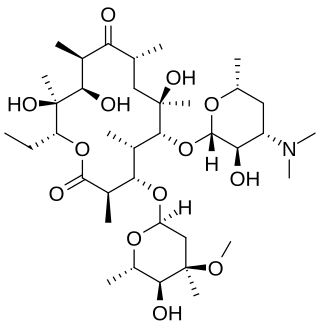
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used during pregnancy to prevent Group B streptococcal infection in the newborn, and to improve delayed stomach emptying. It can be given intravenously and by mouth. An eye ointment is routinely recommended after delivery to prevent eye infections in the newborn.

Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but is now used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic.

Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against Gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds.

Cytochromes P450 are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these enzymes oxidize steroids, fatty acids, xenobiotics, and participate in many biosyntheses. CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. In almost all of the transformations that they catalyze, P450's affect hydroxylation.

Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Different strains of the same species may colonize very diverse environments.

Lincosamides are a class of antibiotics, which include lincomycin, clindamycin, and pirlimycin.
The rpoB gene encodes the β subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase and the homologous plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP). It codes for 1342 amino acids in E. coli, making it the second-largest polypeptide in the bacterial cell. It is targeted by the rifamycin family of antibacterials, such as rifampin. Mutations in rpoB that confer resistance to rifamycins do so by altering the protein's drug-binding residues, thereby reducing affinity for these antibiotics.

Platensimycin, a metabolite of Streptomyces platensis, is an antibiotic, which act by blocking enzymes.

Oleandomycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is synthesized from strains of Streptomyces antibioticus. It is weaker than erythromycin.

Streptomyces griseus is a species of bacteria in the genus Streptomyces commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, S. griseus strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of S. griseus. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed.
6-deoxyerythronolide B hydroxylase is an Actinomycetota Cytochrome P450 enzyme originally from Saccharopolyspora erythraea, catalyzes the 6S-hydroxylate of 6-deoxyerythronolide B (6-DEB) to erythronolide B (EB) which is the first step of biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic erythromycin. This bacterial enzyme belongs to CYP family CYP107, with the CYP Symbol CYP107A1.
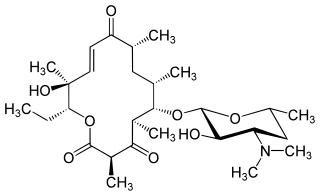
Pikromycin was studied by Brokmann and Hekel in 1951 and was the first antibiotic macrolide to be isolated. Pikromycin is synthesized through a type I polyketide synthase system in Streptomyces venezuelae, a species of Gram-positive bacterium in the genus Streptomyces. Pikromycin is derived from narbonolide, a 14-membered ring macrolide. Along with the narbonolide backbone, pikromycin includes a desosamine sugar and a hydroxyl group. Although Pikromycin is not a clinically useful antibiotic, it can be used as a raw material to synthesize antibiotic ketolide compounds such as ertythromycins and new epothilones.

Carbomycin, also known as magnamycin, is a colorless, optically active crystalline macrolide antibiotic with the molecular formula C42H67N O16. It is derived from the bacterium Streptomyces halstedii and active in inhibiting the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and "certain Mycoplasma strains." Its structure was first proposed by Robert Woodward in 1957 and was subsequently corrected in 1965.
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of Actinomycetota, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants. Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.

Streptomyces antibioticus is a gram-positive bacterium discovered in 1941 by Nobel-prize-winner Selman Waksman and H. Boyd Woodruff. Its name is derived from the Greek "strepto-" meaning "twisted", alluding to this genus' chain-like spore production, and "antibioticus", referring to this species' extensive antibiotic production. Upon its first characterization, it was noted that S. antibioticus produces a distinct soil odor.
Streptomyces virginiae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces virginiae produces actithiazic acid, virginiamycins and cycloserine. Streptomyces virginiae also produces monensin A, monensin B, monensin C, monensin D, actithiazic acid.
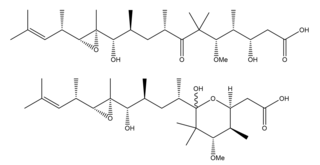
Gephyronic acid is a polyketide that exists as an equilibrating mixture of structural isomers. In nature, gephyronic acid is produced by slow growing myxobacterium: Archangium gephyra strain Ar3895 and Cystobacter violaceus strain Cb vi76. It is the first antibiotic in myxobacteria that was reported to specifically inhibit eukaryotic protein synthesis.
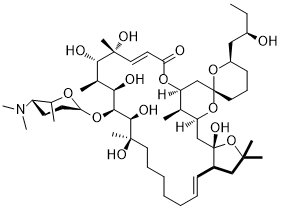
Ossamycin is a fermentation-derived natural product belonging to a family of 22- to 26-membered macrocyclic polyketides which is featured with a 6,6-spiroacetal (1,7-dioxaspiro[5,5]-undecanyl) moiety connected to one side of the macrocycle. Widely-studied 26-membered oligomycins/rutamycins, 24-membered dunaimycins, and 22-membered cytovaricin are also in this family.
Cytochrome P450 family 107 subfamily G member 1 is an actinobacterial Cytochrome P450 enzyme originally from Streptomyces rapamycinicus, which catalyzes the oxidation reaction of C27 of pre-rapamycin in the biosynthesis pathway of the macrolide antibiotic rapamycin.
Cytochrome P450, family 107, also known as CYP107, is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family in bacteria, found to be conserved and highly populated in Streptomyces and Bacillus species. The first gene identified in this family is Cytochrome P450 eryF (CYP107A1) from Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Many enzymes of this family are involved in the synthesis of macrolide antibiotics. The members of this family are widely distributed in Alphaproteobacteria, cyanobacterial, Mycobacterium, Bacillota, and Streptomyces species, which may be due to horizontal gene transfer driven by selection pressure.