In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone and methylene groups: [−C(=O)−CH2−]n. First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi-domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share striking similarities with fatty acid biosynthesis.
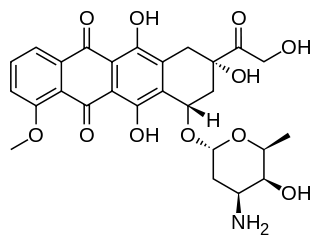
Doxorubicin (DXR) is a 14-hydroxylated version of daunorubicin, the immediate precursor of DXR in its biosynthetic pathway. Daunorubicin is more abundantly found as a natural product because it is produced by a number of different wild type strains of Streptomyces. In contrast, only one known non-wild type species, Streptomyces peucetius subspecies caesius ATCC 27952, was initially found to be capable of producing the more widely used doxorubicin. This strain was created by Arcamone et al. in 1969 by mutating a strain producing daunorubicin, but not DXR, at least in detectable quantities. Subsequently, Hutchinson's group showed that under special environmental conditions, or by the introduction of genetic modifications, other strains of streptomyces can produce doxorubicin. His group has also cloned many of the genes required for DXR production, although not all of them have been fully characterized. In 1996, Strohl's group discovered, isolated and characterized dox A, the gene encoding the enzyme that converts daunorubicin into DXR. By 1999, they produced recombinant Dox A, a Cytochrome P450 oxidase, and found that it catalyzes multiple steps in DXR biosynthesis, including steps leading to daunorubicin. This was significant because it became clear that all daunorubicin producing strains have the necessary genes to produce DXR, the much more therapeutically important of the two. Hutchinson's group went on to develop methods to improve the yield of DXR, from the fermentation process used in its commercial production, not only by introducing Dox A encoding plasmids, but also by introducing mutations to deactivate enzymes that shunt DXR precursors to less useful products, for example baumycin-like glycosides. Some triple mutants, that also over-expressed Dox A, were able to double the yield of DXR. This is of more than academic interest because at that time DXR cost about $1.37 million per kg and current production in 1999 was 225 kg per annum. More efficient production techniques have brought the price down to $1.1 million per kg for the non-liposomal formulation. Although DXR can be produced semi-synthetically from daunorubicin, the process involves electrophilic bromination and multiple steps and the yield is poor. Since daunorubicin is produced by fermentation, it would be ideal if the bacteria could complete DXR synthesis more effectively.
Streptogramin A is a group of antibiotics within the larger family of antibiotics known as streptogramins. They are synthesized by the bacteria Streptomyces virginiae. The streptogramin family of antibiotics consists of two distinct groups: group A antibiotics contain a 23-membered unsaturated ring with lactone and peptide bonds while group B antibiotics are depsipeptides. While structurally different, these two groups of antibiotics act synergistically, providing greater antibiotic activity than the combined activity of the separate components. These antibiotics have until recently been commercially manufactured as feed additives in agriculture, although today there is increased interest in their ability to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria, particularly vancomycin-resistant bacteria.
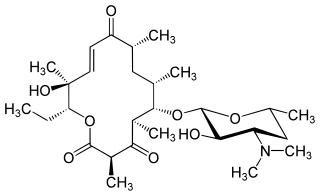
Pikromycin was studied by Brokmann and Hekel in 1951 and was the first antibiotic macrolide to be isolated. Pikromycin is synthesized through a type I polyketide synthase system in Streptomyces venezuelae, a species of Gram-positive bacterium in the genus Streptomyces. Pikromycin is derived from narbonolide, a 14-membered ring macrolide. Along with the narbonolide backbone, pikromycin includes a desosamine sugar and a hydroxyl group. Although Pikromycin is not a clinically useful antibiotic, it can be used as a raw material to synthesize antibiotic ketolide compounds such as ertythromycins and new epothilones.
Streptomyces caelestis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Utah in the United States. Streptomyces caelestis produces desalicetin, isocelesticetin B, caelesticetin, citreamicin θ A, citreamicin θ B, citreaglycon A and dehydrocitreaglycon.
Streptomyces cuspidosporus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Kyoto in Japan. Streptomyces cuspidosporus produces xylanase, sparsomycin and tubercidin.
Streptomyces actuosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces actuosus produces nosiheptide and staurosporin.
Streptomyces glaucescens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces glaucescens produces tetracenomycin C, tetracenomycin D and tetracenomycin E.
Streptomyces glomeratus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces glomeratus produces beromycin and nogalamycin.
Streptomyces halstedii is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from deeper soil layers. Streptomyces halstedii produces magnamycin B, vicenistatin deltamycin A2, deltamycin A3, bafilomycin B1 and bafilomycin C1. Streptomyces halstedii also produces complex antifungal antibiotics like oligomycins and the antibiotics anisomycin and sinefungin.
Streptomyces platensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces platensis produces oxytetracycline, platensimycin, migrastatin, isomigrastatin, platencin, dorrigocin A, dorrigocin B and terramycine.
Streptomyces roseiscleroticus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Gujarat State in India. Streptomyces roseiscleroticus produces sultriecin.
Streptomyces roseofulvus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces roseofulvus produces deoxyfrenolicin and frenolicin B.
Streptomyces violaceoruber is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces violaceoruber produces protoactinorhodin, kendomycin, phospholipase A2, granaticin and methylenomycin A.
Streptomyces virginiae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces virginiae produces actithiazic acid, virginiamycins and cycloserine. Streptomyces virginiae also produces monensin A, monensin B, monensin C, monensin D, actithiazic acid.

Borrelidin is an 18-membered polyketide macrolide derived from several Streptomyces species. First discovered in 1949 from Streptomyces rochei, Borrelidin shows antibacterial activity by acting as an inhibitor of threonyl-tRNA synthetase and features a nitrile moiety, a unique functionality in natural products., Borrelidin also exhibits potent angiogenesis inhibition, which was shown in a rat aorta matrix model. Other studies have been performed to show that low concentrations of borrelidin can suppress growth and induce apoptosis in malignant acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Borredlidin's antimalarial activity has also been shown in vitro and in vivo.
Butyrolactol A is an organic chemical compound of interest for its potential use as an antifungal antibiotic.
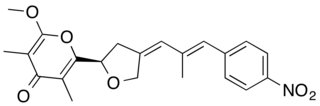
Aureothin is a natural product of a cytotoxic shikimate-polyketide antibiotic with the molecular formula C22H23NO6. Aureothin is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces thioluteus that illustrates antitumor, antifungal, and insecticidal activities and the new aureothin derivatives can be antifungal and antiproliferative. In addition, aureothin, a nitro compound from Streptomyces thioluteus, was indicated to have pesticidal activity against the bean weevil by interfering with mitochondrial respiratory complex II.

Tetracenomycin C is an antitumor anthracycline-like antibiotic produced by Streptomyces glaucescens GLA.0. The pale-yellow antibiotic is active against some gram-positive bacteria, especially against streptomycetes. Gram-negative bacteria and fungi are not inhibited. In considering the differences of biological activity and the functional groups of the molecule, tetracenomycin C is not a member of the tetracycline or anthracyclinone group of antibiotics. Tetracenomycin C is notable for its broad activity against actinomycetes. As in other anthracycline antibiotics, the framework is synthesized by a polyketide synthase and subsequently modified by other enzymes.




