
Paul Bunyan is a giant lumberjack and folk hero in American and Canadian folklore. His tall tales revolve around his superhuman labors, and he is customarily accompanied by Babe the Blue Ox, his pet and working animal. The character originated in the oral tradition of North American loggers, and was later popularized by freelance writer William B. Laughead (1882–1958) in a 1916 promotional pamphlet for the Red River Lumber Company. He has been the subject of various literary compositions, musical pieces, commercial works, and theatrical productions. His likeness is displayed in a number of oversized statues across North America.

Dame Julie Andrews is an English actress, singer, and author. She has garnered numerous accolades throughout her career spanning over seven decades, including an Academy Award, a BAFTA Award, two Emmy Awards, three Grammy Awards, and six Golden Globe Awards as well as nominations for three Tony Awards. One of the biggest box office draws of the 1960s, Andrews has been honoured with the Kennedy Center Honors in 2001, the Screen Actors Guild Life Achievement Award in 2007, and the AFI Life Achievement Award in 2022. She was made a Dame (DBE) by Queen Elizabeth II in 2000.
In Norse mythology, Hoddmímis holt is a location where Líf and Lífþrasir are foretold to survive the long winters of Fimbulvetr. Hoddmímis holt is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. Like the very similarly named Mímameiðr, scholars generally consider Hoddmímis holt to be another name for Yggdrasil and connect it to folklore recorded from continental Germanic folklore.

The Little House on the Prairie books comprise a series of American children's novels written by Laura Ingalls Wilder. The stories are based on her childhood and adolescence in the American Midwest between 1870 and 1894. Eight of the novels were completed by Wilder, and published by Harper & Brothers in the 1930s and 1940s, during her lifetime. The name "Little House" appears in the first and third novels in the series, while the third is identically titled Little House on the Prairie. The second novel, meanwhile, was about her husband's childhood.
A tall tale is a story with unbelievable elements, related as if it were true and factual. Some tall tales are exaggerations of actual events, for example fish stories such as, "That fish was so big, why I tell ya', it nearly sank the boat when I pulled it in!" Other tall tales are completely fictional tales set in a familiar setting, such as the European countryside, the American frontier, the Canadian Northwest, the Australian outback, or the beginning of the Industrial Revolution.
The Whangdoodle is a fanciful or humorous being whose undefined appearance and essence is left to individual imagination. Other connotations may include an object of humor, something noisy but of no consequence and insignificant.

The Last of the Really Great Whangdoodles is a children's novel written by Julie Edwards, the married name of singer and actress Dame Julie Andrews. More recent editions credit the book to "Julie Andrews Edwards".

Talking trees are a form of sapient trees in mythologies and stories.
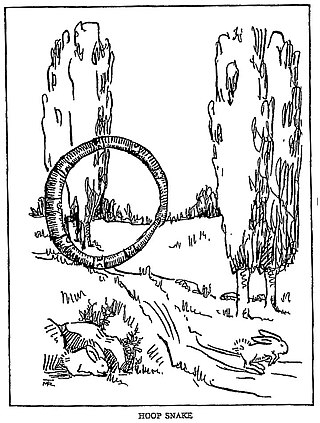
The hoop snake is a legendary creature of the United States, Canada, and Australia. It appears in the Pecos Bill stories; although his description of hoop snakes is the one with which people are most familiar, stories of the creature predate those fictional tales considerably. Several sightings of the hoop snake have been alleged along the Minnesota-Wisconsin border in the St. Croix River valley, Wake County in North Carolina, Prince Edward Island, and Kamloops, British Columbia.
Fearsome Creatures of the Lumberwoods, With a Few Desert and Mountain Beasts is a 1910 fantasy field guide by William Thomas Cox (1878–1961), Minnesota’s first State Forester and Commissioner of Conservation, with illustrations by Coert du Bois and Latin classifications by George Bishop Sudworth The text is a noteworthy resource on folklore, as a century after its initial publication Fearsome Creatures remains one of the principal sources on legendary creatures of the United States and Canada.

In North American folklore, fearsome critters were tall tale animals jokingly said to inhabit the wilderness in or around logging camps, especially in the Great Lakes region. Today, the term may also be applied to similar fabulous beasts.

In American folklore, the axehandle hound is a "fearsome critter" of Minnesota and Wisconsin. The animal resembles a dog with a body axe-like in shape. It has a head shaped like an axe blade, hence the name, complemented by a handle-shaped body atop short stubby legs. It subsists on a diet consisting entirely on the handles of axes which have been left unattended. A nocturnal creature, the axehandle hound travels from camp to camp searching for its next meal. In Minnesota, there is a canoe-access campground named Ax-Handle Hound after the folklore creature. It can be found on the Little Fork River near Voyageurs National Park and very near the town of Linden Grove.

In folklore and fantasy, an enchanted forest is a forest under, or containing, enchantments. Such forests are described in the oldest folklore from regions where forests are common, and occur throughout the centuries to modern works of fantasy. They represent places unknown to the characters, and situations of liminality and transformation. The forest can feature as a place of threatening danger, or one of refuge, or a chance at adventure.

Folklore of the Low Countries, often just referred to as Dutch folklore, includes the epics, legends, fairy tales and oral traditions of the people of Belgium, Netherlands and Luxembourg. Traditionally this folklore is written or spoken in Dutch or in one of the regional languages of these countries.
French folklore encompasses the fables, folklore, fairy tales and legends of the French people.
Cruel Coppinger is a semi-legendary figure in Cornish folklore. Coppinger was a real person, but various legends grew up around him, lending him near superhuman powers and a fearsome reputation. He is portrayed as huge and fearsome Dane who after being shipwrecked off Cornwall became the leader of a feared band of smugglers.
Mythic humanoids are legendary, folkloric, or mythological creatures that are part human, or that resemble humans through appearance or character. Each culture has different mythical creatures that come from many different origins, and many of these creatures are humanoids. They are often able to talk and in many stories they guide the hero on their journey.

Grandma Marta Day is a holiday celebrated in Bulgaria, on March 1. Martenitsas, usually in the form of a wrist band, small yarn dolls, or tassels, are created by combining red and white colored threads and are worn on that day and throughout March. They are worn until a stork or a swallow is seen, symbolizing the coming of spring, warmer weather, and well-being. Once the stork or a swallow appears the Martenitsa is taken off and hung on a blooming tree. It is common in the spring to see trees festooned in Martenitsas.

In American folklore, the hugag is a fearsome critter similar to a moose with an extensive upper-lip, preventing it from grazing, and joint-less legs preventing it from lying down.











