
Moringua edwardsi, the common spaghetti eel, is an eel in the family Moringuidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Harvey Bollman in 1889, originally under the genus Stilbiscus. It is a subtropical, marine eel known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, Cuba, Dominica, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Honduras, Jamaica, Martinique, Mexico, Montserrat, Nicaragua, Puerto Rico, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, Florida, Venezuela, the Virgin Islands, British, and the Virgin Islands of the United States. Males can reach a maximum total length of 15 cm, while females can reach a maximum of 50 cm. The eels feed primarily off of burrowing invertebrates.

The bandtooth conger, also known as the Baleares conger or the Balearic conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by François Étienne Delaroche in 1809, originally under the genus Muraena. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic and the western Indian Ocean, including North Carolina, United States; the northern Gulf of Mexico, northern South America, Canada, Portugal, Angola, the Mediterranean, and the Red Sea. It inhabits reefs and littoral shelves, and burrows into sand and mud. It dwells at a depth range of 1–732 meters (3–2,402 ft), but most frequently between 20–100 m (66–328 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length (TL) of 35 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 25 centimetres (9.8 in)
Gnathophis capensis, the Southern Atlantic conger or southern conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Leptocephalus. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the southeastern Atlantic Ocean, including from False Bay to Plettenberg Bay, South Africa and also on Tristan da Cunha Island. It is known to dwell at a depth of 100 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 37 cm.
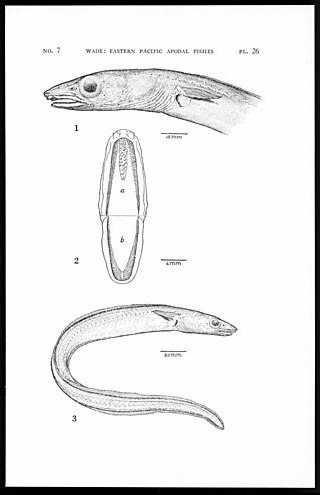
Gnathophis cinctus, the hardtail conger or Catalina conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Atopichthys. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 9–336 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, burrowing into loose sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 42 cm.
The white-ring garden eel, also known as the Cape garden eel in Mexico, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Garry I. McTaggart-Cowan and Richard Heinrich Rosenblatt in 1974, originally under the genus Taenioconger. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Gulf of California, in the eastern central Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 20 m (66 ft), and inhabits sand sediments near reefs, where it forms burrows in nonmigratory colonies. Males can reach a maximum total length of 80 cm.
The pale green eel, also known as the pale garden eel or the Cortez garden eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Jacques Pellegrin in 1923, originally under the genus Taenioconger. It is a nonmigratory marine, deepwater-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including the Gulf of California and Mexico. It dwells at a depth of 230 to 275 m and inhabits sandy sediments near reefs in large colonies. Males can reach a maximum total length of 63 cm.

The enigma garden eel is a species of eel in the conger/garden eel family Congridae.
The Galapagos garden eel is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Irenäus Eibl-Eibesfeldt and Friedmann Köster in 1983, originally under the genus Taenioconger. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, the Galapagos Islands in Ecuador, and Panama. It dwells at a depth of 10 to 30 m, and lives in large, nonmigratory colonies in clean, sandy substrates. Males can reach a maximum total length of 70 cm.
Heteroconger obscurus, the obscure garden eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Wolfgang Klausewitz and Irenäus Eibl-Eibesfeldt in 1959, originally under the genus Xarifania. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern Indian Ocean, including the Nicobar Islands in India, and Andaman Island. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 15 m (49 ft), and inhabits silty sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 33.6 cm.

The zebra garden eel, also known as the banded garden eel, is a species of eel in the conger/garden eels family Congridae. It was described by Pieter Bleeker in 1868. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific, including the Philippines, the Ryukyu Islands, New Guinea, Indonesia and Vanuatu. It inhabits shallow waters at a depth range of 1 to 10 m, and forms burrows in colonies of moderate size on sand sediments in bays, slopes and reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 34.7 cm.
The Johnston snake eel, also known as the peppered worm eel in Micronesia and Hawaii is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Leonard Peter Schultz and Loren Paul Woods in 1949. It is a marine, tropical eel, which is known from the Indo-Pacific region, including the Chagos Islands, Hawaii, the Marquesan Islands, the Society Islands, Australia, and New Caledonia. It dwells at a depth range of 2–23 m, and inhabits sand sediments in coral reefs. It can reach a maximum total length of 35 cm.

Aplatophis chauliodus, the fangtooth snake-eel, also known as the tusky eel in Cuba and the United States, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by James Erwin Böhlke in 1956. It is a marine, tropical eel known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico and French Guiana. It is also known to occur on the northeastern coast of Brasil. It dwells at a depth range of 33–91 m (100–300 ft), and dwells in both marine waters and brackish estuaries. It inhabits burrows on a permanent or semipermanent basis, and leaves its eyes and snout exposed. Males can reach a maximum total length of 84 cm (33 in). The fangtooth snake-eel's diet consists of bony fish and crustaceans.
Callechelys springeri, the ridgefin eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951, originally under the genus Gordiichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern Gulf of Mexico, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 22 to 36 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 80.1 centimeters (31.5 in).
The Pacific spoon-nose eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by José Luis Castro-Aguirre and Sergio Suárez de los Cobos in 1983, originally under the genus Notophtophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including the Gulf of California, Colombia, Mexico, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Ecuador and Panama. It dwells at a maximum depth of 10 metres (33 ft), and inhabits sand and mud sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 140 centimetres (55 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 60 centimetres (24 in).

Echiophis punctifer, the stippled spoon-nose eel, spoon-nose eel or snapper eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1859. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico, Cuba, northern South America, Senegal, and Angola. It dwells at a depth range of 40 to 100 metres, and inhabits shallow bays and lagoons, in which it forms burrows in mud and sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 180 centimetres (71 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 100 centimetres (39 in).

The goldspotted eel, also known as the goldspotted snake eel or the dark-spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1825, originally under the genus Muraenophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, southern Florida, USA; the Bahamas, Santa Catarina, and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 15 metres (49 ft), and inhabits rocky and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres (3.6 ft).

The highfin snake eel (Ophichthus altipennis, also known as the blackfin snake eel or the black-finned snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1856, originally under the genus Microdonophis. It is a marine, tropical eel known from the eastern Indian Ocean and northwestern and western central Pacific Ocean, including Australia, French Polynesia, Indonesia, Japan, the Marshall Islands, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Papua New Guinea. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 40 m, and forms burrows in soft inshore sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 103 cm.
The yellow snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1882. It is a marine, subtropical eel known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Chile, Costa Rica, Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Mexico, Panama, Peru, and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 110 m, and forms burrows in rocky and sandy regions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 98 cm (39 in), but more commonly reach a length of 50 cm (20 in).

The rice-paddy eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton in 1822, originally in the genus Ophisurus. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-West Pacific, including Somalia, Tanzania, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Polynesia, Australia, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Kenya, Madagascar, the Philippines, Malaysia, Mozambique, Seychelles, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan, China, Thailand, Vietnam, and southern Yemen. It is an anadromous species and spawns in freshwater, often in rice paddies during the rainy season, earning it its common name. It also spends time in lagoons, estuaries and coastal rivers, in which it lives in burrows in the river bottom and bank. Males can reach a maximum total length (TL) of 100 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 70 cm.

The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 and 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).














