
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carbonate in minute crystalline form, which has deposited in concentric layers. The ideal pearl is perfectly round and smooth, but many other shapes, known as baroque pearls, can occur. The finest quality of natural pearls have been highly valued as gemstones and objects of beauty for many centuries. Because of this, pearl has become a metaphor for something rare, fine, admirable and valuable.

A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event.

Pleuronectidae, also known as righteye flounders, are a family of flounders. They are called "righteye flounders" because most species lie on the sea bottom on their left sides, with both eyes on their right sides. The Paralichthyidae are the opposite, with their eyes on the left side. A small number of species in Pleuronectidae can also have their eyes on the left side, notably the members of the genus Platichthys.

The common dab is an edible flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish native to shallow seas around Northern Europe, in particular the North Sea, where it lives on sandy bottoms down to depths of about 100 metres (330 ft). It can reach 40 centimetres (16 in) in length and can weigh up to 1 kilogram (2.2 lb), though most specimens grow no longer than 20 centimetres (7.9 in).

The speckled bush-cricket is a flightless species of bush-cricket belonging to the family Tettigoniidae. The species was originally described as Locusta punctatissima in 1792.

Knipowitschia punctatissima, the Italian spring goby, is a species of goby endemic to Italy where it inhabits fresh, clear waters of springs, streams, and channels with slow water movements. This species can reach a length of 4.5 centimetres (1.8 in) SL.

The yellowtail flounder, also known as the rusty dab, is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae. Reaching 56 cm (22 in) in length, it has reddish brown upperparts, pale underparts and yellow fins. Both its eyes are on the right (upper) side of its body. Found in the western North Atlantic, it has been fished commercially by North American fisheries for food. A victim of overfishing, the yellowtail flounder is categorized as "Vulnerable" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.

Limanda is a genus of righteye flounders native to the northern Atlantic and Pacific oceans.

Pleuronectinae is a subfamily of fish in the family Pleuronectidae, comprising 14 genera and 33 species. Members of the subfamily are demersal carnivores that live in arctic and northern seas.

The yellowfin sole is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on soft, sandy bottoms at depths of up to 700 metres (2,300 ft), though it is most commonly found at depths of around 91 metres (299 ft). Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the northern Pacific, from Korea and the Sea of Japan to the Sea of Okhotsk, the Bering Sea and Barkley Sound on the west coast of Canada. Males grow up to 49 cm (19 in) in length, though the common length is around 33.5 cm (13.2 in). The maximum recorded weight is 1.7 kg (3.7 lb), and the maximum recorded lifespan is 26 years.

The longhead dab is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms at depths of up to 160 metres (520 ft), though it is most commonly found between 10 and 125 metres. Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the northern Pacific, and it range stretches from the Sea of Okhotsk and the Kuril Islands to the Bering Sea and the arctic west coast of Canada. Males grow up to 40 centimetres (16 in) in length, though the common length is around 17.5 centimetres (6.9 in).

The Sakhalin sole is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms at depths of between 10 and 360 metres, though it is most commonly found between around 50 and 100 metres. Its native habitat is the polar waters of the northwestern Pacific, from the Sea of Okhotsk to the west and central Bering Sea, as far as the Pribilof Islands. It can reach up to 36 centimetres (14 in) in length, though the common length is around 21.5 centimetres (8.5 in). The maximum recorded weight is 500 grams (18 oz), and the maximum recorded lifespan is 8 years.

Plataspidae are a family of shield bugs native to the Old World. They are a family of hemipteran insects of the suborder Heteroptera.

Polychalca punctatissima is a species of tortoise beetles belonging to the family Chrysomelidae.

Amphiura filiformis is a species of brittle star belonging to the family Amphiuridae. It is found on the seabed in the north east Atlantic Ocean and adjoining seas to a depth of 200 metres (660 ft). It digs itself a shallow burrow in the sand and waves its arms in the water above to suspension feed on plankton.
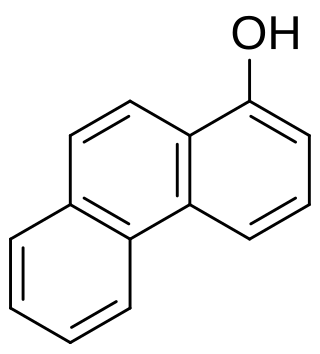
1-Hydroxyphenanthrene is a phenanthrol and a human metabolite of phenanthrene that can be detected in urine of persons exposed to PAHs.

Trachylepis punctatissima, commonly called the montane speckled skink or speckled rock skink, is a lizard in the skink family (Scincidae) which is widespread in southern Africa. The common and adaptable species occurs in a variety of habitat types at middle to high altitudes. It was for a time treated as a southern race of the African striped skink, T. striata.

Canthigaster janthinoptera, known as the honeycomb toby, is a species of pufferfish in the family Tetraodontidae. It is native to the Indo-Pacific, where it can be found along the east coast of Africa south to South Africa's Eastern Cape province, east to Oeno Island and the Line and Marquesas Islands, north to Japan, and south to Lord Howe Island. It is replaced by its relative C. jactator near the Hawaiian Islands and by C. punctatissima in the Eastern Pacific. It occurs in reef environments, often near sponges, at a depth range of 1 to 30 m, and it reaches 9 cm in total length. The species is reported to feed on sponges, polychaetes, and algae, in addition to small quantities of tunicates, crustaceans, echinoderms and corals. It is an oviparous species usually encountered alone or in pairs.

Canthigaster punctatissima, known as the spotted sharpnose puffer or the spotted sharpnosed puffer, is a species of pufferfish in the family Tetraodontidae. It is native to the Eastern Pacific, where it ranges from Guaymas, Mexico to Panama and the Galápagos Islands. It is replaced by its close relatives C. janthinoptera and C. jactator in the Western Pacific and the Hawaiian Islands, respectively. It is found in sheltered areas of rocky reefs at a depth range of 3 to 21 m and reaches 9 cm in total length. The species is reported to be monogamous.


















