
Bambusa is a large genus of clumping bamboos. Most species of Bambusa are rather large, with numerous branches emerging from the nodes, and one or two much larger than the rest. The branches can be as long as 11 m (35 ft).

Dendrocalamus is a tropical Asian genus of giant clumping bamboos in the grass family. It is found in the Indian subcontinent, China, and Southeast Asia.

Antidesma is a genus of tropical plant in the family Phyllanthaceae formally described by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to tropical Africa, S + E + SE Asia, Australia, and various oceanic islands. The greatest diversity occurs in Southeast Asia.

Olea is a genus of about 40 species in the family Oleaceae, native to warm temperate and tropical regions of the Middle East, southern Europe, Africa, southern Asia, and Australasia. They are evergreen trees and shrubs, with small, opposite, entire leaves. The fruit is a drupe. Leaves of Olea contain trichosclereids.

Arisaema is a large and diverse genus of the flowering plant family Araceae. The largest concentration of species is in China and Japan, with other species native to other parts of southern Asia as well as eastern and central Africa, Mexico and eastern North America. Asiatic species are often called cobra lilies, while western species are often called jack-in-the-pulpit; both names refer to the distinctive appearance of the flower, which consists of an erect central spadix rising from a spathe.
Megistostigma is a genus of plant of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1887. It is native to southern China, Assam, and Southeast Asia.
- Megistostigma burmanicum - Assam, Myanmar, Thailand, Perlis
- Megistostigma cordatum - Sumatra, Sabah, Samar
- Megistostigma glabratum - Peninsular Malaysia, Anamba Islands, N Sumatra
- Megistostigma peltatum - Siberut, Natuna, Java
- Megistostigma yunnanense - Yunnan

Cleistanthus is a plant genus of the family Phyllanthaceae, tribe Bridelieae, first described as a genus in 1848. It is widespread in much of the Old World Tropics in Asia, Africa, Australia, and various oceanic islands. Cleistanthus collinus is known for being toxic and may be the agent of homicides or suicides.

Cephalantheropsis is a genus of orchids, comprising 4 accepted species distributed in China, Japan, the Eastern Himalayas and Southeast Asia.

Tainia, commonly known as ribbon orchids or 带唇兰属 is a genus of about thirty species of evergreen, terrestrial orchids in the distributed from India, China, Japan, Southeast Asia to New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Queensland.

Odontochilus is a small genus from the orchid family (Orchidaceae). These terrestrial, mycoparasitic orchids occur from China, Japan, the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Melanesia. The genus is related to Gonatostylis, endemic to New Caledonia.

Phoebe is a genus of evergreen trees and shrubs belonging to the Laurel family, Lauraceae. There are 75 accepted species in the genus, distributed in tropical and subtropical Asia and New Guinea. 35 species occur in China, of which 27 are endemic. The first description of the genus was of the type species P. lanceolata made in 1836 by Christian Gottfried Daniel Nees von Esenbeck in Systema Laurinarum, p. 98.

Homalomena is a genus of flowering plants within the family Araceae. Homalomena are primarily found in southern Asia and the southwestern Pacific, but there are a few species that are known to be indigenous to Latin America. Many Homalomena have a strong smell of anise. The name derives apparently from a mistranslated Malayan vernacular name, translated as homalos, meaning flat, and mene = moon.

Scindapsus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Queensland, and a few western Pacific islands. The species Scindapsus pictus is common in cultivation.

Steudnera is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to southern China, the Himalayas, and Indochina. The genus was first described by Karl Koch in 1862. The genus is also believed to be closely related to Remusatia.
- Steudnera assamicaHook.f. - Arunachal Pradesh, Assam
- Steudnera capitellataHook.f. - Myanmar
- Steudnera colocasiifoliaK.Koch - Yunnan, Guangxi, Assam, Bangladesh, Indochina
- Steudnera discolorW.Bull - Assam, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand
- Steudnera gageiK.Krause - Assam
- Steudnera griffithii(Schott) Hook.f. - Assam, Myanmar, Yunnan
- Steudnera henryanaEngl. - Yunnan, Laos, Vietnam
- Steudnera kerriiGagnep. - Guangxi, Laos, Vietnam, Thailand

