
Hornets are the largest of the eusocial wasps, and are similar in appearance to their close relatives yellowjackets. Some species can reach up to 5.5 cm (2.2 in) in length. They are distinguished from other vespine wasps by the relatively large top margin of the head and by the rounded segment of the abdomen just behind the waist. Worldwide, 22 species of Vespa are recognized. Most species only occur in the tropics of Asia, though the European hornet, is widely distributed throughout Europe, Russia, North America, and Northeast Asia. Wasps native to North America in the genus Dolichovespula are commonly referred to as hornets, but are actually yellowjackets.

The Oriental turtle dove or rufous turtle dove is a member of the bird family Columbidae. The species has a wide native distribution range from Europe, east across Asia to Japan. The populations show variations in the patterning of plumage and have been designated into at least six named subspecies. Populations in the higher latitudes tend to migrate south in winter, while those closer to the tropics are sedentary. Vagrants have been recorded in North America. The species is predominantly granivorous and forages on the ground.

Platycladus is a monotypic genus of evergreen coniferous trees in the cypress family Cupressaceae, containing only one species, Platycladus orientalis, also known as Chinese thuja, Oriental arborvitae, Chinese arborvitae, biota or Oriental thuja. It is native to northeastern parts of East Asia and North Asia, but is also now naturalised as an introduced species in other regions of the Asian continent.

Securigera varia, commonly known as crownvetch or purple crown vetch, is a low-growing legume vine. It is native to Africa, Asia and Europe and is commonly used throughout the United States and Canada for erosion control, roadside planting and soil rehabilitation. It has become an invasive species in many states of the US.

The short-tailed blue or tailed Cupid is a butterfly that forms part of the family Lycaenidae. It is found from Europe to Japan and in India.

Thenus orientalis is a species of slipper lobster from the Indian and Pacific oceans.

The tribe Loteae is a subdivision of the plant family Fabaceae, in the Robinioids. These genera are recognized by the USDA:

The genus Securigera contains a number of plant species commonly referred to as crownvetch. It is a segregate of the genus Coronilla. The name Securigera was first published by A. P. de Candolle in 1805 with the single species Securigera coronilla, which is now considered to be a synonym of Securigera securidaca(L.) Degen & Dörfl. (1897), based on the earlier publication of the same taxon as Coronilla securidacaL. in 1753.

The genus Coronilla contains 8 species of flowering plants native to Europe and North Africa. It cointained about 20 species before being split into Securigera.
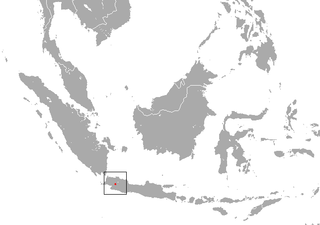
The Oriental shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Indonesia. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Javan ferret-badger is a mustelid endemic to Java and Bali, Indonesia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List and occurs from at least 260 to 2,230 m elevation in or close to forested areas.
Under Pope Pius XII, there were the several reforms of Oriental canon law and the Codex Iuris Canonici Orientalis, applying mainly to the Oriental Churches united with the Latin Church in communion with the Roman Pontiff. The Holy See's policy in this area had always two objectives, the pastoral care of approximately ten million Christians united with Rome and the creation of positive ecumenical signals to the two-hundred and fifty million Eastern Orthodox Christians outside the Church of Rome.

Trema orientalis is a species of flowering tree in the hemp family, Cannabaceae. It is known by many common names, including charcoal-tree, Indian charcoal-tree, pigeon wood, Oriental trema, and in Hawaii, where it has become naturalized, gunpowder tree, or nalita. It has a near universal distribution in tropical and warm temperate parts of the Old World, with a range extending from South Africa, through the Middle East, the Indian subcontinent and southern China to Southeast Asia and Australia.
S. orientalis may refer to:
Leucoptera lotella is a moth in the Lyonetiidae family. It is found from Denmark to Portugal, Italy and Croatia, and from Great Britain to Poland and Hungary.
Orientalis Ecclesiae is an encyclical of Pope Pius XII signed on 9 April 1944. Its topic is St. Cyril, Patriarch of Alexandria.

Mirificarma maculatella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in most of Europe, except Ireland, Great Britain, Portugal, the Benelux, Denmark, Fennoscandia, the Baltic region and Greece. It has also been recorded from Turkey and Syria.

Syncopacma coronillella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in most of Europe, except Ireland, Great Britain, Fennoscandia, the Baltic region, the Benelux, Portugal and part of the Balkan Peninsula.

The eastern carrion crow is a member of the crow family and a subspecies of the carrion crow. Differences from the nominate subspecies include a larger size, at a length about 500 millimetres (20 in), and more graduated outer tail feathers. The eastern carrion crow is found in Siberia from the Yenisei to Japan, south to Central Asia, Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, Kashmir, Tibet and northern China. They generally lay three to five eggs in trees or buildings. The eggs show no difference from the nominate subspecies.

Securigera elegans is a plant species in the genus Securigera.














