
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.
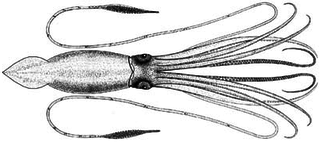
The giant squid is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around 12–13 m (39–43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle of the giant squid is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.
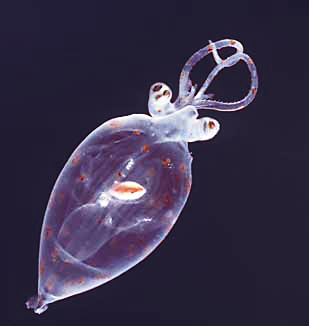
The family Cranchiidae comprises the approximately 60 species of glass squid, also known as cockatoo squid, cranchiid, cranch squid, or bathyscaphoid squid. Cranchiid squid occur in surface and midwater depths of open oceans around the world. They range in mantle length from 10 cm (3.9 in) to over 3 m (9.8 ft), in the case of the colossal squid. The common name, glass squid, derives from the transparent nature of most species. Cranchiid squid spend much of their lives in partially sunlit shallow waters, where their transparency provides camouflage. They are characterised by a swollen body and short arms, which bear two rows of suckers or hooks. The third arm pair is often enlarged. Many species are bioluminescent organisms and possess light organs on the undersides of their eyes, used to cancel their shadows. Eye morphology varies widely, ranging from large and circular to telescopic and stalked. A large, fluid-filled chamber containing ammonia solution is used to aid buoyancy. This buoyancy system is unique to the family and is the source of their common name "bathyscaphoid squid", after their resemblance to a bathyscaphe. Often the only organ that is visible through the transparent tissues is a cigar-shaped digestive gland, which is the cephalopod equivalent of a mammalian liver. This is usually held in a vertical position to reduce its silhouette and a light organ is sometimes present on the lower tip to further minimise its appearance in the water.

The Enoploteuthidea are a family of squid comprising approximately 40 species in four genera. Most species have a mantle length ranging from 3–13 cm. Hooks are present on all arms and tentacles. The family is best known for the large array of photophores throughout the body.

Ommastrephidae is a family of squid containing three subfamilies, 11 genera, and over 20 species. They are widely distributed globally and are extensively fished for food. One species, Todarodes pacificus, comprised around half of the world's cephalopod catch annually.

Lepidoteuthis grimaldii, also known as the Grimaldi scaled squid, is a large squid growing to 1 m in mantle length. It is named after the Grimaldi family, reigning house of Monaco. Prince Albert I of Monaco was an amateur teuthologist who pioneered the study of deep sea squids by collecting the 'precious regurgitations' of sperm whales. The Grimaldi scaled squid was first collected from the stomach contents of a sperm whale. It is a widely distributed species in tropical and subtropical areas of the North and South Atlantic, the southern Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, where it has been recorded off Japan and in the west Pacific.

Georg Johann Pfeffer (1854–1931) was a German zoologist, primarily a malacologist, a scientist who studies mollusks.

Abralia is a genus of squid comprising around 20 species from the family Enoploteuthidae. They are small squid which can be found in the epipelagic to mesopelagic zones while some species are found in water with shallow substrates on steep slopes on the boundary of the mesopelagic zone. They are distinguished from other members of the Enoploteuthidae by not normally having large, black photophores at the tips of arms IV, although if these are present they are not covered in black chromatophores, and having fins which extend beyond their tail. The photophores of the integument are characteristicand are found in the three types. "Lensed" photophores are a blue color with a white ring, "simple" photophores are small and violet-colored and the "complex" photophores are surrounded by small green satellite points and have a green centre. The complex photophores will frequently appear to be blue depending on their physiological state. The integument also has small black chromatophores which look like dots. They have 5-12 variably sized photophores on the eye. Either the right or left arm IV is hectocotylized.

Taoniinae is a subfamily containing ten genera of glass squids.

Liocranchia is a genus of glass squid from the family Cranchiidae. They are moderate-sized with a long, spindle-shaped mantle which tapers to a point at the rear and they can attain mantle lengths of 250 mm. The species in Liocranchia have a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical and subtropical oceans although it has been suggested that on especies, Liocranchia reinhardti is associated with land masses. In seas off Hawaii waters L. reinhardti undergoes vertical migrations while L. valdiviae occurs in deep water is sedentary. They are eaten by many oceanic predator species.

Ancistroteuthis lichtensteinii, also known as the angel clubhook squid or simply angel squid, is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae and the sole member of the genus Ancistroteuthis. It grows to a mantle length of 30 cm. It lives in the western Mediterranean Sea, subtropical and tropical eastern Atlantic Ocean and western north Atlantic Ocean. Its diet include mesopelagic fish and pelagic crustaceans. It is sometimes taken as bycatch by commercial fisheries, but is not a targeted species.

Onychoteuthis banksii, the common clubhook squid, is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae. It is the type species of the genus Onychoteuthis. This species was thought to have a worldwide distribution but with the revision of the genus Onychoteuthis in 2010, it is now accepted that Onychoteuthis banksii is restricted to the central and northern Atlantic and the Gulf of Mexico while a recently described species, Onychoteuthis horstkottei, is found in the Pacific Ocean. The type locality is the Gulf of Guinea.

Chiroteuthis veranii, commonly known as the long-armed squid, is a species of chiroteuthid squid. It grows to a mantle length of 12.5 cm and a total length of 130 cm.

Stigmatoteuthis hoylei, commonly called the flowervase jewel squid, is a species of cock-eyed squid. It is native to tropical and subtropical waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It grows to 20 cm in mantle length. The eyes of this species are highly dimorphic.
Stigmatoteuthis arcturi, commonly known as the jewelled squid, is a species of cock-eyed squid from the family Histioteuthidae. It occurs throughout the subtropical and tropical Atlantic Ocean in the mesopelagic zone.

Cephalopod ink is a dark-colored or luminous ink released into water by most species of cephalopod, usually as an escape mechanism. All cephalopods, with the exception of the Nautilidae and the Cirrina, are able to release ink to confuse predators.
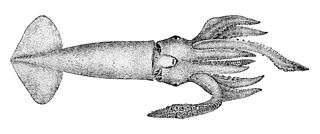
Nototodarus is a genus of squid. Example species in this genus include Nototodarus sloanii, a species sought for human food; in the process of harvesting N. sloanii Australian sea lions are frequently killed, since that marine mammal preys upon this squid species. Furthermore, New Zealand arrow squid, N. sloanii, is an important food source for the endangered yellow-eyed penguin, Megadyptes antipodes.

Teuthowenia megalops, sometimes known as the Atlantic cranch squid, is a species of glass squid from the subarctic and temperate waters of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They are moderately sized squid with a maximum mantle length of 40 cm (16 in). Their very large eyes are the source for the specific name megalops. Like other members of the genus Teuthowenia, they are easily recognizable by the presence of three bioluminescent organs (photophores) on their eyeballs.
Richard E. Young is a teuthologist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii's School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology.
Histioteuthis meleagroteuthis is a species of small to medium squids that have a dark, wine red skin pigment. Females at maturity average at 114mm in length, while males at maturity average at 65-102mm in length. This species is characterized by tubercles, photophores, and asymmetric features. This species can be found in circumglobal, mesopelagic waters.
















