
Kumquats are a group of small fruit-bearing trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae. They were previously classified as forming the now-historical genus Fortunella, or placed within Citrus sensu lato.

Solanum is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, which include three food crops of high economic importance, the potato, the tomato and the eggplant. It also contains the nightshades and horse nettles, as well as numerous plants cultivated for their ornamental flowers and fruit.

The persimmon is the edible fruit of a number of species of trees in the genus Diospyros. The most widely cultivated of these is the Asian or Japanese persimmon, Diospyros kaki. Diospyros is in the family Ebenaceae, and a number of non-persimmon species of the genus are grown for ebony timber.

Artocarpus integer, commonly known as chempedak or cempedak is a species of tree in the family Moraceae, and in the same genus as breadfruit and jackfruit. It is native to southeast Asia. Cempedak is an important crop in Malaysia and is also popularly cultivated in southern Thailand and parts of Indonesia, and has the potential to be utilized in other areas. Cempedak is currently limited in range to south-east Asia, with some trees in Australia and Hawaii.

Rubus phoenicolasius is an Asian species of raspberry in the rose family, native to China, Japan, and Korea.

Diospyros virginiana is a persimmon species commonly called the American persimmon, common persimmon, eastern persimmon, simmon, possumwood, possum apples, or sugar plum. It ranges from southern Connecticut/Long Island to Florida, and west to Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Iowa. The tree grows wild but has been cultivated for its fruit and wood since prehistoric times by Native Americans.

The tamarillo is a small tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Solanaceae. It is best known as the species that bears the tamarillo, an egg-shaped edible fruit. It is also known as the tree tomato, tomate de árbol, tomate andino, tomate serrano, blood fruit, tomate de yuca, tomate de españa, sachatomate, berenjena and tamamoro in South America, and terong Belanda in Indonesia. They are popular globally, especially in New Zealand, Ecuador, Rwanda, Australia, and the United States.

Solanum quitoense, known as naranjilla in Ecuador and Panama and as lulo in Colombia, is a tropical perennial plant from northwestern South America. The specific name for this species of nightshade means "from Quito."

Solanum sessiliflorum, the cocona, is a tropical shrub of the family Solanaceae. The cocona plant has sturdy branches and huge, serrate and hairy leaves. Cocona closely resembles a number of close relatives, including naranjilla and pseudolulo. It can be distinguished from those plants by its lack of spines. It will hybridize with those and other close relatives. Cocona also lacks the characteristic purple coloring usually seen in the naranjilla. Its flowers resemble large potato flowers, with light green petals. Cocona is harvested in parts of South America around the Amazon rainforest such as Purús Province in eastern Peru.

Oemleria cerasiformis, a shrub commonly known as osoberry or Indian plum, is the sole species in genus Oemleria.

Solanum sibundoyense is a species of plant in the family Solanaceae. It is endemic to Colombia, specifically to Sibundoy and surrounding areas, and usually resides in cloud forests, 1400–2300 meters in elevation. It is also known as tomate salvaje or tomate silvestre to natives of Colombia, and also sometimes called Cyphomandra sibundoyensis. It's a small tree 4–8 m tall. Stems glabrous or sparsely puberulent with glandular and eglandular hairs less than 0.5 mm long.
Citrus halimii or Mountain citron is a sour fruit variety belonging to the citrus papedas, not related to the true citron. It was first discovered and catalogued in 1973.
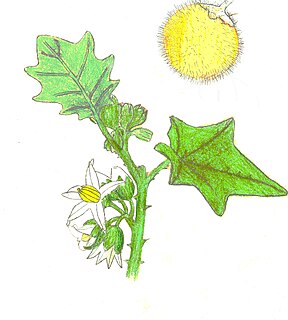
Solanum lasiocarpum, synonym Solanum feroxL., otherwise known as Indian nightshade or hairy-fruited eggplant, is a plant that produces edible fruit. Its flowers are white and its fruits are pale yellow.
Solanum caripense is a species of evergreen shrub native to South America and grown for its edible fruit.

Solanum abutiloides is a species of plant in the family Solanaceae. It is endemic to Argentina and Bolivia, and thrives as a weedy plant in rocky land, on stream banks, and scrub land between 900–3,600 metres (3,000–11,800 ft) in elevation. It is also known as dwarf tamarillo, due to superficial similarities with Solanum betaceum. Both plants are noted for very rapid growth from seed, and very strongly fragrant foliage. Solanum abutiloides is also sometimes known by the archaic Cyphomandra sibundoyensis.
Solanum candidum is a species of evergreen shrub native to South America and occasionally grown for its edible fruit.
Solanum repandum is a species of evergreen shrub native to various island groups across the southern Pacific Ocean and occasionally grown for its edible fruit.
Solanum vestissimum is a subtropical perennial plant from northwestern South America. Also known within its native range as toronjo, tumo, or coquina melón, S. vestissimum is a large semi-woody plant or shrub, up to 8 meters in height, though usually much smaller. The very large heart-shaped leaves are lined with spines along the top and bottom of the dorsal vein, similar to the naranjilla or pseudolulo. The leaves and stems of the plant are otherwise covered in short, felt-like hairs.

Cenarrhenes is a monytypic genus in the family Proteaceae containing the single species Cenarrhenes nitida, known as the Port Arthur plum or native plum. Cenarrhenes nitida is an evergreen shrub to small tree endemic to the rainforests and scrublands of western Tasmania. It bears white flowers in late spring followed by the development of fleshy fruit.
Vascular wilt in the perennial shrub lulo or naranjilla is a disease caused by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. quitoense.














