
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cells that function as receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen receptors, namely ERα and ERβ, which belong to the nuclear receptor family. The second class consists of membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), such as GPER (GPR30), ER-X, and Gq-mER, which are primarily G protein-coupled receptors. This article focuses on the nuclear estrogen receptors.

The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone.

A selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM) is an agent that acts on the progesterone receptor (PR), the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. A characteristic that distinguishes such substances from full receptor agonists and full antagonists is that their action differs in different tissues, i.e. agonist in some tissues while antagonist in others. This mixed profile of action leads to stimulation or inhibition in tissue-specific manner, which further raises the possibility of dissociating undesirable adverse effects from the development of synthetic PR-modulator drug candidates.
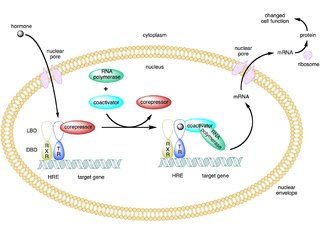
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage.

Proline-, glutamic acid- and leucine-rich protein 1 (PELP1) also known as modulator of non-genomic activity of estrogen receptor (MNAR) and transcription factor HMX3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PELP1 gene. is a transcriptional corepressor for nuclear receptors such as glucocorticoid receptors and a coactivator for estrogen receptors.

Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1, is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ESR1.
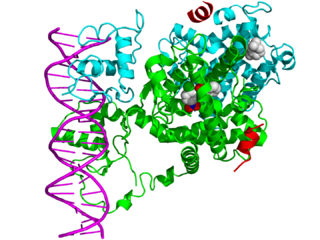
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These intracellular receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes, thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism.
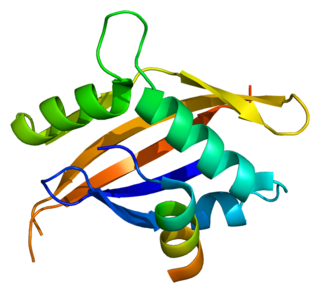
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1), also called steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1), is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor–interacting domains and possesses intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. It is encoded by the gene NCOA1.
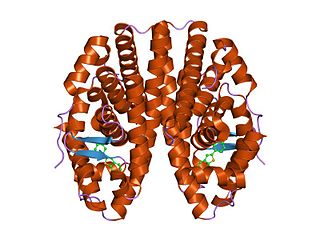
The nuclear receptor coactivator 2 also known as NCoA-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA2 gene. NCoA-2 is also frequently called glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (GRIP1), steroid receptor coactivator-2 (SRC-2), or transcriptional mediators/intermediary factor 2 (TIF2).

The nuclear receptor coactivator 3 also known as NCOA3 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the NCOA3 gene. NCOA3 is also frequently called 'amplified in breast 1' (AIB1), steroid receptor coactivator-3 (SRC-3), or thyroid hormone receptor activator molecule 1 (TRAM-1).

Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) also known as NR3A2 is one of two main types of estrogen receptor—a nuclear receptor which is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans ERβ is encoded by the ESR2 gene.

Bert W. O'Malley is an endocrinologist from the United States. He was born in 1936 in the Garfield section of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He received his early education at Catholic primary schools and Central Catholic High School, before pursuing higher education at the University of Pittsburgh, where he completed both his undergraduate and medical studies, graduating first in his class. It was here that he met Sally, who would become his wife and lifelong partner. The couple went on to have four children.

Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), also known as NR3B1, is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRA gene. ERRα was originally cloned by DNA sequence homology to the estrogen receptor alpha, but subsequent ligand binding and reporter-gene transfection experiments demonstrated that estrogens did not regulate ERRα. Currently, ERRα is considered an orphan nuclear receptor.

Nuclear receptor coactivator 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA6 gene.

Breast carcinoma amplified sequence 3, also known as BCAS3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BCAS3 gene. BCAS3 is a gene that is amplified and overexpressed in breast cancer cells.

RNA-binding protein 39 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBM39 gene.
Nuclear receptor coregulators are a class of transcription coregulators that have been shown to be involved in any aspect of signaling by any member of the nuclear receptor superfamily. A comprehensive database of coregulators for nuclear receptors and other transcription factors was previously maintained at the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas website which has since been replaced by the Signaling Pathways Project website.

ERX-11, also known as ERα coregulator-binding modulator-11, is a novel antiestrogen and experimental hormonal antineoplastic agent which is being researched for the potential treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. It is not a competitive antagonist of the estrogen receptor (ER) like conventional antiestrogens such as tamoxifen or fulvestrant; instead of binding to the ligand-binding site of the ER, ERX-11 interacts with a different part of the ERα and blocks protein–protein interactions of the ERα with coregulators that are necessary for the receptor to act and regulate gene expression. It was designed to bind to the coregulator binding region of the ERα and inhibit the ERα/coactivator interaction, although its precise binding site and mode of action have yet to be fully elucidated and understood. Nonetheless, it is clear that ERX-11 binds within the AF-2 domain of the ERα.
Endocrine therapy is a common treatment for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. However, resistance to this therapy can develop, leading to relapse and progression of disease. This highlights the need for new strategies to combat this resistance.





















