
Sepiadariidae is a family of cuttlefish, cephalopods in the order Sepiida.

Sepiidae is a family of cephalopods in the order Sepiida.

Sabertooth or sabretooth fish are small, fierce-looking deep-sea aulopiform fish comprising the family Evermannellidae. The family is small, with just eight species in three genera represented; they are distributed throughout tropical to subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans.

Brachaelurus is the sole genus of sharks in the family Brachaeluridae in the order Orectolobiformes. Only two species of blind sharks occur, both of which are native to shallow coastal waters up to 110 m (360 ft) deep, off the eastern coast of Australia.

Octopodiformes is a superorder of the subclass Coleoidea, comprising the octopuses and the vampire squid. All members of Octopodiformes have eight arms.

Metasepia pfefferi, also known as the flamboyant cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish occurring in tropical Indo-Pacific waters off northern Australia, southern New Guinea, as well as numerous islands of the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia. The flesh of this colorful cephalopod contains unique acids, making it unsuitable for consumption.

Metasepia is a small genus of small cuttlefish from the Pacific Ocean. The two members of this genus are characterised by a small, thick, diamond-shaped cuttlebone.

Tillandsioideae is a subfamily of plants in the bromeliad family Bromeliaceae. This subfamily contains the greatest number of species (1,277). Most are epiphytic or lithophytic, growing in trees or on rocks where they absorb water and nutrients from the air. Spanish moss of the Tillandsia genus is a well-known variety. Bromeliads in the genera Guzmania and Vriesea are the more commonly cultivated members of this subfamily.

Sepia is a genus of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae encompassing some of the best known and most common species. The cuttlebone is relatively ellipsoid in shape. The name of the genus is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek σηπία, sēpía, cuttlefish.

Sepiella cyanea is a species of cuttlefish native to the southwestern Indian Ocean, from Port Elizabeth and Durban north to central Mozambique (26ºN) and Madagascar. It lives at depths of 13 to 73 m.
Sepiella mangkangunga is a species of cuttlefish native to the Indo-Pacific, specifically off the Northern Territory in Australia. It lives at depths from 1.1 to 3.3 m.
Sepiella ocellata is a species of cuttlefish known only from the type locality off Java. The depth range of this species is unknown. Only a single male specimen has been recorded. The status of S. ocellata is questionable.

All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles.

Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous ink released into water by most species of cephalopod, usually as an escape mechanism. All cephalopods, with the exception of the Nautilidae and the Cirrina, are able to release ink.

Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda, which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy.
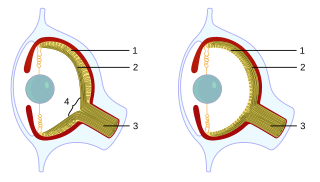
Cephalopods, as active marine predators, possess sensory organs specialized for use in aquatic conditions. They have a camera-type eye which consists of an iris, a circular lens, vitreous cavity, pigment cells, and photoreceptor cells that translate light from the light-sensitive retina into nerve signals which travel along the optic nerve to the brain. For the past 140 years, the camera-type cephalopod eye has been compared with the vertebrate eye as an example of convergent evolution, where both types of organisms have independently evolved the camera-eye trait and both share similar functionality. Contention exists on whether this is truly convergent evolution or parallel evolution. Unlike the vertebrate camera eye, the cephalopods' form as invaginations of the body surface, and consequently the cornea lies over the top of the eye as opposed being a structural part of the eye. Unlike the vertebrate eye, a cephalopod eye is focused through movement, much like the lens of a camera or telescope, rather than changing shape as the lens in the human eye does. The eye is approximately spherical, as is the lens, which is fully internal.
Belosaepia, occasionally incorrectly Belosepia, is an extinct genus of cuttlefish-like cephalopod known from the Eocene.

Sepiella inermis, common name spineless cuttlefish, is an edible species of cuttlefish.
Chaudhuria is a genus of spineless eels native to Southeast Asia.














