
An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is also an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid, the formula of the anhydride being (RC(O))2O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by replacing the word acid in the name of the parent carboxylic acid by the word anhydride. Thus, (CH3CO)2O is called acetic anhydride.Mixed (or unsymmetrical) acid anhydrides, such as acetic formic anhydride (see below), are known, whereby reaction occurs between two different carboxylic acids. Nomenclature of unsymmetrical acid anhydrides list the names of both of the reacted carboxylic acids before the word "anhydride" (for example, the dehydration reaction between benzoic acid and propanoic acid would yield "benzoic propanoic anhydride").

Indole-3-acetic acid is the most common naturally occurring plant hormone of the auxin class. It is the best known of the auxins, and has been the subject of extensive studies by plant physiologists. IAA is a derivative of indole, containing a carboxymethyl substituent. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents.

Indole is an organic compound with the formula C6H4CCNH3. Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by substituent groups. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid tryptophan and neurotransmitter serotonin.
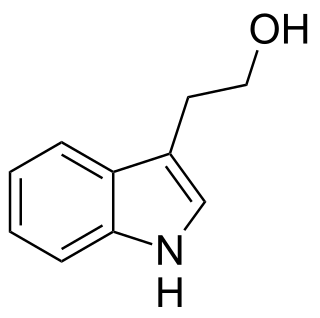
Tryptophol is an aromatic alcohol that induces sleep in humans. It is found in wine as a secondary product of ethanol fermentation. It was first described by Felix Ehrlich in 1912. It is also produced by the trypanosomal parasite in sleeping sickness.
Streptomyces ascomycinicus is a bacterium species from the genus Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Kobe City in Japan. Streptomyces ascomycinicus produces ascomycin.
Streptomyces bangladeshensis is a thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Natore in Bangladesh. Streptomyces bangladeshensis produces bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate.
Streptomyces bottropensis is a bacterium species from the genus Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces bottropensis produces bottromycin, dunaimycin and mensacarcin. Streptomyces bottropensis can metabolize (+)-carvone to (+)-bottrospicatol.
Streptomyces celluloflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Streptomyces celluloflavus produces aureothricin and has the ability to degrade cellulose.
Streptomyces cinnamoneus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Streptomyces cinnamoneus produces duramycin A, duramycin B, duramycin C, carbomycin, cinnomycin and fungichromin.
Streptomyces guanduensis is an acidophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from pine forest soil from Guandu in the Yunnan Province in China.
Streptomyces labedae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil.
Streptomyces lydicus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in the United States. Streptomyces lydicus produces actithiazic acid, natamycin, lydimycin, streptolydigin, and 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin. Streptomyces lydicus can be used as an agent against fungal plant pathogens like Fusarium, Pythium, Phytophthora, Rhizoctonia and Verticillum.
Streptomyces paucisporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from acidic soil from the Yunnan Province in China.
Streptomyces roseiscleroticus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Gujarat State in India. Streptomyces roseiscleroticus produces sultriecin.
Streptomyces ruber is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Baikal-region in Russia. Streptomyces ruber produces mycoticins. The strain EKH2 from Streptomyces ruber has activity against virulent fish pathogens.
Streptomyces rubidus is an acidophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a pine forest in Yanglin in the Yunnan province in China.
Streptomyces synnematoformans is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a sand dune in Egypt.
Streptomyces virginiae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces virginiae produces actithiazic acid, virginiamycins and cycloserine. Streptomyces virginiae also produces monensin A, monensin B, monensin C, monensin D, actithiazic acid.
Streptomyces wedmorensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Pennsylvania in the United States. Streptomyces wedmorensis produces (S)-2-hydroxypropylphosphonic acid epoxidase, fosfomycin and phosphonomycin B.
Streptomyces yanglinensis is an acidophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a pine forest in Yanglin in the Yunnan province in China.



