
Freesia is a genus of herbaceous perennial flowering plants in the family Iridaceae, first described as a genus in 1866 by Christian Friedrich Ecklon (1886) and named after the German botanist and medical practitioner, Friedrich Freese (1795-1876). It is native to the eastern side of southern Africa, from Kenya south to South Africa, most species being found in Cape Provinces. Species of the former genus Anomatheca are now included in Freesia. The plants commonly known as "freesias", with fragrant funnel-shaped flowers, are cultivated hybrids of a number of Freesia species. Some other species are also grown as ornamental plants.

Stapeliinae is a subtribe of flowering plants within the tribe Ceropegieae of the subfamily Asclepiadoideae of the family Apocynaceae. The subtribe comprises about 35 genera, including both the stem-succulent "stapeliads" and the horticulturally popular genera Brachystelma and Ceropegia. The largest number of genera are native to Africa, but a more limited number of genera are widespread in Arabia and Asia. Historically, a similarly circumscribed taxon was treated as a separate tribe, Stapelieae.

Stapelia is a genus of low-growing, spineless, stem succulent plants, predominantly from South Africa with a few from other parts of Africa. Several Asian and Latin American species were formerly included but they have all now been transferred to other genera. The flowers of certain species, most notably Stapelia gigantea, can reach 41 cm (16 inches) in diameter when fully open. Most Stapelia flowers are visibly hairy and generate the odor of rotten flesh when they bloom.

The genus Huernia consists of perennial, stem succulents from Eastern and Southern Africa and Arabia, first described as a genus in 1810.

Aloidendron dichotomum, formerly Aloe dichotoma, the quiver tree or kokerboom, is a tall, branching species of succulent plant, indigenous to Southern Africa, specifically in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, and parts of Southern Namibia.

Gasteria is a genus of succulent plants, native to South Africa and the far south-west corner of Namibia.

Duvalia is a succulent plant genus in the subfamily Asclepiadoideae, in the family Apocynaceae (dogbane).

Tridentea is a genus of succulent plant in the family Apocynaceae, endemic to southern Africa.

The genus Quaqua falls within the tribe of plants known collectively as stapeliads. All stapeliads, including Quaqua, are Old World stem succulents.
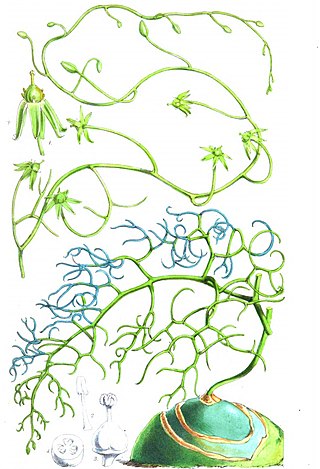
Bowiea is a genus of bulbous, perennial, succulent plants which thrive in dry and desert regions of eastern and southern Africa. It is native to a region stretching from Kenya to Cape Province. The genus contains a single species, Bowiea volubilis.

AnacampserosL. is a genus comprising about a hundred species of small perennial succulent plants native to Southern Africa, Ethiopia and Latin America. The botanical name Anacampseros is an ancient one for herbs supposed to restore lost love.

Microloma is a small genus of Ceropegia-like twiners and twiggy bushes occurring in mainly arid or fynbos regions in South Africa. They are generally nondescript when not in bloom, but the flowers of most species are incongruously decorative.

Tromotriche is a genus of plant in family Apocynaceae. It is native to southern Africa.

Tavaresia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1902. It is native to southern Africa.
- Tavaresia angolensisWelw. - Angola
- Tavaresia barklyi(Dyer) N.E.Br. - South Africa
- Tavaresia grandifloraBerger - South Africa
- Tavaresia meintjesiiR.A. Dyer - Limpopo

Piaranthus is a succulent plant genus in the subfamily Asclepiadoideae, in the family Apocynaceae.

Orbea is a genus of flowering plants of the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1812. It is native to Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
Pectinaria is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1819. The entire genus is endemic to South Africa.

Stapelia hirsuta, common name starfish flower or carrion plant, is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Apocynaceae.
















