
The Mygalomorphae, or mygalomorphs, are an infraorder of spiders, and comprise one of three major groups of living spiders with over 3,000 species, found on all continents except Antarctica. Many members are known as trapdoor spiders due to their creation of trapdoors over their burrows. Other prominent groups include Australian funnel web spiders and tarantulas, with the latter accounting for around one third of all mygalomorphs.

The family Cyrtaucheniidae, known as wafer-lid trapdoor spiders, are a widespread family of Mygalomorphae spiders.

Idiopidae, also known as armored or spiny trapdoor spiders, is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1889.

Nemesiidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1889, and raised to family status in 1985. Before becoming its own family, it was considered part of "Dipluridae". The family is sometimes referred to as wishbone spiders due to the shape of their burrows.

Barychelidae, also known as brushed trapdoor spiders, is a spider family with about 300 species in 39 genera.

Migidae, also known as tree trapdoor spiders, is a family of spiders with about 100 species in eleven genera. They are small to large spiders with little to no hair and build burrows with a trapdoor. Some species live in tree fern stems. They have a Gondwanan distribution, found almost exclusively on the Southern Hemisphere, occurring in South America, Africa, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand and New Caledonia.
Spider behavior refers to the range of behaviors and activities performed by spiders. Spiders are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other groups of organisms which is reflected in their large diversity of behavior.

Sason is a genus of bark-dwelling brushed trapdoor spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1887. It is distributed from the Seychelles through India to northern Australia. The closest related genus seems to be the monotypic Paracenobiopelma.
Paracenobiopelma is a monotypic genus of South American brushed trapdoor spiders containing the single species, Paracenobiopelma gerecormophilum. It was first described in 1952, and has only been found in Brazil. Their closest relatives are found in the genus Sason, which occur in south Asia.
Sason colemani is a species of barychelid trapdoor spiders that has only been found in a natural swamp in the Botanical Gardens in Cairns, Queensland. Its retreat is a short tube with a door at each end which it builds on the bark of trees. When one door opens, the other is pressed closed. Paracenobiopelma gerecormophilum and spiders of the genus Cyphonisia build similar but slightly longer retreats.

Sason robustum is a species of barychelid trapdoor spiders. It is only found in southern India, Sri Lanka and the Seychelles.

Cyclocosmia is a genus of mygalomorph trapdoor spiders in the family Halonoproctidae, first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871. Originally placed with the Ctenizidae, when the family split in 2018, this genus was placed with the Halonoproctidae as the type genus. The name is derived from the Greek "kyklos" (κυκλος), meaning "circle", and "kosmeo" (κοσμεω), meaning "to adorn".

Liphistius is a genus of basal trapdoor spiders in the family Liphistiidae. They are found in Japan, China, and Southeast Asia.

Liphistius batuensis is a species of trapdoor spider from Malaysia. It is thought to be restricted to the Batu Caves and a cave in Templer Park, near Kuala Lumpur. It was first collected by H. C. Abraham in 1923, and has been described as a living fossil.
Prothemenops is a genus of Southeast Asian armored trapdoor spiders that was first described by Peter J. Schwendinger in 1991.
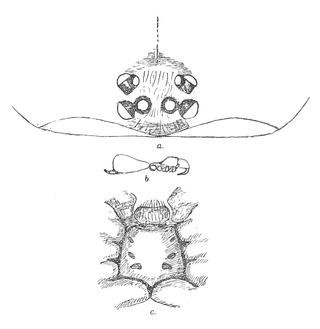
Cantuaria dendyi is a species of trapdoor spider in the family Idiopidae. It can be found in the South Island of New Zealand and is limited to the Christchurch and Banks Peninsula area.
Sason hirsutum is a species of spiders in the family Barychelidae, found in Indonesia.

Qiongthela is a genus of spiders in the family Heptathelidae. As of 2021, it contains 14 species.

Cantuaria borealis is a native New Zealand species of trapdoor spider.

Cyclocosmia ricketti, commonly known as the Chinese hourglass spider, is a species of trapdoor spider of the genus Cyclocosmia, which refers specifically to mygalomorphus animals. Cyclocosmia ricketti is native to China and it was first described in 1901 by Mary Agard Pocock. They are characterized by their truncated abdomen and the rigid disk at the bottom with a pattern.












