
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships, gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons.

Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.

Human-powered transport is the transport of person(s) and/or goods (freight) using human muscle power. Unlike animal-powered transport, human-powered transport has existed since time immemorial in the form of walking, running and swimming, as well as small vehicles such as litters, rickshaws, wheelchairs and wheelbarrows. Modern technology has allowed mechanical advantage devices and machines to enhance human-power.

A hovercraft, also known as an air-cushion vehicle or ACV, is an amphibious craft capable of travelling over land, water, mud, ice, and various other surfaces.

An amphibious vehicle is a vehicle that works both on land and on or under water. Amphibious vehicles include amphibious bicycles, ATVs, cars, buses, trucks, railway vehicles, combat vehicles, and hovercraft.

The Bonneville Salt Flats are a densely packed salt pan in Tooele County in northwestern Utah, United States. A remnant of the Pleistocene Lake Bonneville, it is the largest of many salt flats west of the Great Salt Lake. It is public land managed by the Bureau of Land Management and is known for land speed records at the Bonneville Speedway. Access to the Flats is open to the public.
A mode of transport is a method or way of travelling, or of transporting people or cargo. The different modes of transport include air, water, and land transport, which includes rails or railways, road and off-road transport. Other modes of transport also exist, including pipelines, cable transport, and space transport. Human-powered transport and animal-powered transport are sometimes regarded as distinct modes, but they may lie in other categories such as land or water transport.
Ocean rowing is the sport of rowing across oceans. Some ocean rowing boats can hold as many as fourteen rowers; however, the most common ocean rowboats are designed for singles, doubles, and fours.
The Atlantic Rowing Race is an ocean rowing race from the Canary Islands to the West Indies, a distance of approximately 2,550 nm. The race was founded in 1997 by Sir Chay Blyth with subsequent races roughly every two years since. The early races were run by Challenge Business Ltd. until the race was bought by Woodvale Events Ltd., managed by Simon Chalk, in October 2003. In May 2012, Atlantic Campaigns SL, managed by Carsten Heron Olsen bought the rights to the Atlantic Rowing Race, now called The "Talisker Whisky Atlantic Challenge" – The World's Toughest Row. Since 2015, the race has been held annually starting each December.

Land transport is the transport or movement of people, animals or goods from one location to another location on land. This is in contrast with other main types of transport such as maritime transport and aviation. The two main forms of land transport can be considered to be rail transport and road transport.

A ground-effect vehicle (GEV), also called a wing-in-ground-effect (WIG), ground-effect craft, wingship, flarecraft or ekranoplan, is a vehicle that is able to move over the surface by gaining support from the reactions of the air against the surface of the earth or water. Typically, it is designed to glide over a level surface by making use of ground effect, the aerodynamic interaction between the moving wing and the surface below. Some models can operate over any flat area such as frozen lakes or flat plains similar to a hovercraft.
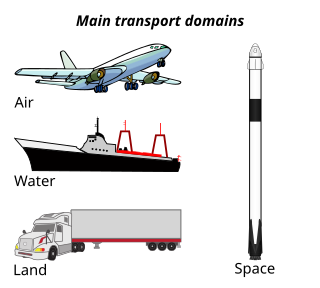
Transport or transportation is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land, water, cable, pipelines, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations.

An amphibious warfare ship is an amphibious vehicle warship employed to land and support ground forces, such as marines, on enemy territory during an amphibious assault.
The Sara G is an ocean rowing boat which holds multiple world records.

Fiann Paul is a Polish-Icelandic explorer known for his exploits in ocean rowing.

Anders Johan Svedlund,, was a Swedish born, naturalized New Zealand ocean rowing pioneer. Anders performed 2 of 14 Historic ocean rows listed by Ocean Rowing Society, the official Guinness Adjudicator for ocean rowing. He was the first to row the Indian Ocean, the first to row on the Pacific solo, and the fastest ocean rower of his times.

Eugene Smurgis was a Russian Arctic marine explorer, ultra-long distance rower and Arctic rowing pioneer. From 1967 to 1993 Eugene rowed a total of 48,000 km on oceans, seas and rivers; a distance longer than the circumference of the Earth and the greatest distance ever rowed by a solo ultra-endurance rower. He completed 9900 km of coastal polar ocean rows. Most of his pioneering rows were completed in the Arctic in a primitive open boat with no cabin or crawl space. He was the first recorded polar ocean rower, as the earlier Antarctic expedition by Ernest Shackleton predominantly relied on sails and used oars only to a marginal degree, therefore not meeting the criteria of ocean rowing.

Ocean Rowing Society International (ORSI) (prior to 2006 known as ORS), is the governing body for international ocean rowing and official adjudicator of ocean rowing records for Guinness World Records. ORSI was founded in 1983 in California by ocean rower Peter Bird and Kenneth F.Crutchlow FRGS. Current coordinators of ORSI are Tatiana Rezvaya-Crutchlow and Chris Martin, and Fiann Paul.

The Ocean Explorers Grand Slam is an adventurer goal to complete open-water crossings on all five oceans using human-powered vessel.













