
Affondatore was an armoured ram of the Regia Marina, built in the 1860s by Harrison, Millwall, London. Construction commenced in 1863; the ship, despite being incomplete, was brought to Italy during the Third Italian War of Independence. Affondatore, which translates as "Sinker", was initially designed to rely on her ram as her only weapon, but during construction she was also equipped with two 300-pounder guns.

SMS Kaiser was a 92-gun wooden ship of the line of the Austrian Navy, the last vessel of the type, and the only screw-driven example, to be built by the Austrians. She was built by the naval shipyard in Pola; she was laid down in March 1855, was launched in October 1858, and was completed the following year. The ship took part in the Second Schleswig War of 1864, but saw no action during her deployment to the North Sea. Kaiser did see action during the Seven Weeks' War two years later, during which she took part in the Battle of Lissa as the flagship of Anton von Petz, commander of the Austrian 2nd Division. Kaiser engaged several Italian ironclads simultaneously, rammed one—Re di Portogallo—and damaged another—Affondatore—with gunfire. In doing so, she became the only wooden ship of the line to engage an ironclad warship in battle.

SMS Drache was the first of two Drache-class armored frigates built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the 1860s, the other being Salamander. Drache was laid down in February 1861, launched in September, and completed in November 1862. She remained in the Adriatic during the Second Schleswig War in 1864 while other ships were sent to attack Denmark. Two years later, Prussia and Italy attacked Austria in the Seven Weeks' War. The ship participated in the Austrian victory over the Italians in the Battle of Lissa, where she inflicted serious damage on the coastal defense ship Palestro, setting her on fire and ultimately destroying her. Drache was modernized immediately after the war, but saw little use thereafter. Badly rotted by 1875, she was stricken from the Navy List that year and eventually broken up in 1883.

SMS Salamander was a Drache-class armored frigate built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the 1860s; she was laid down in February 1861, launched in August that year, and completed in May 1862, six months before her sister Drache. She was a broadside ironclad, mounting a battery of twenty-eight guns in gun ports along the length the hull. During the Second Schleswig War in 1864, Salamander remained in the Adriatic to protect Austria from a possible Danish attack that did not materialize. Two years later, during the Seven Weeks' War, she participated in the Austrian victory over a superior Italian fleet in the Battle of Lissa in July 1866. Immediately after the war, she was modernized with a battery of more powerful guns. Little used thereafter owing to reduced naval budgets, she was stricken from the Navy List in 1883 and hulked for use as a mine storage ship before being broken up in 1895–1896.

Regina Maria Pia was the lead ship of the Regina Maria Pia class of ironclad warships built in French shipyards for the Italian Regia Marina in the 1860s. She and her three sister ships were broadside ironclads, mounting a battery of four 203-millimetre (8 in) and twenty-two 164 mm (6.5 in) guns on the broadside. Regina Maria Pia was laid down in July 1862, was launched in April 1863, and was completed in April 1864.

San Martino was a Regina Maria Pia-class ironclad warship, the second member of her class. She was built for the Italian Regia Marina in the 1860s; like her three sister ships, she was built in France. San Martino was laid down in July 1862, was launched in September 1863, and was completed in November 1864. The ships were broadside ironclads, mounting a battery of four 200-millimetre (8 in) and twenty-two 164 mm (6.5 in) guns on the broadside.

Castelfidardo was the third of four Regina Maria Pia-class ironclad warships built in French shipyards for the Italian Regia Marina in the 1860s. Castelfidardo was laid down in July 1862, was launched in August 1863, and was completed in May 1864. She and her three sister ships were broadside ironclads, mounting a battery of four 200-millimetre (8 in) and twenty-two 164 mm (6.5 in) guns on the broadside.

Ancona was an ironclad warship, the last member of the Regina Maria Pia class built in French shipyards for the Italian Regia Marina in the 1860s. Ancona was laid down in August 1862, was launched in October 1864, and completed in April 1866. She and her three sister ships were broadside ironclads, mounting a battery of four 200-millimeter (8 in) and twenty-two 164 mm (6.5 in) guns on the broadside.

Re di Portogallo was an ironclad warship built for the Italian Regia Marina in the 1860s, the second and final member of the Re d'Italia class. She was laid down at the William H. Webb Shipyard in New York in December 1861, was launched in August 1863, and was completed a year later in August 1864; the two Re d'Italia-class ships were the only Italian ironclads built in the United States. The ships were broadside ironclads, armed with a battery of six 72-pounder guns and thirty-two 164 mm (6.5 in) guns.

Principe di Carignano was the lead ship of the Principe di Carignano class of ironclad warships built for the Italian Regia Marina in the 1860s. She was the first ironclad built in Italy; her keel was laid January 1861, her hull was launched in September 1863, and she was completed in June 1865. Principe di Carignano was a broadside ironclad armed with a battery of ten 203-millimetre (8 in) guns and twelve 164-millimeter (6.5 in) guns.

