Related Research Articles

Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Estabrook, Cooper, and Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.
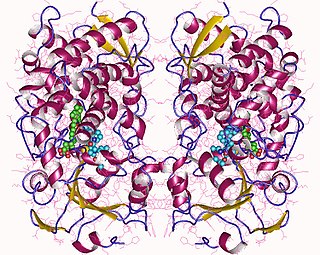
Cytochrome P450 3A4 is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme.
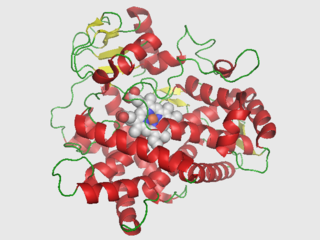
Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP2D6 gene. CYP2D6 is primarily expressed in the liver. It is also highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system, including the substantia nigra.

Cytochrome P450 2A6 is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and cotinine. It is also involved in the metabolism of several pharmaceuticals, carcinogens, and a number of coumarin-type alkaloids. CYP2A6 is the only enzyme in the human body that appreciably catalyzes the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin, such that the formation of the product of this reaction, 7-hydroxycoumarin, is used as a probe for CYP2A6 activity.
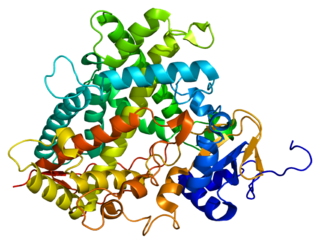
Cytochrome P450 1A2, a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the human body. In humans, the CYP1A2 enzyme is encoded by the CYP1A2 gene.

Cytochrome P450 1B1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP1B1 gene.

Bietti's crystalline dystrophy (BCD) is a rare autosomal recessive eye disease named after G. B. Bietti.
Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, also known as CYP3A, is a human gene locus. A homologous locus is found in mice.

Cytochrome P450 2A13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP2A13 gene.

Cytochrome P450 3A43 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP3A43 gene.

Cytochrome P450 2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP2F1 gene.

Cytochrome P450 4F8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F8 gene.

CYP2A7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP2A7 gene.
The DAF-12 gene encodes the nuclear receptor of dafachronic acid in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans, with the NRNC Symbol NR1J1 as the homolog of nuclear hormone receptor HR96 in Drosophila melanogaster. DAF-12 has been implicated by Cynthia Kenyon and colleagues in the formation of Dauer larva.
The Daf-9 gene encodes a cytochrome p450 enzyme catalysis the generation of dafachronic acid in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans, with the CYP Symbol CYP22A1. After generation, dafachronic acid will binding it's nuclear receptor Daf-12 and has been implicated by Cynthia Kenyon and colleagues related to the formation of Dauer larva.
The Dod-13 gene in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans encoding a cytochrome p450 enzyme, which have steroid hydroxylase activity, with the CYP Symbol CYP35B1. Dod-13 is downstream gene of Daf-16 influenced the lifespan of C. elegans.
Cytochrome P450, family 12, also known as CYP12, is a cytochrome P450 family found in insect genome belongs to Mitochondrial clan CYPs, which is located in the inner membrane of mitochondria(IMM). The first gene identified in this family is the CYP12A1 from the Musca domestica, which is involved in insecticide resistance. CYP12A1 protein localization in mitochondria by immunohistochemistry and absolute dependence on mitochondrial electron donors adrenodoxin reductase and adrenodoxin.
Cytochrome P450, family 13, also known as CYP13, is a nematoda cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP13A1 from the Caenorhabditis elegans.
Cytochrome P450, family 14, also known as CYP14, is a nematoda cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP14A1 from the Caenorhabditis elegans. The function of most genes in this family is unknown.
Cytochrome P450, family 23, also known as CYP23, is a nematoda cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP23A1 from the Caenorhabditis elegans, is a homolog of the human gene CYP7B1.
References
- ↑ Nelson, DR (November 1998). "Metazoan cytochrome P450 evolution". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part C, Pharmacology, Toxicology & Endocrinology. 121 (1–3): 15–22. doi:10.1016/s0742-8413(98)10027-0. PMID 9972448.
- ↑ Ladage, ML; King, SD; Burks, DJ; Quan, DL; Garcia, AM; Azad, RK; Padilla, PA (13 October 2016). "Glucose or Altered Ceramide Biosynthesis Mediate Oxygen Deprivation Sensitivity Through Novel Pathways Revealed by Transcriptome Analysis in Caenorhabditis elegans". G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics. 6 (10): 3149–3160. doi:10.1534/g3.116.031583. PMC 5068937 . PMID 27507791.