The Alaska–Yukon–Pacific Exposition, acronym AYP or AYPE, was a world's fair held in Seattle in 1909 publicizing the development of the Pacific Northwest. It was originally planned for 1907 to mark the 10th anniversary of the Klondike Gold Rush, but the organizers learned of the Jamestown Exposition being held that same year and rescheduled.

Red Square, officially Central Plaza or the Suzzallo Quadrangle, is a large open square on the Seattle campus of the University of Washington that serves as a hub for two of the university's major axes, connecting the campus's northern Liberal Arts Quadrangle with the science and engineering buildings found on the lower campus. The plaza is paved with red brick, and becomes notoriously slippery during rain.

Lorado Zadok Taft was an American sculptor, writer and educator. Part of the American Renaissance movement, his monumental pieces include, Fountain of Time, Spirit of the Great Lakes, and The Eternal Indian. His 1903 book, The History of American Sculpture, was the first survey of the subject and stood for decades as the standard reference. With what were seen as progressive views on the subject, he has been credited with helping to advance the status of women as sculptors.

James Earle Fraser was an American sculptor during the first half of the 20th century. His work is integral to many of Washington, D.C.'s most iconic structures.
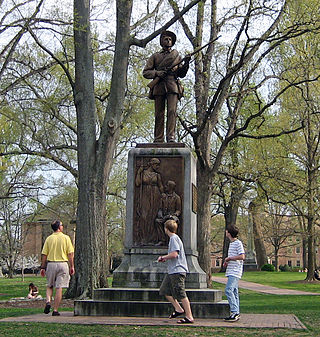
The Confederate Monument, University of North Carolina, commonly known as Silent Sam, is a bronze statue of a Confederate soldier by Canadian sculptor John A. Wilson, which once stood on McCorkle Place of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC) from 1913 until it was pulled down by protestors on August 20, 2018. Its former location has been described as "the front door" of the university and "a position of honor".

Wheeler Williams was an American sculptor.

Christopher Columbus is a bronze statue of Italian explorer and navigator Christopher Columbus. It was installed during 1933 in Chicago's Grant Park, in the U.S. state of Illinois. Created by the Milanese-born sculptor Carlo Brioschi, it was set on an exedra and pedestal designed with the help of architect Clarence H. Johnston. It was removed and put in storage in 2020.

The Robert E. Lee Monument was an outdoor bronze equestrian statue of Confederate general Robert E. Lee and his horse Traveller located in Charlottesville, Virginia's Market Street Park in the Charlottesville and Albemarle County Courthouse Historic District. The statue was commissioned in 1917 and dedicated in 1924, and in 1997 was listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It was removed on July 10, 2021, and melted down in 2023.

The Robert E. Lee Monument in Richmond, Virginia, was the first installation on Monument Avenue in 1890, and would ultimately be the last Confederate monument removed from the site. Before its removal on September 8, 2021, the monument honored Confederate General Robert E. Lee, depicted on a horseback atop a large marble base that stood over 60 feet (18 m) tall. Constructed in France and shipped to Virginia, it remained the largest installation on Monument Avenue for over a century; it was first listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2007 and the Virginia Landmarks Register in 2006.

A 1926–27 statue of George Washington by Italian American artist Pompeo Coppini was installed in northeast Portland, Oregon, United States. The bronze sculpture was the second of three statues of Washington by the artist, following a similar statue installed in Mexico City in 1912 and preceding another installed on the University of Texas at Austin campus in February 1955. The Portland statue was created to commemorate the 1926 sesquicentennial of the Declaration of Independence and dedicated in 1927. It was part of the City of Portland and Multnomah County Public Art Collection. In June 2020, it was toppled by protestors.

Thomas Jefferson is a 1911 bronze statue of a seated Thomas Jefferson created by Karl Bitter for the Cuyahoga County Courthouse in Cleveland, Ohio, United States.

Drumheller Fountain is an outdoor fountain on the University of Washington campus in Seattle, Washington, in the United States. The fountain was given its name in 1961 to honor the University Regent Joseph Drumheller, who gifted the central fountain machinery to the University for its centennial celebration.

There are more than 160 Confederate monuments and memorials to the Confederate States of America and associated figures that have been removed from public spaces in the United States, all but five of which have been since 2015. Some have been removed by state and local governments; others have been torn down by protestors.

A statue of Frank Rizzo, sometimes called the Frank L. Rizzo Monument, was installed in Philadelphia, in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Erected in 1998, the bronze sculpture was removed in June 2020. Black Lives Matter activists and others protested the statue's presence, and the statue was taken down during the George Floyd protests.

The Stonewall Jackson Monument in Richmond, Virginia, was erected in honor of Thomas Jonathon "Stonewall" Jackson, a Confederate general. The monument was located at the centre of the crossing of Monument Avenue and North Arthur Ashe Boulevard, in Richmond, Virginia. The bronze equestrian statue was unveiled in 1919. Along this avenue were other statues including Robert E. Lee, J. E. B. Stewart, Jefferson Davis, Matthew Maury and more recently Arthur Ashe. Thomas Jackson is best known as one of Robert E. Lee's most trusted commanders throughout the early period of the American Civil War between Southern Confederate states and Northern Union states. He rose to prominence after his vital role in the Confederate victory at the First Battle of Bull Run in July 1861, continuing to command troops until his untimely death on May 10, 1863, after falling fatally ill following the amputation of his wounded arm.

The Matthew Fontaine Maury Monument, is a partially deconstructed memorial installed along Richmond, Virginia's Monument Avenue depicting Matthew Fontaine Maury and commemorating his Confederate naval service and contributions to oceanography and naval meteorology. It features the engraved moniker "Pathfinder of the Seas". Between July 2–9, 2020, the bronze statue of Maury and other sculptural elements were removed from the monument by the city of Richmond, in response to local protests connected to nationwide unrest sparked by the murder of George Floyd in police custody in Minneapolis.

A 1959 statue of Christopher Columbus by Alfred Solani was installed on the Columbus State Community College's downtown campus in Columbus, Ohio, United States. The monument is one of three in Columbus commemorating the explorer. The statue was removed June 19, 2020.

A number of statues and memorials were the subject of protests and petitions during the George Floyd protests in the United Kingdom in 2020.