Terribile was the first ironclad warship to be built for the Italian Regia Marina, and the second member of the Formidabile class. Terribile and her sister, Formidabile, were both built in France. A broadside ironclad, she was laid down in June 1860, launched in February 1861, and was completed in September that year. She was the first Italian ironclad to enter service and was equipped with four 203 mm (8 in) and sixteen 164 mm (6.5 in) guns.

Formidabile was the lead ship of the Formidabile-class ironclad warships, the first ships of that type to be built for the newly formed Italian Regia Marina. Formidabile and her sister, Terribile, were both built in France; Formidabile was laid down in December 1860, was launched in October 1861, and was completed in May 1862. She was a broadside ironclad, equipped with four 203 mm (8 in) and sixteen 164 mm (6.5 in) guns.

SMS Prinz Eugen was an ironclad warship built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the 1870s, the third and final member of the Kaiser Max class. The ship was supposedly the same vessel that had been laid down in 1861, and had simply been reconstructed. In reality, the head of the Austro-Hungarian Navy could not secure funding for new ships, but reconstruction projects were uncontroversial, so he "rebuilt" the three earlier Kaiser Max-class ironclads. Only the engines and parts of the armor plate were reused in the new Prinz Eugen, which was laid down in October 1874, launched in September 1877, and commissioned in November 1878. The ship spent significant periods out of service, in part due to slender naval budgets that prevented much active use. In 1880, she took part in an international naval demonstration against the Ottoman Empire, and she went to Spain in 1888 for the Barcelona Universal Exposition. Prinz Eugen was stricken in 1904 and converted into a repair ship in 1906–1909. She was renamed Vulkan and served in this capacity through World War I; after the war, she was seized by Italy but was awarded to Yugoslavia in the postwar peace negotiations. Italy refused to hand the ship over, however, and her ultimate fate is unknown.

The Erzherzog Ferdinand Max class consisted of a pair of ironclad warships—Erzherzog Ferdinand Max and Habsburg—built for the Austrian Navy in the 1860s. They were the last broadside armored frigates to be built for the Austrian Empire, and the last vessels completed to see action against the Italians at the Battle of Lissa in 1866. Intended to have been armed with new breech-loading Krupp guns, the outbreak of the Seven Weeks' War prevented the delivery of the guns, forcing the Austrian Navy to arm the ships with a battery of sixteen older 48-pounder muzzle-loading guns.

SMS Erzherzog Ferdinand Max was the lead ship of the Erzherzog Ferdinand Max class of broadside ironclads built for the Austrian Navy in the 1860s. She was built by the Stabilimento Tecnico Triestino, with her keel laying in October 1863, launching in May 1865, and commissioning in June 1866 at the outbreak of the Third Italian War of Independence and the Austro-Prussian War, fought concurrently. The ship was armed with a main battery of sixteen 48-pounder guns, though the rifled guns originally intended, which had been ordered from Prussia, had to be replaced with old smoothbore guns until after the conflicts ended.

SMS Habsburg was the second and final member of the Erzherzog Ferdinand Max class of broadside ironclads built for the Austrian Navy in the 1860s. She was built by the Stabilimento Tecnico Triestino; her keel was laid down in June 1863, she was launched in June 1865, and commissioning in June 1866 at the outbreak of the Third Italian War of Independence and the Austro-Prussian War, fought concurrently. The ship was armed with a main battery of sixteen 48-pounder guns, though the rifled guns originally intended, which had been ordered from Prussia, had to be replaced with old smoothbore guns until after the conflicts ended.

The Kaiser Max class of broadside ironclads was a group of three vessels built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the 1860s. The class consisted of Kaiser Max, the lead ship, Prinz Eugen, and Juan de Austria. They were an improved version of the preceding Drache class, being larger, carrying a larger gun battery, and having more powerful engines. The three ships were all laid down in 1861, launched in 1862, and completed in 1863.
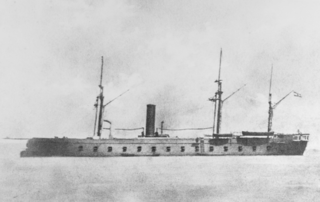
SMS Kaiser Max was the lead ship of the Kaiser Max class of armored frigates built for the Austrian Navy in the 1860s. Her keel was laid in October 1861 at the Stabilimento Tecnico Triestino shipyard; she was launched in March 1862, and was completed in 1863. She carried her main battery—composed of sixteen 48-pounder guns and fifteen 24-pounders—in a traditional broadside arrangement, protected by an armored belt that was 110 mm (4.3 in) thick.

SMS Don Juan d'Austria was the third member of the Kaiser Max class built for the Austrian Navy in the 1860s. Her keel was laid in October 1861 at the Stabilimento Tecnico Triestino shipyard; she was launched in July 1862, and was completed in 1863. She carried her main battery—composed of sixteen 48-pounder guns and fifteen 24-pounders—in a traditional broadside arrangement, protected by an armored belt that was 110 mm (4.3 in) thick.



















