
Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

The Maotianshan Shales (帽天山页岩) are a series of Early Cambrian sedimentary deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Nektaspida is an extinct order of non-mineralised artiopodan arthropods. They are known from the lower-Cambrian to the upper Silurian. Originally classified as trilobites, which they superficially resemble, they are now placed as close relatives as members of the Trilobitomorpha within Artiopoda. The order is divided into three major families; Emucarididae, Liwiidae, and Naraoiidae.

Emuellidae are a small family of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods, that lived during the late Lower Cambrian of the East Gondwana supercontinent, in what are today South-Australia and Antarctica.

Naraoia is a genus of small to average size marine arthropods within the family Naraoiidae, that lived from the early Cambrian to the late Silurian period. The species are characterized by a large alimentary system and sideways oriented antennas.

Yunnanocephalus is a genus of ptychopariid trilobite. It lived during the late Atdabanian and Botomian stages, in what are currently Antarctica, Australia and China. It was a "moderately common" member of the Chengjiang Fauna. Yunnanocephalus is the only genus currently assigned to the Yunnanocephalidae family.

Tsunyidiscus is a trilobite belonging to the suborder Eodiscina. Tsunyidiscus appeared near the end of the Lower Cambrian, during the late Atdabanian stage of geologic time and some collections suggest it may have survived into the Botomian. The genus is very small, oculate and isopypous with a narrow dome-shaped glabella and a narrow bullet-shaped pygidial axis. Thorax consists of three segments. Tsunyidiscus is the only genus currently attributed to the family Tsunyidiscidae.

Xystridura Whitehouse, 1936 is a genus of Redlichiid trilobite described originally from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian) strata of Queensland, Australia. The genus ranges upwards from Ordian into Florian Stages in terms of Australian Cambrian stratigraphic nomenclature.

Vetulicola cuneata is a species of extinct marine animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China. It was described by Hou Xian-guang in 1987 from the Lower Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation, and became the first animal under an eponymous phylum Vetulicolia.

Pagetia is a genus of small trilobite, assigned to the Eodiscinid family Pagetiidae and which had global distribution during the Middle Cambrian. The genus contains 55 currently recognized species, each with limited spatial and temporal ranges.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2012 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2012. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.

Eodiscina is trilobite suborder. The Eodiscina first developed near the end of the Lower Cambrian period and became extinct at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Species are tiny to small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. Eodiscina includes six families classified under one superfamily, Eodiscoidea.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2014 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2014. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.

The Artiopoda is a grouping of extinct arthropods that includes trilobites and their close relatives. It was erected by Hou and Bergström in 1997 to encompass a wide diversity of arthropods that would traditionally have been assigned to the Trilobitomorpha. Trilobites, in part due to abundance of findings owing to their mineralized exoskeletons, are by far the best recorded, diverse, and long lived members of the clade. Other members, which lack mineralised exoskeletons, are known mostly from Cambrian deposits.
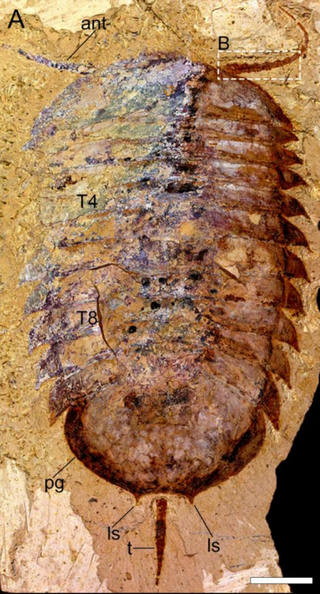
Retifacies abnormalis is an extinct arthropod that lived in the lower Cambrian. Its fossil remains have been found in the Maotianshan Shales of Yunnan, China. It is a member of the Artiopoda, and closely related to Pygmaclypeatus.
Calodiscus is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite in the family Calodiscidae. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in Canada, the United States, Greenland, The United Kingdom (England), Sweden, France, Germany, Italy (Sardinia), Kazakhstan, the Russian Federation and China.
2021 in arthropod paleontology is a list of new arthropod fossil taxa, including arachnids, crustaceans, insects, trilobites, and other arthropods that were announced or described, as well as other significant arthropod paleontological discoveries and events which occurred in 2021.
2022 in arthropod paleontology is a list of new arthropod fossil taxa, including arachnids, crustaceans, insects, trilobites, and other arthropods that were announced or described, as well as other significant arthropod paleontological discoveries and events which occurred in 2022.
2023 in arthropod paleontology is a list of new arthropod fossil taxa, including arachnids, crustaceans, trilobites, and other arthropods that were announced or described, as well as other significant arthropod paleontological discoveries and events which occurred in 2023.













