Related Research Articles

Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used during pregnancy to prevent Group B streptococcal infection in the newborn, as well as to improve delayed stomach emptying. It can be given intravenously and by mouth. An eye ointment is routinely recommended after delivery to prevent eye infections in the newborn.

Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.

Cytochrome P450 2A6 is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and cotinine. It is also involved in the metabolism of several pharmaceuticals, carcinogens, and a number of coumarin-type alkaloids. CYP2A6 is the only enzyme in the human body that appreciably catalyzes the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin, such that the formation of the product of this reaction, 7-hydroxycoumarin, is used as a probe for CYP2A6 activity.

Aldosterone synthase is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone. It is a protein which is only expressed in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex and is primarily regulated by the renin–angiotensin system. It is the sole enzyme capable of synthesizing aldosterone in humans and plays an important role in electrolyte balance and blood pressure.

Cytochrome P450 17A1, also called steroid 17α-monooxygenase, 17α-hydroxylase, 17,20-lyase, or 17,20-desmolase, is an enzyme of the hydroxylase type that in humans is encoded by the CYP17A1 gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types, including the zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex and zona fasciculata as well as gonadal tissues. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are generally regarded as monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids, and other lipids, including the remarkable carbon-carbon bond scission catalyzed by this enzyme. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum. It has both 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase activities, and is a key enzyme in the steroidogenic pathway that produces progestins, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. More specifically, CYP17A1 acts upon pregnenolone and progesterone to add a hydroxyl (-OH) group at carbon 17 of the steroid D ring, or acts upon 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone to split the side-chain off the steroid nucleus. The CYP17A1 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

CYP27A1 is a gene encoding a cytochrome P450 oxidase, and is commonly known as sterol 27-hydroxylase. This enzyme is located in many different tissues where it is found within the mitochondria. It is most prominently involved in the biosynthesis of bile acids.

Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7A1 gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis.
Steroid 21-hydroxylase, also called steroid 21-monooxygenase, 21α-hydroxylase, P45021A2, and, less commonly, 21β-hydroxylase, is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that is involved with the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones aldosterone and cortisol. These syntheses take place in the adrenal cortex. Specifically, 21-hydroxylase converts progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, by hydroxylating at the C21 position. The products of the conversions then continue through their appropriate pathways towards creation of aldosterone and cortisol.

Steroid 11β-hydroxylase is a steroid hydroxylase found in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata. Named officially the cytochrome P450 11B1, mitochondrial, it is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP11B1 gene.
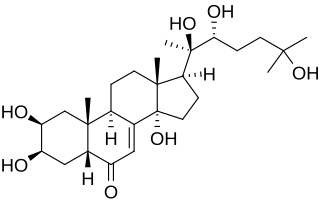
In enzymology, a 5beta-cholestane-3alpha,7alpha-diol 12alpha-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.96) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Leukotriene-B(4) omega-hydroxylase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F2 gene.

25-hydroxycholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase also known as oxysterol and steroid 7-alpha-hydroxylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7B1 gene. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids.

Cytochrome P450 4F8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F8 gene.

Leukotriene-B(4) omega-hydroxylase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F3 gene. CYP4F3 encodes two distinct enzymes, CYP4F3A and CYP4F3B, which originate from the alternative splicing of a single pre-mRNA precursor molecule; selection of either isoform is tissue-specific with CYP3F3A being expressed mostly in leukocytes and CYP4F3B mostly in the liver.

Vitamin D 25-hydroxylase also known as cytochrome P450 2R1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP2R1 gene.

CYP4F11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F11 gene. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This gene is part of a cluster of cytochrome P450 genes on chromosome 19. Another member of this family, CYP4F2, is approximately 16 kb away. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.
The halloween genes are a set of genes identified in Drosophila melanogaster that influence embryonic development. All of the genes code for cytochrome P450 enzymes in the ecdysteroidogenic pathway (biosynthesis of ecdysone from cholesterol). Ecdysteroids such as 20-hydroxyecdysone and ecdysone influence many of the morphological, physiological, biochemical changes that occur during molting in insects.

Saccharopolyspora erythraea, formerly known as Streptomyces erythraeus, is a species of actinomycete bacteria within the genus Saccharopolyspora.
Erythromycin 12 hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.154, EryK) is an enzyme with systematic name erythromycin-D,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (12-hydroxylating) . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Erythromycin 3''-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:erythromycin C 3''-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Weber JM, Leung JO, Swanson SJ, Idler KB, McAlpine JB (April 1991). "An erythromycin derivative produced by targeted gene disruption in Saccharopolyspora erythraea". Science. 252 (5002): 114–7. Bibcode:1991Sci...252..114W. doi:10.1126/science.2011746. PMID 2011746.
- ↑ Andersen JF, Hutchinson CR (February 1992). "Characterization of Saccharopolyspora erythraea cytochrome P-450 genes and enzymes, including 6-deoxyerythronolide B hydroxylase". Journal of Bacteriology. 174 (3): 725–35. doi:10.1128/jb.174.3.725-735.1992. PMC 206148 . PMID 1732208.
- ↑ Cupp-Vickery JR, Poulos TL (February 1995). "Structure of cytochrome P450eryF involved in erythromycin biosynthesis". Nature Structural Biology. 2 (2): 144–53. doi:10.1038/nsb0295-144. PMID 7749919.
- ↑ Harris DL (September 2002). "Oxidation and electronic state dependence of proton transfer in the enzymatic cycle of cytochrome P450eryF". Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry. 91 (4): 568–85. doi:10.1016/s0162-0134(02)00477-4. PMID 12237223.
| This enzyme-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |