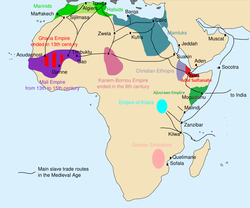
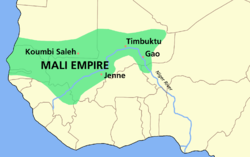
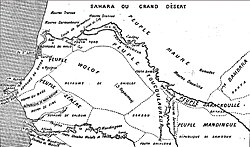
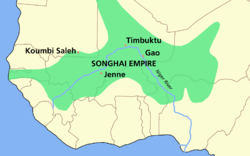
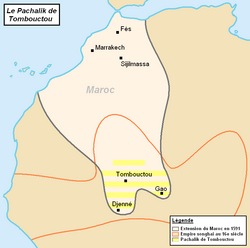
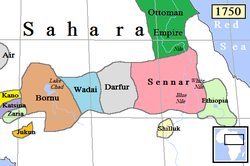
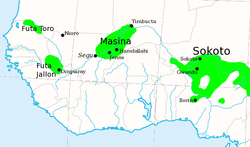
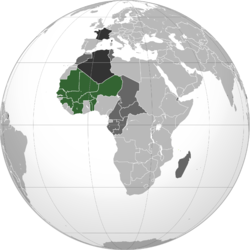
The Sahelian kingdoms were a series of centralized kingdoms or empires that were centered on the Sahel, the area of grasslands south of the Sahara, from the 8th century to the 19th. The wealth of the states came from controlling the trade routes across the desert. Their power came from having large pack animals like camels and horses that were fast enough to keep a large empire under central control and were also useful in such kind of battle. All of these empires were also quite decentralized with member cities having a great deal of autonomy.
Contents
The Sahel states were limited from expanding south into the forest zone of the Bono and Yoruba as mounted warriors were all but useless in the forests and the horses and camels could not survive the diseases of the region.