
Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin.

Phenylacetic acid, also known by various synonyms, is an organic compound containing a phenyl functional group and a carboxylic acid functional group. It is a white solid with a strong honey-like odor. Endogenously, it is a catabolite of phenylalanine. As a commercial chemical, because it can be used in the illicit production of phenylacetone, it is subject to controls in countries including the United States and China.
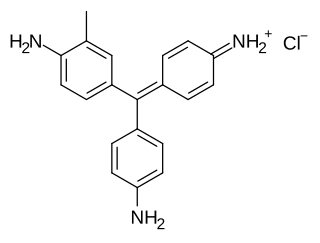
Carbol fuchsin, carbol-fuchsin, carbolfuchsin, or Castellani's paint is a mixture of phenol and basic fuchsin that is used in bacterial staining procedures. It is commonly used in the staining of mycobacteria because it has an affinity for the mycolic acids found in their cell membranes.

Dipicolinic acid is a chemical compound which plays a role in the heat resistance of bacterial endospores. It is also used to prepare dipicolinato ligated lanthanide and transition metal complexes for ion chromatography.
Streptomyces neyagawaensis is an Actinomycetota species in the antibiotic producing genus Streptomyces.
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of Actinomycetota, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants. Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.
Nocardiopsis umidischolae is a species of bacteria. It produces methanol-soluble toxins that paralyse the motility of boar spermatozoa. Its type strain is 66/93T.
Streptomyces albidoflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Poland. Streptomyces albidoflavus produces dibutyl phthalate and streptothricins.
Streptomyces chattanoogensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Tennessee in the United States. Streptomyces chattanoogensis produces natamycin, pimaricin and tennecetin.
Streptomyces flaveus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil.
Streptomyces ipomoeae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from rot from potatoes. Streptomyces ipomoeae produces thaxtomin C and ipomycin. Streptomyces ipomoeae can cause soft rot disease on sweet potatoes.
Streptomyces lydicus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in the United States. Streptomyces lydicus produces actithiazic acid, natamycin, lydimycin, streptolydigin, and 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin. Streptomyces lydicus can be used as an agent against fungal plant pathogens like Fusarium, Pythium, Phytophthora, Rhizoctonia and Verticillum.
Streptomyces malachitofuscus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces malachitofuscus has antifungal metabolites.
Streptomyces pactum is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces pactum produces pactamycin, actinopyrones, and piericidins.
Streptomyces pluricolorescens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Streptomyces pluricolorescens produces chrothiomycin, pluramycin A and pluramycin B.
Streptomyces rishiriensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Hokkaido in Japan. Streptomyces rishiriensis produces coumermycin A1, notomycin, 2-chloroadenosine, phosphophenylalanarginine and lactonamycin.
Streptomyces rochei is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces rochei produces borrelidin, butyrolactol A, butyrolactol B, uricase and streptothricin. Streptomyces rochei has antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici and Aspergillus fumigatus. Streptomyces rochei produces moenomycin and bambermycin. Streptomyces rochei produces amicetin A, amicetin B, amicetin C and streptolin. Streptomyces rochei produces endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase mithramycin, amicetin, bamicetin, and plicacetin.
Streptomyces roseiscleroticus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Gujarat State in India. Streptomyces roseiscleroticus produces sultriecin.
Streptomyces violaceusniger is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces violaceusniger has antifungal activity. Streptomyces violaceusniger produces isoafricanol and spirofungin.
Phenylacetyl-CoA (C29H42N7O17P3S) is a form of acetyl-CoA formed from the condensation of the thiol group from coenzyme A with the carboxyl group of phenylacetic acid.



