Streptomyces aureoverticillatus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces aureoverticillatus produces Aureoverticillactam.
Streptomyces chartreusis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Africa. Streptomyces chartreusis produces N-deacyltunicamycin, elsamicin A, aminoacylase and chartreusin.
Streptomyces coeruleorubidus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from marine sediment. Streptomyces coeruleorubidus produces the following medications: pacidamycin 1, baumycin B1, baumycin B2, baumycin C1, feudomycin A, feudomycin B, feudomycin C, ficellomycin, feudomycinone A, and rubomycin.
Streptomyces diastaticus is an alkaliphilic and thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces diastaticus produces oligomycin A, oligomycin C, rimocidin and the leukotriene-A4 hydrolase-inhibitor 8(S)-amino-2(R)-methyl-7-oxononanoic acid. Streptomyces diastaticus also produces gougerotin and diastaphenazine and the antibiotic ruticin.
Streptomyces actuosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces actuosus produces nosiheptide and staurosporin.
Streptomyces griseoluteus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Tokyo in Japan. Streptomyces griseoluteus produces griseoluteic acid, griseolutein A and griseolutein B.
Streptomyces griseorubens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces griseorubens produces althiomycin. Streptomyces griseorubens produces matamycin and althiomycin.
Streptomyces griseorubiginosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces griseorubiginosus produces arylsulfatase, biphenomycin A, cinerubin A and cinerubin B.
Streptomyces hawaiiensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Hawaii in the United States. Streptomyces hawaiiensis produces bryamycin and acyldepsipeptides.
Streptomyces lusitanus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces lusitanus produces 7-chlortetracycline, naphthyridinomycin, cyanocycline B, N-desmethylnaphthyridinomycin and tetracycline.
Streptomyces luteogriseus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces luteogriseus produces peliomycin and (+)-(S)-streptonol A.
Streptomyces nitrosporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from garden soil in Japan. Streptomyces nitrosporeus produces Benzastatin E, Benzastatin F, Benzastatin G Nitrosporeusine A and Nitrosporeusine B and the antibiotics nitrosporin and virantomycin and the inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme foroxymithine. Streptomyces nitrosporeus can degrade cellulose.
Streptomyces pactum is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces pactum produces pactamycin, actinopyrones, and piericidins.
Streptomyces pulveraceus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Fukuchiyama in Japan. Streptomyces pulveraceus produces zygomycine and fostriecin.
Streptomyces ramulosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces ramulosus produces acetomycin, beta-oxotryptamine, oxyplicacetin and pepsinostreptin.
Streptomyces rishiriensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Hokkaido in Japan. Streptomyces rishiriensis produces coumermycin A1, notomycin, 2-chloroadenosine, phosphophenylalanarginine and lactonamycin.
Streptomyces roseofulvus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces roseofulvus produces deoxyfrenolicin and frenolicin B.
Streptomyces showdoensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Shōdoshima, Japan. Streptomyces showdoensis produces terferol, actinomycin and showdomycin.
Streptomyces tendae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in France. Streptomyces tendae produces carbomycin, streptofactin, geosmin, cervimycin A-D and nikkomycins. Also said to be the source of Tendamistat, an alpha amylase inhibitor.
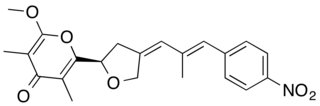
Aureothin is a natural product of a cytotoxic shikimate-polyketide antibiotic with the molecular formula C22H23NO6. Aureothin is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces thioluteus that illustrates antitumor, antifungal, and insecticidal activities and the new aureothin derivatives can be antifungal and antiproliferative. In addition, aureothin, a nitro compound from Streptomyces thioluteus, was indicated to have pesticidal activity against the bean weevil by interfering with mitochondrial respiratory complex II.
