
Schaerbeek or Schaarbeek is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Etterbeek, Evere and Saint-Josse-ten-Noode. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch).

De Wallen is the largest and best known red-light district in Amsterdam. It consists of a network of alleys containing approximately 300 one-room cabins rented by prostitutes who offer their sexual services from behind a window or glass door, typically illuminated with red lights and blacklight. Window prostitution is the most visible and typical kind of red-light district sex work in Amsterdam.

Prostitution in Germany is legal, as are other aspects of the sex industry, including brothels, advertisement, and job offers through HR companies. Full-service sex work is widespread and regulated by the German government, which levies taxes on it. In 2016, the government adopted a new law, the Prostitutes Protection Act, in an effort to improve the legal situation of sex workers, while also now enacting a legal requirement for registration of prostitution activity and banning prostitution which involves no use of condoms. The social stigmatization of sex work persists and many workers continue to lead a double life. Human rights organizations consider the resulting common exploitation of women from Eastern and Southeastern Europe to be the main problem associated with the profession.

The City of Brussels is the largest municipality and historical centre of the Brussels-Capital Region, as well as the capital of the Flemish Region and Belgium. The City of Brussels is also the administrative centre of the European Union, as it hosts a number of principal EU institutions in its European Quarter.

Prostitution in the Netherlands is legal and regulated. Operating a brothel is also legal. De Wallen, the largest and best-known Red-light district in Amsterdam, is a destination for international sex tourism.

Brussels-Schuman railway station is a railway station in the City of Brussels, Belgium, serving the European Quarter. The station received its name from the aboveground Robert Schuman Roundabout, itself named after Robert Schuman, one of the founding fathers of the European Union, the Council of Europe and NATO.

Brussels-South railway station is a major railway station in Brussels, Belgium. Geographically, it is located in Saint-Gilles/Sint-Gillis on the border with the adjacent municipality of Anderlecht and just south of the City of Brussels.

Procuring, pimping, or pandering is the facilitation or provision of a prostitute or other sex worker in the arrangement of a sex act with a customer. A procurer, colloquially called a pimp or a madam or a brothel keeper, is an agent for prostitutes who collects part of their earnings. The procurer may receive this money in return for advertising services, physical protection, or for providing and possibly monopolizing a location where the prostitute may solicit clients. Like prostitution, the legality of certain actions of a madam or a pimp vary from one region to the next.

Prostitution in Belgium is legal and was decriminalized on 1 June 2022. Human trafficking or exploiting individuals involved in prostitution is punishable by a maximum prison sentence of 30 years.

Brussels-North railway station is one of the three major railway stations in Brussels, Belgium; the other two are Brussels-Central and Brussels-South. Every regular domestic and international train passing there has a planned stop. The station has 200,000 passengers per week, mainly commuters, making it one of the busiest in Belgium.
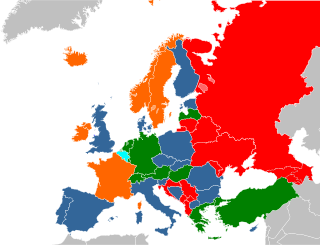
The legality of prostitution in Europe varies by country.

The Robert Schuman Roundabout, sometimes called Robert Schuman Square, is a roundabout in the European Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. It lies at the end of the Rue de la Loi/Wetstraat and serves as a focus for major institutions of the European Union (EU). It is named after Robert Schuman, one of the founding fathers of the European Union, the Council of Europe and NATO, and gives its name to the surrounding district and Brussels-Schuman railway station.

The Northern Quarter is the central business district of Brussels, Belgium. Like La Défense in Paris, the Docklands in London or the Zuidas in Amsterdam, the Northern Quarter consists of a concentrated collection of high-rise buildings where many Belgian and multinational companies have their headquarters.

The Rue Royale or Koningsstraat is a street in Brussels, Belgium, running through the municipalities of Schaerbeek, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode and the City of Brussels. It is limited to the south by the Place Royale/Koningsplein in the city centre and to the north by the Place de la Reine/Koninginplein in Schaerbeek.
Prostitution is legal in Belgium, but related activities such as organising prostitution and other forms of pimping are illegal. Enforcement varies, and in some areas brothels are unofficially tolerated.

The history of prostitution in France has similarities with the history of prostitution in other countries in Europe, namely a succession of periods of tolerance and repression, but with certain distinct features such as a relatively long period of tolerance of brothels.

The Place Charles Rogier or Karel Rogierplein (Dutch), usually shortened to the Place Rogier, or Rogier by locals, is a major square in the Saint-Josse-ten-Noode municipality of Brussels, Belgium. It is named in honour of Charles Rogier, a former Prime Minister of Belgium who played a great political role during the Belgian Revolution of 1830.

The Art Deco movement of architecture and design appeared in Brussels, Belgium, immediately after World War I when the famed architect Victor Horta began designing the Centre for Fine Arts, and continued until the beginning of World War II in 1939. It took its name from the International Exposition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts held in Paris in 1925. At the end of World War II, Art Deco in Brussels faded to make way for the modernist and international architectural styles that would mark the postwar period.
Eunice Osayande was a Nigerian sex worker in Belgium, where she was murdered in June 2018. The city of Brussels is set to name a new street after her to promote a campaign that recognizes women in Belgium. The new street named after Osayande connects the Quai des Peniches and Quai de Willebroeck. This would be the first time a street is named after a sex worker. This is in recognition of sexual violence, female victims, and femicide. Osayande came to Europe in 2016, hoping for a brighter future in the film industry.





