Pholidota, commonly known as rattlesnake orchids, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are clump-forming epiphytes or lithophytes with pseudobulbs, each with a single large leaf and a large number of small, whitish flowers arranged in two ranks along a thin, wiry flowering stem that emerges from the top of the pseudobulb. There are about thirty five species native to areas from tropical and subtropical Asia to the southwestern Pacific.
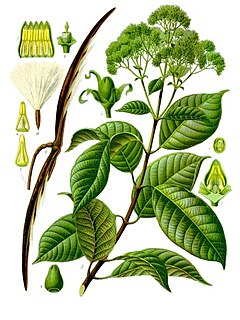
Urceola is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1798. It is native to China, the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea.
- Urceola brachysepalaHook.f. - Borneo, Java, W Malaysia, Sumatra, Philippines
- Urceola elasticaRoxb. - Borneo, Java, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Urceola huaitingii(Chun & Tsiang) Mabb. - Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan
- Urceola javanica(Blume) Boerl. - Borneo, Java, Maluku, Sumatra, Sulawesi, New Guinea
- Urceola laevis(Elmer) Merr. - Palawan, Sabah, Sulawesi
- Urceola lakhimpurensis(S.K.Srivast. & Mehrotra) Karthik. & Moorthy - Assam
- Urceola latifolia(Pierre ex Spire) Mabb. - Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola lucida(A.DC.) Benth. ex Kurz - Myanmar, Thailand, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Urceola malayanaMabb. - Cameron Highlands of W Malaysia
- Urceola micrantha(Wall. ex G.Don) Mabb. - Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Tibet, Yunnan, Ryukyu Islands, Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, W Malaysia
- Urceola minutiflora(Pierre) Mabb. - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola napeensis(Quint.) Mabb. - Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi
- Urceola quintaretii(Pierre) Mabb. - Laos, Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi
- Urceola rosea(Hook. & Arn.) D.J.Middleton - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, W Malaysia, Java, Sumatra, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hainan, Hunan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Yunnan
- Urceola torulosaHook.f. - W Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo
- Urceola tournieri(Pierre) Mabb. - Yunnan, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola xylinabariopsoides(Tsiang) Mabb. - Hainan, Vietnam
Brachytome is a genus of 8 species of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It was described by Joseph Dalton Hooker in 1871. It occurs in mainland Southeast Asia from Bangladesh, east to south central China and south to Peninsular Malaysia.

Gomphostemma is a genus of flowering plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae, first described in 1830. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, and the Indian subcontinent.
- Gomphostemma aborensisDunn - Arunachal Pradesh
- Gomphostemma arbusculumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma callicarpoides(Yamam.) Masam. - Taiwan
- Gomphostemma chinenseOliv. - Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Jiangxi, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma crinitumWall. ex Benth. - Indochina, Yunnan, Assam, Bangladesh
- Gomphostemma curtisiiPrain - Malaya, Sumatra, Borneo
- Gomphostemma deltodonC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma dolichobotrysMerr. - Sumatra
- Gomphostemma eriocarpumBenth. - southern India
- Gomphostemma grandiflorumDoan ex Suddee & A.J.Paton - Vietnam
- Gomphostemma hainanenseC.Y.Wu - Hainan
- Gomphostemma hemsleyanumPrain ex Collett & Hemsl. - Java, Myanmar
- Gomphostemma heyneanumWall. ex Benth. - southern India
- Gomphostemma hirsutumWalsingham - Sabah
- Gomphostemma inopinatumPrain - Myanmar
- Gomphostemma javanicum(Blume) Benth. - Indochina, Andaman Islands, Borneo, Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, Bali, Lombok, Timor, Philippines
- Gomphostemma keralensisVivek., Gopalan & R.Ansari. - Kerala
- Gomphostemma laceiMukerjee - Myanmar
- Gomphostemma latifoliumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan, Guangdong
- Gomphostemma leptodonDunn - Guangxi, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma lucidumWall. ex Benth. - Indochina, Assam, Bangladesh, Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan
- Gomphostemma mastersiiBenth. ex Hook.f. - Assam, Bangladesh, Thailand
- Gomphostemma melissifoliumWall. ex Benth. - Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal
- Gomphostemma microcalyxPrain - Borneo, Malaya, Sumatra
- Gomphostemma microdonDunn - Yunnan, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma nayariiA.S.Chauhan - Assam
- Gomphostemma niveumHook.f. - Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma nutansHook.f. - Assam, Myanmar
- Gomphostemma ovatumWall. ex Benth. - Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal
- Gomphostemma parviflorumWall. ex Benth. - Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Yunnan, Indochina, Borneo, Java, Sumatra
- Gomphostemma pedunculatumBenth. ex Hook.f. - Assam, Yunnan, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma pseudocrinitumC.Y.Wu - Guangxi
- Gomphostemma salarkhanianumKhanam & M.A.Hassan - Sylhet District in Bangladesh
- Gomphostemma scortechiniiPrain - Myanmar, Thailand, Malaya
- Gomphostemma stellatohirsutumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma strobilinum Wall. ex Benth. - Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma sulcatumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma thomsoniiBenth. ex Hook.f. - Assam
- Gomphostemma velutinumBenth. - Assam, Bangladesh
- Gomphostemma wallichiiPrain - Assam, Myanmar, Thailand

Genianthus is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1883. It is native to southern China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.
Lygisma is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1883. It is native to southern China, Indochina, Malaysia, and the Himalayas.
- Lygisma angustifolia(Wight) Hook.f. - Himalayas
- Lygisma flavum(Ridl.) Kerr - Peninsular Malaysia
- Lygisma inflexum(Costantin) Kerr - Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan
- Lygisma nervosumKerr - Thailand

















