Related Research Articles

Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d.

Cytochromes P450 are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Estabrook, Cooper, and Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.
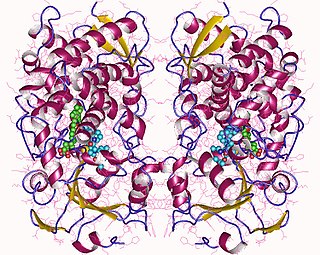
Cytochrome P450 3A4 is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme.
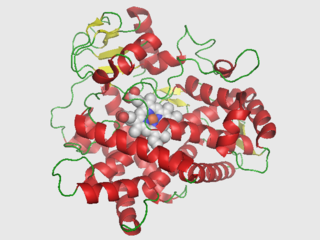
Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP2D6 gene. CYP2D6 is primarily expressed in the liver. It is also highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system, including the substantia nigra.

Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin. These proteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, and DNA repair. The flavoproteins are some of the most-studied families of enzymes.
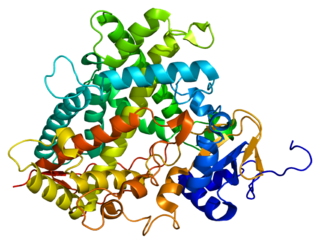
Cytochrome P450 1A2, a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the human body. In humans, the CYP1A2 enzyme is encoded by the CYP1A2 gene.

Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7A1 gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis.

Steroid 21-hydroxylase is an enzyme that hydroxylates steroids at the C21 position and is involved in biosynthesis of aldosterone and cortisol. The enzyme converts progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, within metabolic pathways that ultimately lead to aldosterone and cortisol. Deficiency in the enzyme may cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia.

Cytochrome P450 reductase is a membrane-bound enzyme required for electron transfer from NADPH to cytochrome P450 and other heme proteins including heme oxygenase in the endoplasmic reticulum of the eukaryotic cell.

Cytochrome P450 2B6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP2B6 gene. CYP2B6 is a member of the cytochrome P450 group of enzymes. Along with CYP2A6, it is involved with metabolizing nicotine, along with many other substances.

Lanosterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51A1) is the animal version of a cytochrome P450 enzyme that is involved in the conversion of lanosterol to 4,4-dimethylcholesta-8(9),14,24-trien-3β-ol. The cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are a conserved group of proteins that serve as key players in the metabolism of organic substances and the biosynthesis of important steroids, lipids, and vitamins in eukaryotes. As a member of this family, lanosterol 14α-demethylase is responsible for an essential step in the biosynthesis of sterols. In particular, this protein catalyzes the removal of the C-14α-methyl group from lanosterol. This demethylation step is regarded as the initial checkpoint in the transformation of lanosterol to other sterols that are widely used within the cell.

Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase, also commonly known as cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase, cholesterol 24-monooxygenase, CYP46, or CYP46A1, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol. It is responsible for the majority of cholesterol turnover in the human central nervous system. The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (24-hydroxylating).
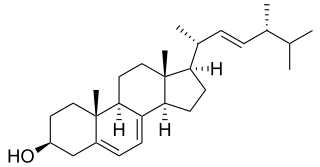
In enzymology, a sterol 14-demethylase (EC 1.14.13.70) is an enzyme of the Cytochrome P450 (CYP) superfamily. It is any member of the CYP51 family. It catalyzes a chemical reaction such as:

Cytochrome P450 3A5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP3A5 gene.
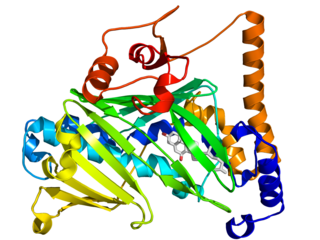
The oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related proteins (ORPs) are a family of lipid transfer proteins (LTPs). Concretely, they constitute a family of sterol and phosphoinositide binding and transfer proteins in eukaryotes that are conserved from yeast to humans. They are lipid-binding proteins implicated in many cellular processes related with oxysterol, including signaling, vesicular trafficking, lipid metabolism, and nonvesicular sterol transport.

CYP27C1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP27C1 gene. The Enzyme Commission number (EC) for this protein is EC 1.14.19.53. The full accepted name is all-trans-retinol 3,4-desaturase and the EC number 1 classifies CYP27C1 as a oxidoreductase that acts on paired donor by reducing oxygen. It is also identifiable by the UniProt code Q4G0S4.
Penicillium coprobium is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces pyripyropene A, roquefortine C, penicillic acid and patulin.
Cytochrome c oxidase assembly factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COA5 gene. This gene encodes an ortholog of yeast Pet191, which in yeast is a subunit of a large oligomeric complex associated with the mitochondrial inner membrane, and required for the assembly of the cytochrome c oxidase complex. Mutations in this gene are associated with mitochondrial complex IV deficiency.
ERG5 or Sterol 22-desaturase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway of fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae, with the CYP Symbol CYP61A1. CYP61A1 is one of only three P450 enzyme found in baker's yeast, the other two are CYP51F1 and CYP56A1. The ortholog in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, was named CYP61A3 for historical reasons, and is only one of two P450 enzyme found with CYP51F1. ERG5 catalyzes the C22-C23 double bond formation on the sterol side chain of ergostatrienol to convert it into ergostatetraenol, then the C24 double bond of ergostatetrenol will be hydrogenation reduced into ergosterol by ERG4.
Cytochrome P450, family 52, also known as CYP52, is a cytochrome P450 family in fungi participate in the assimilation of alkanes and fatty acids, which the most ancient function was the oxidation of C4-C11 alkanes. The first gene identified in this family is the alkane-inducible cytochrome P450 (P450alk) gene from the yeast Candida tropicalis, with CYP Symbol CYP52A1.
References
- ↑ Nelson DR (January 2018). "Cytochrome P450 diversity in the tree of life". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics. 1866 (1): 141–154. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.05.003. PMC 5681887 . PMID 28502748.
- ↑ "UniProtKB - P21595 (CP56_YEAST)". UniProt.