
Ploidy is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present : monoploid, diploid, triploid, tetraploid, pentaploid, hexaploid, heptaploid or septaploid, etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets.

Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual.

In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents, but can show hybrid vigour, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are.
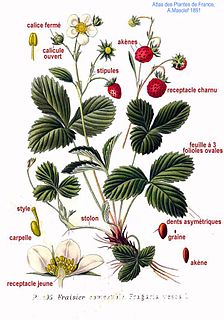
Fragaria is a genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, commonly known as strawberries for their edible fruits. There are more than 20 described species and many hybrids and cultivars. The most common strawberries grown commercially are cultivars of the garden strawberry, a hybrid known as Fragaria × ananassa. Strawberries have a taste that varies by cultivar, and ranges from quite sweet to rather tart. Strawberries are an important commercial fruit crop, widely grown in all temperate regions of the world.

Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, some organisms are polyploid, and polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally haploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.

Triticale is a hybrid of wheat (Triticum) and rye (Secale) first bred in laboratories during the late 19th century in Scotland and Germany. Commercially available triticale is almost always a second-generation hybrid, i.e., a cross between two kinds of primary (first-cross) triticales. As a rule, triticale combines the yield potential and grain quality of wheat with the disease and environmental tolerance of rye. Only recently has it been developed into a commercially viable crop. Depending on the cultivar, triticale can more or less resemble either of its parents. It is grown mostly for forage or fodder, although some triticale-based foods can be purchased at health food stores and can be found in some breakfast cereals.

In botany, apomixis is asexual reproduction without fertilization. Its etymology is Greek for "away from" + "mixing". This definition notably does not mention meiosis. Thus "normal asexual reproduction" of plants, such as propagation from cuttings or leaves, has never been considered to be apomixis, but replacement of the seed by a plantlet or replacement of the flower by bulbils were categorized as types of apomixis. Apomictically produced offspring are genetically identical to the parent plant.

The peony or paeony is a flowering plant in the genus Paeonia, the only genus in the family Paeoniaceae. Peonies are native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. Scientists differ on the number of species that can be distinguished, ranging from 25 to 40, although the current consensus is 33 known species. The relationships between the species need to be further clarified.

Hibiscus rosa-sinensis, known colloquially as Chinese hibiscus, China rose, Hawaiian hibiscus, rose mallow and shoeblackplant, is a species of tropical hibiscus, a flowering plant in the Hibisceae tribe of the family Malvaceae. It is widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions, but is not known in the wild, so that its native distribution is uncertain. An origin in some part of tropical Asia is likely. It is widely grown as an ornamental plant in the tropics and subtropics.
Haploidisation is the process of halving the chromosomal content of a cell, creating a haploid cell. Within the normal reproductive cycle, haploidisation is one of the major functional consequences of meiosis, the other being a process of chromosomal crossover that mingles the genetic content of the parental chromosomes. Usually, haploidisation creates a monoploid cell from a diploid progenitor, or it can involve halving of a polyploid cell, for example to make a diploid potato plant from a tetraploid lineage of potato plants.
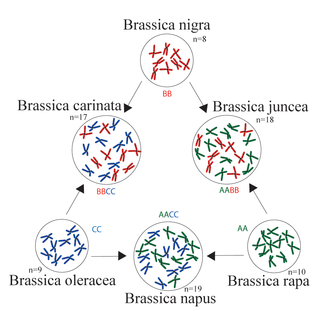
The triangle of U is a theory about the evolution and relationships among members of the plant genus Brassica. The theory states that the genomes of three ancestral diploid species of Brassica combined to create three common tetraploid vegetables and oilseed crop species. It has since been confirmed by studies of DNA and proteins.
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur.

The jostaberry is a complex-cross fruit bush in the genus Ribes, involving three original species, the blackcurrant R. nigrum, the North American coastal black gooseberry R. divaricatum, and the European gooseberry R. uva-crispa. It is similar to Ribes × culverwellii, the jochelbeere, which is descended from just two of these species, R. nigrum and R. uva-crispa.
A doubled haploid (DH) is a genotype formed when haploid cells undergo chromosome doubling. Artificial production of doubled haploids is important in plant breeding.

Hordeum brachyantherum, known by the common name meadow barley, is a species of barley. It is native to western North America from Alaska to northern Mexico, coastal areas of easternmost Russia (Kamchatka), and a small area of coastal Newfoundland.
Plant tissue culture is a collection of techniques used to maintain or grow plant cells, tissues or organs under sterile conditions on a nutrient culture medium of known composition. It is widely used to produce clones of a plant in a method known as micropropagation. Different techniques in plant tissue culture may offer certain advantages over traditional methods of propagation, including:

Rosa × alba, the white rose of York, is a hybrid rose of unknown parentage that has been cultivated in Europe since ancient times. It may have originally been grown mainly for the sweet scent of the flowers, but is now also used as a winter-hardy garden shrub. Cultivated forms have white or pink flowers, and most have many petals. Hybrid cultivars have also been produced with red or yellow flowers.

Frank Harlan Lewis, known professionally as Harlan Lewis, was an American botanist, geneticist, taxonomist, systematist, and evolutionist who worked primarily with plants in the genus Clarkia. He is best known for his theories of "catastrophic selection" and "saltational speciation", which are closely aligned with the concepts of quantum evolution and sympatric speciation. The concepts were first articulated in 1958 by Lewis and Peter H. Raven, and later refined in a 1962 paper by Lewis in which he coined the term "catastrophic selection". In 1966, he referred to the same mechanism as "saltational speciation".
Maryam Jafarkhani Kermani is an Associate Professor in the Department of Tissue and Cell Culture at the Administration of Agriculture and Biotechnology Research Institute of Iran (ABRII). She is an Iranian scientist whose main research area is agricultural tissue culture and mainly studies plants in the Rosaceous family.

Margaret Campbell Mann Lesley (1891-1988) was an American cytologist and geneticist who specialized in plant breeding cytogenetics. Her primary work focused on cytological analyses of tomatoes and citrus. She was an active research assistant to Howard B. Frost (1881-1969), an Associate Plant Breeder at the Citrus Experiment Station, and to James W. Lesley (1888-1982), her husband, whom she extensively collaborated and conducted research on tomato breeding.
















