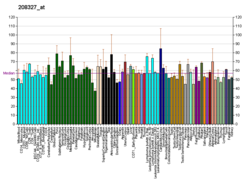
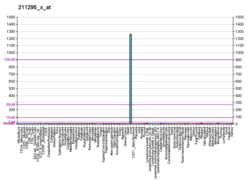
Cytochrome P450 2A13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP2A13 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Contents
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum. Although its endogenous substrate has not been determined, it is known to metabolize 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, a major nitrosamine specific to tobacco. This gene is part of a large cluster of cytochrome P450 genes from the CYP2A, CYP2B and CYP2F subfamilies on chromosome 19q. [7]