
Rosaceae, the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants, including 4,828 known species in 91 genera.
The MaloideaeC.Weber was the apple subfamily, a grouping used by some taxonomists within the rose family, Rosaceae. Recent molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown that the traditional Spiraeoideae and Amygdaloideae form part of the same clade as the traditional Maloideae, and the correct name for this group is Amygdaloideae. Earlier circumscriptions of Maloideae are more-or-less equivalent to subtribe Malinae or to tribe Maleae. The group includes a number of plants bearing commercially important fruits, such as apples and pears, while others are cultivated as ornamentals.

Amygdaloideae is a subfamily within the flowering plant family Rosaceae. It was formerly considered by some authors to be separate from Rosaceae, and the family names Prunaceae and Amygdalaceae have been used. Reanalysis from 2007 has shown that the previous definition of subfamily Spiraeoideae was paraphyletic. To solve this problem, a larger subfamily was defined that includes the former Amygdaloideae, Spiraeoideae, and Maloideae. This subfamily, however, is to be called Amygdaloideae rather than Spiraeoideae under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants as updated in 2011.

Malus is a genus of about 30–55 species of small deciduous trees or shrubs in the family Rosaceae, including the domesticated orchard apple – also known as the eating apple, cooking apple, or culinary apple. The other species are commonly known as crabapples, crab apples, crabtrees, or wild apples.

Sorbus is a genus of about 100–200 species of trees and shrubs in the rose family, Rosaceae. Species of Sorbus (s.l.) are commonly known as whitebeam, rowan, service tree, and mountain-ash. The exact number of species is disputed depending on the circumscription of the genus, and also due to the number of apomictic microspecies, which some treat as distinct species, but others group in a smaller number of variable species. Recent treatments treat Sorbus in a narrower sense to include only the pinnate leaved species of subgenus Sorbus, raising several of the other subgenera to generic rank.

Aronia is a genus of deciduous shrubs, the chokeberries, in the family Rosaceae native to eastern North America and most commonly found in wet woods and swamps. The genus is usually considered to contain two or three species, one of which is naturalized in Europe. A fourth form that has long been cultivated under the name Aronia is now considered to be an intergeneric hybrid, × Sorbaronia mitschurinii.

Heteromeles arbutifolia, commonly known as toyon, is a common perennial shrub native to extreme southwest Oregon, California, Baja California, and British Columbia. It is the sole species in the genus Heteromeles.

Photinia is a genus of about 40–60 species of small trees and large shrubs, but the taxonomy has recently varied greatly, with the genera Heteromeles, Stranvaesia and Aronia sometimes included in Photinia.

Holodiscus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rosaceae, native to the Americas, from southwestern British Columbia, Canada and the western United States south to Bolivia.

Vauquelinia, commonly known as the rosewoods, is a genus of the rose family, Rosaceae. It consists of two species of shrubs found in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. The genus was named for French chemist Louis Nicolas Vauquelin (1763-1829). The nectar provided by these plants is commonly fed on by wasps such as Polistes instabilis.

Gillenia is a genus of two species of perennial herbs in the family Rosaceae. Common names for plants in this genus include: Bowman's root, Indian-physic, American ipecac. This genus is endemic to dry open woods with acidic soils in eastern North America. Both plants are subshrubs with exposed semi-woody branches and serrated leaves; the larger lower leaves are divided into palmately arranged leaflets. Plants bloom in May, June, or July; blooms are composed of five slender white petals which are loosely arranged and typically appear slightly twisted and limp as if they were wilted. The flowers mature into small capsules. These plants are often planted as ornamentals and used in herbal medicine.

Kageneckia is a genus of flowering plant in family Rosaceae.

Stranvaesia davidiana, the Chinese photinia, is a species of shrub grown as an ornamental plant. Its flowers are white and grow in close clusters, followed by small pome fruits. It originated from east Asia and has been introduced to North America as a garden plant. It is sometimes known as Photinia davidiana.
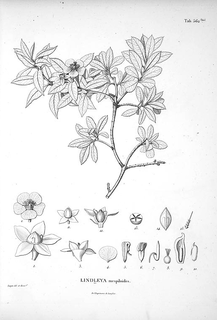
Lindleya is a genus of Mexican evergreen trees of the family Rosaceae. The sole species, L. mespiloides, grows to a height of 6 metres (20 ft) and bears solitary white fragrant flowers in summer. The fruit are dry dehiscent capsules.

Malacomeles, or false serviceberry, is a genus of flowering plants in the Rosaceae. It is most closely related to Amelanchier, Peraphyllum, Crataegus, and Mespilus.
Stranvaesia amphidoxa is a species in the family Rosaceae of flowering plants.
Stranvaesia nussia is a small Evergreen tree species of genus Stranvaesia in the family Rosaceae.

The Maleae are the apple tribe in the rose family, Rosaceae. The group includes a number of plants bearing commercially important fruits, such as apples and pears, while others are cultivated as ornamentals. Older taxonomies separated some of this group as tribe Crataegeae, as the Cydonia group, or some genera were placed in family Quillajaceae.

Malinae is the name for the apple subtribe in the rose family, Rosaceae. This name is required by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, which came into force in 2011 for any group at the subtribe rank that includes the genus Malus but not either of the genera Rosa or Amygdalus. The group includes a number of plants bearing commercially important fruits, such as apples and pears, while others are cultivated as ornamentals.

Prunus davidiana is a species in the genus Prunus in the family Rosaceae. It is also known by the common names David's peach and Chinese wild peach. It is native to China, preferring to grow in forests and thickets, on slopes in mountain valleys, and in waste fields, from 800 to 3200 m. It is resistant to frost, and to a number of pests and diseases of cultivated peach, and is the subject of many studies for the genetic improvement of peaches.

















