acadia, Fort Nashwaak, at present-day Fredericton, New Brunswick. The siege was in retaliation for the French and Indian Siege of Pemaquid (1696) at present day Bristol, Maine. In the English Province of Massachusetts Bay. Colonel John Hathorne and Major Benjamin Church were the leaders of the New England force of 400 men. The siege lasted two days, between October 18–20, 1696, and formed part of a larger expedition by Church against a number of other Acadian communities.
The Northeast Coast campaign was the first major campaign by the French of Queen Anne's War in New England. Alexandre Leneuf de La Vallière de Beaubassin led 500 troops made up of French colonial forces and the Wabanaki Confederacy of Acadia. They attacked English settlements on the coast of present-day Maine between Wells and Casco Bay, burning more than 15 leagues of New England country and killing or capturing more than 150 people. The English colonists protected some of their settlements, but a number of others were destroyed and abandoned. Historian Samuel Drake reported that, "Maine had nearly received her death-blow" as a result of the campaign.

The military history of the Acadians consisted primarily of militias made up of Acadian settlers who participated in wars against the English in coordination with the Wabanaki Confederacy and French royal forces. A number of Acadians provided military intelligence, sanctuary, and logistical support to the various resistance movements against British rule in Acadia, while other Acadians remained neutral in the contest between the Franco–Wabanaki Confederacy forces and the British. The Acadian militias managed to maintain an effective resistance movement for more than 75 years and through six wars before their eventual demise. According to Acadian historian Maurice Basque, the story of Evangeline continues to influence historic accounts of the expulsion, emphasising Acadians who remained neutral and de-emphasising those who joined resistance movements. While Acadian militias were briefly active during the American Revolutionary War, the militias were dormant throughout the nineteenth century. After confederation, Acadians eventually joined the Canadian War efforts in World War I and World War II. The most well-known colonial leaders of these militias were Joseph Broussard and Joseph-Nicolas Gautier.
The Battle of Falmouth was fought at Falmouth, Maine when the Canadiens and Wabanaki Confederacy attacked the English New Casco Fort. The battle was part of the Northeast Coast Campaign (1703) during Queen Anne's War.











