A brief history
The SIGNAL language was first designed for signal processing applications in the beginning of the 1980s. It has been proposed to answer the demand of new domain-specific language for the design of signal processing applications, adopting a dataflow and block-diagram style with array and sliding window operators. P. Le Guernic, A. Benveniste, and T. Gautier have been in charge of the language definition. The first paper on SIGNAL was published in 1982, while the first complete description of SIGNAL appeared in the PhD thesis of T. Gautier. The symbolic representation of SIGNAL via z/3z (over [-1,0,1]) has been introduced in 1986. A full compiler of SIGNAL based on the clock calculus on hierarchy of Boolean clocks, was described by L. Besnard in his PhD thesis in 1992. The clock calculus has been improved later by T. Amagbegnon with the proposition of arborescent canonical forms.
During the 1990s, the application domain of the SIGNAL language has been extended into general embedded and real-time systems. The relation-oriented specification style enabled the increasing construction of the systems, and also led to the design considering multi-clocked systems, compared to the original single-clock-based implementation of Esterel and Lustre. Moreover, the design and implementation of distributed embedded systems were also taken into account in SIGNAL. The corresponding research includes the optimization methods proposed by B. Chéron, the clustering models defined by B. Le Goff, the abstraction and separate compilation formalized by O. Maffeïs, and the implementation of distributed programs developed by P. Aubry.
The Portable Operating System Interface is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers.
A specification language is a formal language in computer science used during systems analysis, requirements analysis, and systems design to describe a system at a much higher level than a programming language, which is used to produce the executable code for a system.

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. MOF may be used for domain-driven software design and object-oriented modelling.
Model-driven architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.

In computing, a visual programming language, also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating program elements graphically rather than by specifying them textually. A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms.
JTAG is an industry standard for verifying designs of and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.
In computer programming, dataflow programming is a programming paradigm that models a program as a directed graph of the data flowing between operations, thus implementing dataflow principles and architecture. Dataflow programming languages share some features of functional languages, and were generally developed in order to bring some functional concepts to a language more suitable for numeric processing. Some authors use the term datastream instead of dataflow to avoid confusion with dataflow computing or dataflow architecture, based on an indeterministic machine paradigm. Dataflow programming was pioneered by Jack Dennis and his graduate students at MIT in the 1960s.
Esterel is a synchronous programming language for the development of complex reactive systems. The imperative programming style of Esterel allows the simple expression of parallelism and preemption. As a consequence, it is well suited for control-dominated model designs.
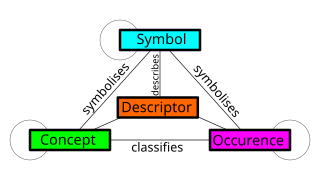
A metamodel is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction, and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models, and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.
A synchronous programming language is a computer programming language optimized for programming reactive systems.
Lustre is a formally defined, declarative, and synchronous dataflow programming language for programming reactive systems. It began as a research project in the early 1980s. A formal presentation of the language can be found in the 1991 Proceedings of the IEEE. In 1993 it progressed to practical, industrial use in a commercial product as the core language of the industrial environment SCADE, developed by Esterel Technologies. It is now used for critical control software in aircraft, helicopters, and nuclear power plants.

Esterel Technologies is a supplier of model-based design, validation, and code generation tools for safety-critical software and hardware applications. Esterel's tools create formal specifications that produce control designs code in software and/or hardware.

ATL is a model transformation language and toolkit developed and maintained by OBEO and AtlanMod. It was initiated by the AtlanMod team. In the field of Model-Driven Engineering (MDE), ATL provides ways to produce a set of target models from a set of source models.
KM3 or Kernel Meta Meta Model is a neutral computer language to write metamodels and to define Domain Specific Languages. KM3 has been defined at INRIA and is available under the Eclipse platform.
Kermeta is a modeling and programming language for metamodel engineering.

Joseph Sifakis is a Greek-French computer scientist. He received the 2007 Turing Award, along with Edmund M. Clarke and E. Allen Emerson, for his work on model checking.
A metaCASE tool is a type of application software that provides the possibility to create one or more modeling methods, languages or notations for use within the process of software development. Often the result is a modeling tool for that language. MetaCASE tools are thus a kind of language workbench, generally considered as being focused on graphical modeling languages.
Globally asynchronous locally synchronous (GALS), in electronics, is an architecture for designing electronic circuits that addresses the problem of safe and reliable data transfer between independent clock domains. GALS is a model of computation that emerged in the 1980s. It allows to design computer systems consisting of several synchronous islands interacting with other islands using asynchronous communication, e.g. with FIFOs.
The Clock Constraint Specification Language or CCSL, is a software language for modeling relations among so-called clocks. It is part of the time model defined in the UML Profile for MARTE.
A language workbench is a tool or set of tools that enables software development in the language-oriented programming software development paradigm. A language workbench will typically include tools to support the definition, reuse and composition of domain-specific languages together with their integrated development environment. Language workbenches were introduced and popularized by Martin Fowler in 2005.





