
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission bandwidth. While MPEG-2 is not as efficient as newer standards such as H.264/AVC and H.265/HEVC, backwards compatibility with existing hardware and software means it is still widely used, for example in over-the-air digital television broadcasting and in the DVD-Video standard.

Standard-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. Standard refers to offering a similar resolution to the analog broadcast systems used when it was introduced.

Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types.

Video CD is a home video format and the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm (4.7 in) optical discs. The format was widely adopted in Southeast Asia, South Asia, East Asia, Central Asia and West Asia, superseding the VHS and Betamax systems in the regions until DVD-Video finally became affordable in the first decade of the 21st century.

Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.
ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601, is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the CCIR for encoding interlaced analog video signals in digital video form. It includes methods of encoding 525-line 60 Hz and 625-line 50 Hz signals, both with an active region covering 720 luminance samples and 360 chrominance samples per line. The color encoding system is known as YCbCr 4:2:2.

Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an International set of standards for broadcast and digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like that standard, is used mostly in the United States, Mexico, Canada, South Korea and Trinidad & Tobago. Several former NTSC users, such as Japan, have not used ATSC during their digital television transition, because they adopted other systems such as ISDB developed by Japan, and DVB developed in Europe, for example.

D-1 or 4:2:2 Component Digital is an SMPTE digital recording video standard, introduced in 1986 through efforts by SMPTE engineering committees. It started as a Sony and Bosch – BTS product and was the first major professional digital video format. SMPTE standardized the format within ITU-R 601, also known as Rec. 601, which was derived from SMPTE 125M and EBU 3246-E standards.

The White Book refers to a standard of compact disc that stores not only sound but also still pictures and motion video. It was released in 1993 by Sony, Philips, Matsushita, and JVC. These discs, most commonly found in Asia, are usually called "Video CDs" (VCD). In some ways, VCD can be thought of as the successor to the Laserdisc and the predecessor to DVD. Note that Video CD should not be confused with CD Video which was an earlier and entirely different format.
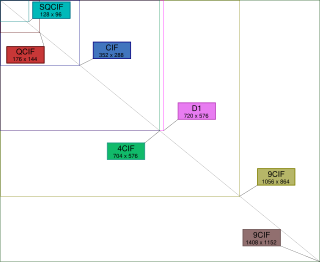
CIF, also known as FCIF, is a standardized format for the picture resolution, frame rate, color space, and color subsampling of digital video sequences used in video teleconferencing systems. It was first defined in the H.261 standard in 1988.

The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.

480i is the video mode used for standard-definition digital video in the Caribbean, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Philippines, Myanmar, Western Sahara, and most of the Americas. The other common standard definition digital standard, used in the rest of the world, is 576i.
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly resolved. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes, to the overall size of a picture, or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter. Photographic lens are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter.

576i is a standard-definition digital video mode, originally used for digitizing 625 line analogue television in most countries of the world where the utility frequency for electric power distribution is 50 Hz. Because of its close association with the legacy colour encoding systems, it is often referred to as PAL, PAL/SECAM or SECAM when compared to its 60 Hz NTSC-colour-encoded counterpart, 480i.
576p is the shorthand name for a video display resolution. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced, the 576 for a vertical resolution of 576 pixels. Usually it corresponds to a digital video mode with a 4:3 anamorphic resolution of 720x576 and a frame rate of 25 frames per second (576p25), and thus using the same bandwidth and carrying the same amount of pixel data as 576i, but other resolutions and frame rates are possible.
Overscan is a behaviour in certain television sets in which part of the input picture is cut off by the visible bounds of the screen. It exists because cathode-ray tube (CRT) television sets from the 1930s to the early 2000s were highly variable in how the video image was positioned within the borders of the screen. It then became common practice to have video signals with black edges around the picture, which the television was meant to discard in this way.
Nominal analogue blanking is the outermost part of the overscan of a standard definition digital television image. It consists of a gap of black pixels at the left and right sides, which correspond to the end and start of the horizontal blanking interval: the front porch at the right side, and the back porch at the left side. Digital television ordinarily contains 720 pixels per line, but only 702 (PAL) to 704 (NTSC) of them contain picture content. The location is variable, since analogue equipment may shift the picture sideways in an unexpected amount or direction.

A Pixel aspect ratio is a mathematical ratio that describes how the width of a pixel in a digital image compared to the height of that pixel.

DVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVDs. DVD-Video was the dominant consumer home video format in Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia in the 2000s until it was supplanted by the high-definition Blu-ray Disc, before eventually both were replaced by streaming services such as Netflix and Disney+. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and an MPEG-2 decoder. Commercial DVD movies are encoded using a combination of MPEG-2 compressed video and audio of varying formats. Typically, the data rate for DVD movies ranges from 3 to 9.5 Mbit/s, and the bit rate is usually adaptive. DVD-Video was first available in Japan on November 1, 1996, followed by a release on March 26, 1997, in the United States—to line up with the 69th Academy Awards that same day.

Super Video CD is a digital format for storing video on standard compact discs. SVCD was intended as a successor to Video CD and an alternative to DVD-Video, and falls somewhere between both in terms of technical capability and picture quality.












