
BCS theory or Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer theory is the first microscopic theory of superconductivity since Heike Kamerlingh Onnes's 1911 discovery. The theory describes superconductivity as a microscopic effect caused by a condensation of Cooper pairs. The theory is also used in nuclear physics to describe the pairing interaction between nucleons in an atomic nucleus.

Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with condensed phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions among them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at extremely low cryogenic temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other physics theories to develop mathematical models.

Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are familiar metals that are noticeably attracted to a magnet, a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. This temporarily induced magnetization, for example, inside a steel plate, accounts for its attraction to the permanent magnet. Whether or not that steel plate acquires a permanent magnetization itself depends not only on the strength of the applied field but on the so-called coercivity of the ferromagnetic material, which can vary greatly.

Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, and some states only exist under extreme conditions, such as Bose–Einstein condensates, neutron-degenerate matter, and quark–gluon plasma. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.
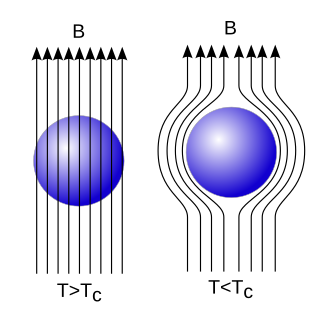
The Meissner effect is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state when it is cooled below the critical temperature. This expulsion will repel a nearby magnet.
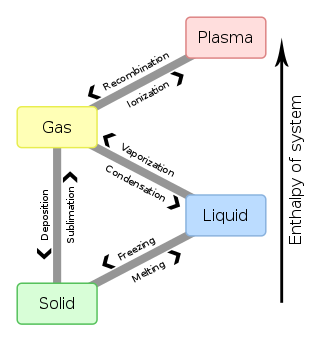
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point.

High-temperature superconductors are defined as materials with critical temperature above 77 K, the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. They are only "high-temperature" relative to previously known superconductors, which function at even colder temperatures, close to absolute zero. The "high temperatures" are still far below ambient, and therefore require cooling. The first break through of high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986 by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller. Although the critical temperature is around 35.1 K, this new type of superconductor was readily modified by Ching-Wu Chu to make the first high-temperature superconductor with critical temperature 93 K. Bednorz and Müller were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-Tc materials are type-II superconductors.
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair is a pair of electrons bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper.

A fermionic condensate is a superfluid phase formed by fermionic particles at low temperatures. It is closely related to the Bose–Einstein condensate, a superfluid phase formed by bosonic atoms under similar conditions. The earliest recognized fermionic condensate described the state of electrons in a superconductor; the physics of other examples including recent work with fermionic atoms is analogous. The first atomic fermionic condensate was created by a team led by Deborah S. Jin using potassium-40 atoms at the University of Colorado Boulder in 2003.

Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.
The superconductor–insulator transition is an example of a quantum phase transition, whereupon tuning some parameter in the Hamiltonian, a dramatic change in the behavior of the electrons occurs. The nature of how this transition occurs is disputed, and many studies seek to understand how the order parameter, , changes. Here is the amplitude of the order parameter, and is the phase. Most theories involve either the destruction of the amplitude of the order parameter - by a reduction in the density of states at the Fermi surface, or by destruction of the phase coherence; which results from the proliferation of vortices.

Andreev reflection (AR), named after the Russian physicist Alexander F. Andreev, is a type of particle scattering which occurs at interfaces between a superconductor (S) and a normal state material (N). It is a charge-transfer process by which normal current in N is converted to supercurrent in S. Each Andreev reflection transfers a charge 2e across the interface, avoiding the forbidden single-particle transmission within the superconducting energy gap.

Proximity effect or Holm–Meissner effect is a term used in the field of superconductivity to describe phenomena that occur when a superconductor (S) is placed in contact with a "normal" (N) non-superconductor. Typically the critical temperature of the superconductor is suppressed and signs of weak superconductivity are observed in the normal material over mesoscopic distances. The proximity effect is known since the pioneering work by R. Holm and W. Meissner. They have observed zero resistance in SNS pressed contacts, in which two superconducting metals are separated by a thin film of a non-superconducting metal. The discovery of the supercurrent in SNS contacts is sometimes mistakenly attributed to Brian Josephson's 1962 work, yet the effect was known long before his publication and was understood as the proximity effect.
Ferromagnetic superconductors are materials that display intrinsic coexistence of ferromagnetism and superconductivity. They include UGe2, URhGe, and UCoGe. Evidence of ferromagnetic superconductivity was also reported for ZrZn2 in 2001, but later reports question these findings. These materials exhibit superconductivity in proximity to a magnetic quantum critical point.
Flux pumping is a method for magnetising superconductors to fields in excess of 15 teslas. The method can be applied to any type II superconductor and exploits a fundamental property of superconductors, namely their ability to support and maintain currents on the length scale of the superconductor. Conventional magnetic materials are magnetised on a molecular scale which means that superconductors can maintain a flux density orders of magnitude bigger than conventional materials. Flux pumping is especially significant when one bears in mind that all other methods of magnetising superconductors require application of a magnetic flux density at least as high as the final required field. This is not true of flux pumping.
Macroscopic quantum phenomena are processes showing quantum behavior at the macroscopic scale, rather than at the atomic scale where quantum effects are prevalent. The best-known examples of macroscopic quantum phenomena are superfluidity and superconductivity; other examples include the quantum Hall effect and topological order. Since 2000 there has been extensive experimental work on quantum gases, particularly Bose–Einstein condensates.

In the field of cryogenics, helium [He] is utilized for a variety of reasons. The combination of helium’s extremely low molecular weight and weak interatomic reactions yield interesting properties when helium is cooled below its critical temperature of 5.2 K to form a liquid. Even at absolute zero (0K), helium does not condense to form a solid under ambient pressure. In this state, the zero point vibrational energies of helium are comparable to very weak interatomic binding interactions, thus preventing lattice formation and giving helium its fluid characteristics. Within this liquid state, helium has two phases referred to as helium I and helium II. Helium I displays thermodynamic and hydrodynamic properties of classical fluids, along with quantum characteristics. However, below its lambda point of 2.17 K, helium transitions to He II and becomes a quantum superfluid with zero viscosity.
Kagome metal is a ferromagnetic quantum material that was first used in literature in 2011 for a compound of Fe3Sn2. However, this material had been created for several decades. In this material, metal atoms are arranged in a lattice resembling the Japanese kagome basket weaving pattern. The same material has also been termed as "kagome magnet" since 2018. Kagome metal refer to a new class of magnetic quantum materials hosting kagome lattice and topological band structure. They include 3-1 materials, 1-1 materials, 1-6-6 materials, 3-2-2 materials, and 3-2 materials, thus demonstrating a variety of crystal and magnetic structures. They generally feature a 3d transition metal based magnetic kagome lattice with an in-plane lattice constant ~5.5 Å. Their 3d electrons dominate the low-energy electronic structure in these quantum materials, thus exhibiting electronic correlation. Crucially, the kagome lattice electrons generally feature Dirac band crossings and flat band, which are the source for nontrivial band topology. Moreover, they all contain the heavy element Sn, which can provide strong spin–orbit coupling to the system. Therefore, this is an ideal system to explore the rich interplay between geometry, correlation, and topology.
Uranium ditelluride, (UTe2), an unconventional superconductor, discovered to be a superconductor in 2018.











