
Oxidative phosphorylation or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.

Heme, or haem, is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.

Cytochromes P450 are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Estabrook, Cooper, and Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.

Thromboxane A synthase 1 , also known as TBXAS1, is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the TBXAS1 gene.

Aldosterone synthase, also called steroid 18-hydroxylase, corticosterone 18-monooxygenase or P450C18, is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and other steroids. The enzyme catalyzes sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18 after initial 11β-hydroxylation. It is encoded by the CYP11B2 gene in humans.

Steroid 11β-hydroxylase, also known as steroid 11β-monooxygenase, is a steroid hydroxylase found in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. Named officially the cytochrome P450 11B1, mitochondrial, it is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP11B1 gene. The enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of adrenal corticosteroids by catalyzing the addition of hydroxyl groups during oxidation reactions.

Prostaglandin-I synthase also known as prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) synthase (PTGIS) or CYP8A1 is an enzyme involved in prostanoid biosynthesis that in humans is encoded by the PTGIS gene. This enzyme belongs to the family of cytochrome P450 isomerases.
Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate synthase is a type of enzyme called a phosphotransferase and is involved in mammalian starch and sucrose metabolism. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to glucose-1-phosphate, yielding 3-phosphoglycerate and glucose-1,6-bisphosphate.

Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), also known as prostaglandin G/H synthase 1, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 or prostaglandin H2 synthase 1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGS1 gene. In humans it is one of two cyclooxygenases.

Cytochrome P450 4A11 is a protein that in humans is codified by the CYP4A11 gene.
3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate dehydrogenase is an enzyme with systematic name 3-(cis-5,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)propanoate:NAD+ oxidoreductase. It is produced by the gene hcaB. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Linoleate 8R-lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.60, linoleic acid 8R-dioxygenase, 5,8-LDS (bifunctional enzyme), 7,8-LDS (bifunctional enzyme), 5,8-linoleate diol synthase (bifunctional enzyme), 7,8-linoleate diol synthase (bifunctional enzyme), PpoA) is an enzyme with systematic name linoleate:oxygen (8R)-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Linolenate 9R-lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.61, NspLOX, (9R)-LOX, linoleate 9R-dioxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name alpha-linolenate:oxygen (9R)-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
5-epiaristolochene 1,3-dihydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.119, 5-epi-aristolochene 1,3-dihydroxylase, EAH) is an enzyme with systematic name 5-epiaristolochene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (1- and 3-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Germacradienol synthase (EC 4.2.3.22, germacradienol/germacrene-D synthase, 2-trans,6-trans-farnesyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase [(1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-1(10),5-dien-11-ol-forming]) is an enzyme with systematic name (2E,6E)-farnesyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase ((1E,4S,5E,7R)-germacra-1(10),5-dien-11-ol-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
9,12-octadecadienoate 8-hydroperoxide 8R-isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name (8R,9Z,12Z)-8-hydroperoxyoctadeca-9,12-dienoate hydroxymutase ( -5,8-dihydroxyoctadeca-9,12-dienoate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
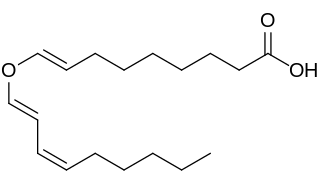
Divinylether fatty acids contain a fatty acid chemically combined with a doubly unsaturated carbon chain linked by an oxygen atom (ether). Fatty acid hydroperoxides generated by plant lipoxygenases from linoleic and linolenic acids are known to serve as substrates for a divinyl ether synthase which produces divinyl ether fatty acids. Up to date divinyl ethers were detected only within the plant kingdom.

12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid (also termed 12-HHT, 12(S)-hydroxyheptadeca-5Z,8E,10E-trienoic acid, or 12(S)-HHTrE) is a 17 carbon metabolite of the 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid. It was first detected and structurally defined by P. Wlodawer, Bengt I. Samuelsson, and M. Hamberg as a product of arachidonic acid metabolism made by microsomes (i.e. endoplasmic reticulum) isolated from sheep seminal vesicle glands and by intact human platelets. 12-HHT is less ambiguously termed 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid to indicate the S stereoisomerism of its 12-hydroxyl residue and the Z, E, and E cis-trans isomerism of its three double bonds. The metabolite was for many years thought to be merely a biologically inactive byproduct of prostaglandin synthesis. More recent studies, however, have attached potentially important activity to it.

Hydroperoxide lyases are enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of C-C bonds in the hydroperoxides of fatty acids. They belong to the cytochrome P450 enzyme family.

18-Hydroxy-11-deoxycorticosterone is an endogenous steroid and a mineralocorticoid. It is a hydroxylated metabolite of 11-deoxycorticosterone.













