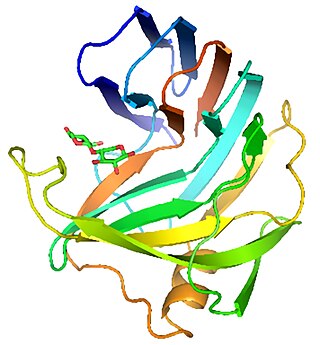
Endo-1,4-β-xylanase is any of a class of enzymes that degrade the linear polysaccharide xylan into xylose, thus breaking down hemicellulose, one of the major components of plant cell walls:
Shanxia is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from the Shanxi Province that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Huiquanpu Formation. Shanxia may possibly represent a junior synonym of Tianzhenosaurus, an ankylosaurine also known from the Huiquanpu Formation of China.

The Emperor in Han Dynasty, also released under the title The Emperor Han Wu in some countries, is a 2005 Chinese historical drama television series based on the life of Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty. It uses the historical texts Records of the Grand Historian and Book of Han as its source material.

In biochemistry, glycoside hydrolases are a class of enzymes which catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes, with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cellulase), hemicellulose, and starch (amylase), in anti-bacterial defense strategies, in pathogenesis mechanisms and in normal cellular function. Together with glycosyltransferases, glycosidases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of glycosidic bonds.
Microbubbles are bubbles smaller than one hundredth of a millimetre in diameter, but larger than one micrometre. They have widespread application in industry, medicine, life science, and food technology. The composition of the bubble shell and filling material determine important design features such as buoyancy, crush strength, thermal conductivity, and acoustic properties.

Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) are polymers of the sugar xylose. They are produced from the xylan fraction in plant fiber. Their C5 structure is fundamentally different from other prebiotics, which are based upon C6 sugars. Xylooligosaccharides have been commercially available since the 1980s, originally produced by Suntory in Japan. They have more recently become more widely available commercially, as technologies have advanced and production costs have fallen. Some enzymes from yeast can exclusively convert xylan into only xylooligosaccharides-DP-3 to 7.

Aspergillus versicolor is a slow-growing species of filamentous fungus commonly found in damp indoor environments and on food products. It has a characteristic musty odor associated with moldy homes and is a major producer of the hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin sterigmatocystin. Like other Aspergillus species, A. versicolor is an eye, nose, and throat irritant.
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are graphene nanoparticles with a size less than 100 nm. Due to their exceptional properties such as low toxicity, stable photoluminescence, chemical stability and pronounced quantum confinement effect, GQDs are considered as a novel material for biological, opto-electronics, energy and environmental applications.

Carbon quantum dots also commonly called carbon nano dots are carbon nanoparticles which are less than 10 nm in size and have some form of surface passivation.
Streptomyces chartreusis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Africa. Streptomyces chartreusis produces N-deacyltunicamycin, elsamicin A, aminoacylase and chartreusin.
Streptomyces coelicoflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces coelicoflavus produces acarviosin-containing oligosaccharides.
Streptomyces diastaticus is an alkaliphilic and thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces diastaticus produces oligomycin A, oligomycin C, rimocidin and the leukotriene-A4 hydrolase-inhibitor 8(S)-amino-2(R)-methyl-7-oxononanoic acid. Streptomyces diastaticus also produces gougerotin and diastaphenazine and the antibiotic ruticin.
Streptomyces actuosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces actuosus produces nosiheptide and staurosporin.
Streptomyces halstedii is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from deeper soil layers. Streptomyces halstedii produces magnamycin B, vicenistatin deltamycin A2, deltamycin A3, bafilomycin B1 and bafilomycin C1. Streptomyces halstedii also produces complex antifungal antibiotics like oligomycins and the antibiotics anisomycin and sinefungin.
Streptomyces hundungensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from a quarry in Tangkhul Hundung in Manipur in India Streptomyces hundungensis has antifungal activity.
Streptomyces olivaceoviridis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces olivaceoviridis produces chitinase and xylanase.
Streptomyces roseolus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces roseolus produces chitosanase and isoflavones .
Streptomyces sporoverrucosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces sporoverrucosus produces the antileukemic naphthocoumarins chrysomycin A, chrysomycin B, and chrysomycin C.
Streptomyces vietnamensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from forest soil in Vietnam.
Reduction-sensitive nanoparticles (RSNP) consist of nanocarriers that are chemically responsive to reduction. Drug delivery systems using RSNP can be loaded with different drugs that are designed to be released within a concentrated reducing environment, such as the tumor-targeted microenvironment. Reduction-Sensitive Nanoparticles provide an efficient method of targeted drug delivery for the improved controlled release of medication within localized areas of the body.






