
Hydropower, also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production. Hydropower is now used principally for hydroelectric power generation, and is also applied as one half of an energy storage system known as pumped-storage hydroelectricity.

Vienna is the capital, most populous city, and one of nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. Its larger metropolitan area has a population of nearly 2.9 million, representing nearly one-third of the country's population. Vienna is the cultural, economic, and political center of the country, the fifth-largest city by population in the European Union, and the most-populous of the cities on the Danube river.

A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the production of many material goods, including flour, lumber, paper, textiles, and many metal products. These watermills may comprise gristmills, sawmills, paper mills, textile mills, hammermills, trip hammering mills, rolling mills, and wire drawing mills.

A water wheel is a machine for converting the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a large wheel, with numerous blades or buckets attached to the outer rim forming the drive mechanism. Water wheels were still in commercial use well into the 20th century, although they are no longer in common use today. Water wheels are used for milling flour in gristmills, grinding wood into pulp for papermaking, hammering wrought iron, machining, ore crushing and pounding fibre for use in the manufacture of cloth.

A noria is a hydropowered scoop wheel used to lift water into a small aqueduct, either for the purpose of irrigation or to supply water to cities and villages.

Haxted Watermill is a much-restored Grade II listed watermill in Surrey, England, close to the border with Kent, and is powered by the River Eden.

The Mur or Mura is a river in Central Europe rising in the Hohe Tauern national park of the Central Eastern Alps in Austria with its source at 1,898 m (6,227 ft) above sea level. It is a tributary of the Drava and subsequently the Danube.
A millwright is a craftsman or skilled tradesman who installs, dismantles, maintains, repairs, reassembles, and moves machinery in factories, power plants, and construction sites.
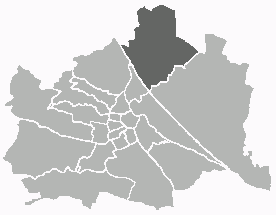
Floridsdorf is the 21st district of Vienna, located in the northern part of the city and comprising seven formerly independent communities: Floridsdorf, Donaufeld, Greater Jedlersdorf, Jedlesee, Leopoldau, Stammersdorf, and Strebersdorf.

Donaustadt is the 22nd district of Vienna, Austria . Donaustadt is the eastern district of Vienna.

The ancient Romans were famous for their advanced engineering accomplishments. Technology for bringing running water into cities was developed in the east, but transformed by the Romans into a technology inconceivable in Greece. The architecture used in Rome was strongly influenced by Greek and Etruscan sources.

A tide mill is a water mill driven by tidal rise and fall. A dam with a sluice is created across a suitable tidal inlet, or a section of river estuary is made into a reservoir. As the tide comes in, it enters the mill pond through a one-way gate, and this gate closes automatically when the tide begins to fall. When the tide is low enough, the stored water can be released to turn a water wheel.

The Reichsbrücke is a major bridge in Vienna, linking Mexikoplatz in Leopoldstadt with the Donauinsel in Donaustadt across the Danube. The bridge is used by 50,000 vehicles per day and carries six lanes of traffic, U-Bahn tracks, two footpaths, two cyclepaths and two utility tunnels.

Donau City, or Vienna DC, is a new part of Vienna's 22nd District Donaustadt, next to both the Reichsbrücke and the left bank of the Danube's 21.1 km new channel, Neue Donau.

Letheringsett Watermill is situated on the River Glaven in the village of Letheringsett, in the English county of Norfolk. Letheringsett is in the district of North Norfolk and is 1.4 miles (2.3 km) west of the town of Holt. The watermill is a Grade II* listed building and is the last fully operational watermill in Norfolk that produces flour.

The Hierapolis sawmill was a water-powered stone sawmill in the Ancient Greek city of Hierapolis in Roman Asia. Dating to the second half of the 3rd century AD, the sawmill is considered the earliest known machine to combine a crank with a connecting rod to form a crank-slider mechanism.

The International Wind- and Watermill Museum, at Gifhorn in the German state of Lower Saxony, is the only one of its kind in Europe. On the museum's open-air site, which covers an area of around 16 hectares, there are currently 16 mills from 12 different countries. The mills are either original or faithful reproductions and are set in landscapes typical of their origins. Right across the site are historic artefacts associated with mills and the milling industry. The museum site is easily accessed by road; nearby is the intersection between the B 4 and B 188 federal highways. The museum is station 65 on the Lower Saxon Mill Road.

A gristmill grinds cereal grain into flour and middlings. The term can refer to either the grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist is grain that has been separated from its chaff in preparation for grinding.

























