
The Araceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, and sometimes partially enclosed in, a spathe. Also known as the arum family, members are often colloquially known as aroids. This family of 140 genera and about 4,075 known species is most diverse in the New World tropics, although also distributed in the Old World tropics and northern temperate regions.

Philodendron is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. As of September 2015, the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families accepted 489 species; other sources accept different numbers. Regardless of number of species, the genus is the second-largest member of the family Araceae, after genus Anthurium. Taxonomically, the genus Philodendron is still poorly known, with many undescribed species. Many are grown as ornamental and indoor plants. The name derives from the Greek words philo- 'love, affection' and dendron 'tree'. The generic name, Philodendron, is often used as the English name.

Xanthosoma is a genus of flowering plants in the arum family, Araceae. The genus is native to tropical America but widely cultivated and naturalized in other tropical regions. Several are grown for their starchy corms, an important food staple of tropical regions, known variously as malanga, otoy, otoe, cocoyam, tannia, tannier, yautía, macabo, ocumo, macal, taioba, dasheen, quequisque, ʻape and as Singapore taro. Many other species, including especially Xanthosoma roseum, are used as ornamental plants; in popular horticultural literature these species may be known as ‘ape due to resemblance to the true Polynesian ʻape, Alocasia macrorrhizos, or as elephant ear from visual resemblance of the leaf to an elephant's ear. Sometimes the latter name is also applied to members in the closely related genera Caladium, Colocasia (taro), and Alocasia.

Cryptocoryne is a genus of aquatic plants from the family Araceae. The genus is naturally distributed in tropical regions of India, Southeast Asia and New Guinea.

Anthurium is a genus of about 1,000 species of flowering plants, the largest genus of the arum family, Araceae. General common names include anthurium, tailflower, flamingo flower, and laceleaf.

Lysichiton is a genus in the family Araceae. These plants are known commonly as skunk cabbage or less often as swamp lantern. The spelling Lysichitum is also found. The genus has two species, one found in north-east Asia, the other in north-west America.

Dracontium is a genus of flowering plants similar to those of Amorphophallus. Unlike Amorphophallus which is found in the Old World, this genus has a New World distribution and is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, and the West Indies.

Sauromatum venosum is a species of plant in the arum family, Araceae. It is native to Asia and Africa, where it grows in forests and riparian meadows.

Rhaphidophora korthalsii is a flowering plant of species Rhaphidophora the family Araceae.

Ambrosina is a genus in the family Araceae that consists of only one species, Ambrosina bassii, and the only genus in the tribe Ambrosineae. This species is the smallest aroid in the Mediterranean, growing only to 8 cm tall. It is usually found growing in woodlands on north faces of hillsides and in humus soil that is covering limestone. It is distributed in Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily, southern mainland Italy, Tunisia, and Algeria.

Asterostigma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Brazil and Argentina. The leaves are pinnate and the plant is tuberous.
- Asterostigma cryptostylumBogner - Brasília, Goiás, Minas Gerais
- Asterostigma cubense(A.Rich.) K.Krause ex Bogner - São Paulo
- Asterostigma lividum(G.Lodd.) Engl. - southern Brazil; Misiones Province of Argentina
- Asterostigma lombardiiE.G.Gonç. - Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo
- Asterostigma luschnathianumSchott - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma reticulatumE.G.Gonç - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma riedelianum(Schott) Kuntze - eastern Brazil
- Asterostigma tweedieanumSchott - Santa Catarina in southern Brazil

Biarum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is composed of plants that are native to the Middle East, southern Europe, and North Africa. Biarum are often found growing in rock crevices and graveled soil composed largely of limestone.

Urospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that consists of approximately 10 known species. They are found growing in South America and Central America in swamps, wet savannahs, and brackish water. The leaves of the species in this genus are upward pointing and sagittate (arrow-shaped). The inflorescences are quite unique; the spathe is mottled and elongated with a spiral twist at the end. The seeds are distributed by water and have a texture similar to cork that allows them to float. They also quickly germinate in water.
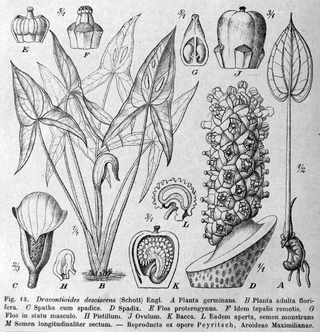
Dracontioides is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It was long thought to contain only a single species until a second species was described in 2005. Both are endemic to Brazil.

Eminium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The genus ranges from Turkey and Egypt east to Central Asia. Usually they can be found growing in barren areas in sand or stony soil. The foliage of Eminium resembles Helicodiceros and its inflorescence and fruit resembles those of Biarum.
- Eminium albertii(Regel) Engl. - Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan
- Eminium heterophyllum(Blume) Schott - Iran, Iraq, Turkey
- Eminium intortum(Banks & Sol.) Kuntze - Turkey, Syria
- Eminium jaegeriBogner & P.C.Boyce - Iran
- Eminium koenenianumLobin & P.C.Boyce - Turkey
- Eminium lehmannii(Bunge) Kuntze - Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan
- Eminium rauwolffii(Blume) Schott - Turkey, Syria
- Eminium regeliiVved. - Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan
- Eminium spiculatum(Blume) Schott - Egypt, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, Iran

Sauromatum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The genus is native to tropical Africa, tropical Asia, and the Arabian Peninsula. Their inflorescences last for only a few hours to a day and give off an unpleasant smell. The inflorescence disperses its odor by heating up.
- Sauromatum brevipes(Hook.f.) N.E.Br. - Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam
- Sauromatum brevipilosum(Hett. & Sizemore) Cusimano & Hett. - Sumatra
- Sauromatum diversifolium(Wall. ex Schott) Cusimano & Hett. - eastern Himalayas, Tibet, Sichuan, Yunnan, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, Myanmar, Cambodia
- Sauromatum gaoligongenseJ.C.Wang & H.Li - Yunnan
- Sauromatum giganteum(Engl.) Cusimano & Hett. - Anhui, Gansu, Hebei, Henan, Jilin, Liaoning, Shandong, Shanxi, Sichuan, Tibet
- Sauromatum hirsutum(S.Y.Hu) Cusimano & Hett. - Yunnan, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Sauromatum horsfieldiiMiq. - Guangxi, Guizhou, Sichuan, Yunnan, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Sumatra, Java, Bali
- Sauromatum tentaculatum(Hett.) Cusimano & Hett. - Thailand
- Sauromatum venosum(Dryand. ex Aiton) Kunth - tropical Africa from Ethiopia south to Mozambique and west to Cameroon; Yemen, Saudi Arabia; Indian Subcontinent; Myanmar; Tibet, Yunnan
Scaphispatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It contains two species, S. gracilis and S. robusta. The genus was believed to be monotypic until 2003 when a new species, S. robusta was discovered by Eduardo Gomes Gonçalves in northern Brazil. The plant had been grown in cultivation for some years, but had always been assumed to be a Caladium until it flowered.
- Scaphispatha gracilisBrongn. ex Schott - Bolivia, Brazil
- Scaphispatha robustaE.G.Gonç. - Pará, Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Goiás

Montrichardia arborescens, the yautia madera, or moco-moco, is a tropical plant grows along river banks, swamps, or creeks to a maximum height of 9'. They consist of arrow shaped leaves that are food sources for animal species. The plant produces inflorescences which then leave a fruit of Montrichardia arborescens which is edible and can be cooked. Its fruiting spadices produces large infructescences, which contain about 80 edible yellow fruits.
Monstera dissecta is a species of flowering plant in the genus Monstera and family Araceae.
















