Related Research Articles

Cytochromes P450 are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown. In 1963, Estabrook, Cooper, and Rosenthal described the role of CYP as a catalyst in steroid hormone synthesis and drug metabolism. In plants, these proteins are important for the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones.

Cytochrome P450 2A6 is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and cotinine. It is also involved in the metabolism of several pharmaceuticals, carcinogens, and a number of coumarin-type alkaloids. CYP2A6 is the only enzyme in the human body that appreciably catalyzes the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin, such that the formation of the product of this reaction, 7-hydroxycoumarin, is used as a probe for CYP2A6 activity.

Cytochrome P450 17A1 is an enzyme of the hydroxylase type that in humans is encoded by the CYP17A1 gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types, including the zona reticularis and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex as well as gonadal tissues. It has both 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase activities, and is a key enzyme in the steroidogenic pathway that produces progestins, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. More specifically, the enzyme acts upon pregnenolone and progesterone to add a hydroxyl (-OH) group at carbon 17 position (C17) of the steroid D ring, or acts upon 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone to split the side-chain off the steroid nucleus.

Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7A1 gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis.

Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP21A2 gene. The protein is an enzyme that hydroxylates steroids at the C21 position on the molecule. Naming conventions for enzymes are based on the substrate acted upon and the chemical process performed. Biochemically, this enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of the adrenal gland hormones aldosterone and cortisol, which are important in blood pressure regulation, sodium homeostasis and blood sugar control. The enzyme converts progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, within metabolic pathways which in humans ultimately lead to aldosterone and cortisol creation—deficiency in the enzyme may cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Ecdysone 20-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome P450 3A5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP3A5 gene.

Cytochrome P450 2C18 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP2C18 gene.

Cytochrome P450 4F2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F2 gene. This protein is an enzyme, a type of protein that catalyzes chemical reactions inside cells. This specific enzyme is part of the superfamily of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, and the encoding gene is part of a cluster of cytochrome P450 genes located on chromosome 19.

Cytochrome P450 4F3, also leukotriene-B(4) omega-hydroxylase 2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F3 gene. CYP4F3 encodes two distinct enzymes, CYP4F3A and CYP4F3B, which originate from the alternative splicing of a single pre-mRNA precursor molecule; selection of either isoform is tissue-specific with CYP3F3A being expressed mostly in leukocytes and CYP4F3B mostly in the liver.
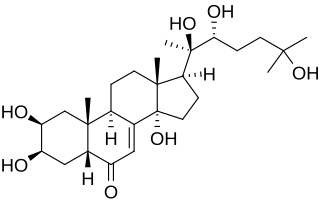
The halloween genes are a set of genes identified in Drosophila melanogaster that influence embryonic development. All of the genes code for cytochrome P450 enzymes in the ecdysteroidogenic pathway (biosynthesis of ecdysone from cholesterol). Ecdysteroids such as 20-hydroxyecdysone and ecdysone influence many of the morphological, physiological, biochemical changes that occur during molting in insects.
Drosophila nigrospiracula is a fly species indigenous to the Sonoran Desert, spanning Arizona, Baja California, and part of Sonora, Mexico. D. nigrospiracula share the Sonoran Desert with three other species of Drosophila: D. pachea, D. mettleri, and D. mojavensis. This fly breeds on the decomposing tissues of two species of cacti that are also endemic to the region: cardón (Pachycereus pringlei) and saguaro (Carnegiea gigantea).
Cyp6g1 or DDT-R is an insecticide resistance gene for resistance to DDT in Drosophila melanogaster. It belongs to the cytochrome P450 family and is located in chromosome 2R. Following up their earlier work, Daborn et al. 2002 find the DDT-R gene induces overtranscription of Cyp6g1, of which there are 4 duplicates. They also find several substrates of Cyp6g1, namely DDT, lufenuron, and nitenpyram.
CYP318A1 is a Drosophila melanogaster gene belongs to the cytochrome P450 family, involved in the insecticide resistance.
Cytochrome P450, family 11, also known as CYP11, is a chordate cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family. This family contains many enzymes involved in steroidogenesis, such as Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (CYP11A1), Steroid 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) and Aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2). CYP11 can be divided into A to E five subfamilies, and CYP11A are the ohonologues to CYP11C, which duplicated during 2R event, and the tetrapod's CYP11B evolved from CYP11C of its fish ancestors, CYP11D and F found in amphioxus. These are not the typical CYP subfamilies, which share at least 40% amino acid identity, members between CYP11A and B subfamily are only 37.5-38.8% identical, and the CYP11D and E genes seen in modern lancelet is 39% identical to catfish CYP11A1.
Cytochrome P450, family 18, also known as CYP18, is an animal cytochrome P450 family found in insect genomes. It is involved in insecticide resistance. The first member gene identified was CYP18A1, from a Drosophila melanogaster fly, acting as a dimethylnitrosamine demethylase.
Cytochrome P450, family 6, also known as CYP6, is a cytochrome P450 family found in Insect genome. CYP6 and CYP9, another insect CYP family, belong to the same clan as mammalian CYP3 and CYP5 families.
Cytochrome P450, family 12, also known as CYP12, is a cytochrome P450 family found in insect genome belongs to Mitochondrial clan CYPs, which is located in the inner membrane of mitochondria(IMM). The first gene identified in this family is the CYP12A1 from the Musca domestica, which is involved in insecticide resistance. CYP12A1 protein localization in mitochondria by immunohistochemistry and absolute dependence on mitochondrial electron donors adrenodoxin reductase and adrenodoxin.
Cytochrome P450, family 305, also known as CYP305, is an animal cytochrome P450 family found in insect genome. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP305A1 from the Drosophila melanogaster.
Cytochrome P450, family 139, also known as CYP139, is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family in bacteria. The first gene identified in this family is CYP139A1 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Most member of this family belonged to the subfamily A, and involved in the synthesis of secondary metabolites in many mycobacterial species.
References
- ↑ Bono JM, Matzkin LM, Castrezana S, Markow TA (July 2008). "Molecular evolution and population genetics of two Drosophila mettleri cytochrome P450 genes involved in host plant utilization". Molecular Ecology. 17 (13): 3211–21. Bibcode:2008MolEc..17.3211B. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03823.x. PMC 2702709 . PMID 18510584.