Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (EC number 4.1.1).

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH4. It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis.
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base. The reaction produces a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen, who first published his work on the reaction in 1887. The reaction has often been displaced by diketene-based chemistry, which affords acetoacetic esters.
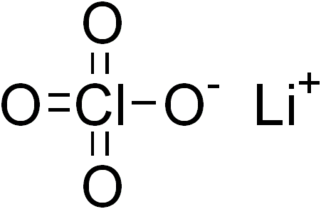
Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a trihydrate.
The Reformatsky reaction is an organic reaction which condenses aldehydes or ketones with α-halo esters using metallic zinc to form β-hydroxy-esters:
The aza-Baylis–Hillman reaction or aza-BH reaction in organic chemistry is a variation of the Baylis–Hillman reaction and describes the reaction of an electron deficient alkene, usually an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, with an imine in the presence of a nucleophile. The reaction product is an allylic amine. The reaction can be carried out in enantiomeric excess of up to 90% with the aid of bifunctional chiral BINOL and phosphinyl BINOL compounds, for example in the reaction of n-(4-chloro-benzylidene)-benzenesulfonamide with methyl vinyl ketone (MVK) in cyclopentyl methyl ether and toluene at -15°C.
The Sakurai reaction is the chemical reaction of carbon electrophiles with allyltrimethylsilane catalyzed by strong Lewis acids. The reaction achieves results similar to the addition of an allyl Grignard reagent to the carbonyl.

Iodine monochloride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ICl. It is a red-brown chemical compound that melts near room temperature. Because of the difference in the electronegativity of iodine and chlorine, this molecule is highly polar and behaves as a source of I+. Discovered in 1814 by Gay-Lussac, iodine monochloride is the first interhalogen compound discovered.

Organolead chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organolead compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a chemical bond between carbon and lead. The first organolead compound was hexaethyldilead (Pb2(C2H5)6), first synthesized in 1858. Sharing the same group with carbon, lead is tetravalent.
The Wurtz–Fittig reaction is the chemical reaction of an aryl halide, alkyl halides, and sodium metal to give substituted aromatic compounds. Following the work of Charles Adolphe Wurtz on the sodium-induced coupling of alkyl halides, Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig extended the approach to the coupling of an alkyl halide with an aryl halide. This modification of the Wurtz reaction is considered a separate process and is named for both scientists.
The reduction of nitro compounds are chemical reactions of wide interest in organic chemistry. The conversion can be effected by many reagents. The nitro group was one of the first functional groups to be reduced. Alkyl and aryl nitro compounds behave differently. Most useful is the reduction of aryl nitro compounds.
Chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) is a chlorofluorocarbon with chemical formula CFCl=CF2. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in cryogenic applications. CTFE has a carbon-carbon double bond and so can be polymerized to form polychlorotrifluoroethylene or copolymerized to produce the plastic ECTFE. PCTFE has the trade name Neoflon PCTFE from Daikin Industries in Japan, and it used to be produced under the trade name Kel-F from 3M Corporation in Minnesota.
1,1,2-Trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane, also called trichlorotrifluoroethane or CFC-113, is a chlorofluorocarbon. It has the formula Cl2FC−CClF2. This colorless, volatile liquid is a versatile solvent.

Fluorine perchlorate, also called perchloryl hypofluorite is the rarely encountered chemical compound of fluorine, chlorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula ClO
4F or FOClO
3. It is an extremely unstable gas that explodes spontaneously and has a penetrating odor.
Difluorocarbene is the chemical compound with formula CF2. It has a short half-life, 0.5 and 20 ms, in solution and in the gas phase, respectively. Although highly reactive, difluorocarbene is an intermediate in the production of tetrafluoroethylene, which is produced on an industrial scale as the precursor to Teflon (PTFE).
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.
The Pinnick oxidation is an organic reaction by which aldehydes can be oxidized into their corresponding carboxylic acids using sodium chlorite (NaClO2) under mild acidic conditions. It was originally developed by Lindgren and Nilsson. The typical reaction conditions used today were developed by G. A. Kraus. H.W. Pinnick later demonstrated that these conditions could be applied to oxidize α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. There exist many different reactions to oxidize aldehydes, but only a few are amenable to a broad range of functional groups. The Pinnick oxidation has proven to be both tolerant of sensitive functionalities and capable of reacting with sterically hindered groups. This reaction is especially useful for oxidizing α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, and another one of its advantages is its relatively low cost.
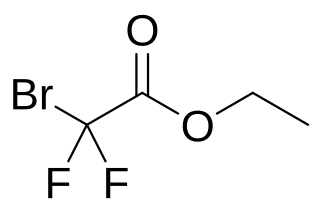
Ethyl bromodifluoroacetate is an ester with the chemical formula F2BrCH−CO2CH2CH3. It can be used to introduce the CF2 group when synthesising chemical compounds. It is a colorless to yellow liquid. It is an ethyl ester of bromodifluoroacetic acid.

Phenylsodium C6H5Na is an organosodium compound. Solid phenylsodium was first isolated by Nef in 1903. Although the behavior of phenylsodium and phenyl magnesium bromide are similar, the organosodium compound is very rarely used.









