
Azo compounds are compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl.
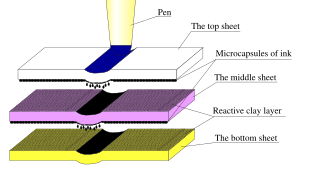
Carbonless copy paper (CCP), non-carbon copy paper, or NCR paper is a type of coated paper designed to transfer information written on the front onto sheets beneath. It was developed by chemists Lowell Schleicher and Barry Green, as an alternative to carbon paper and is sometimes misidentified as such.

Methyl yellow, or C.I. 11020, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N2C6H4N(CH3)2. It is an azo dye derived from dimethylaniline. It is a yellow solid. According to X-ray crystallography, the C14N3 core of the molecule is planar.

Sudan I, is an organic compound, typically classified as an azo dye. It is an intensely orange-red solid that is added to colourise waxes, oils, petrol, solvents, and polishes. Sudan I has also been adopted for colouring various foodstuffs, especially curry powder and chili powder, although the use of Sudan I in foods is now banned in many countries, because Sudan I, Sudan III, and Sudan IV have been classified as category 3 carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Sudan I is still used in some orange-coloured smoke formulations and as a colouring for cotton refuse used in chemistry experiments.
Acid dyes are anionic, soluble in water and are essentially applied from acidic bath. These dyes possess acidic groups, such as SO3H and COOH and are applied on wool, silk and nylon when ionic bond is established between protonated –NH2 group of fibre and acid group of dye. Overall wash fastness is poor although light fastness is quite good. As dye and fibre contain opposite electrical nature, strike rate and uptake of acid dye on these fibres is faster; electrolyte at higher concentration is added to retard dye uptake and to form levelled shades. Acid generates cation on fibre and temperature helps to substitute negative part of acid with anionic dye molecules.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the linkage C-N=N-C. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related to azo dyes are azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
An azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated arene is a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.

Sudan III is a lysochrome diazo dye. It is structurally related to azobenzene.
Solvent Black 3 is an azo dye. It is nonfluorescent, relatively thermostable lysochrome diazo dye used for staining of neutral triglycerides and lipids on frozen sections and some lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of a dark brown to black powder with maximum absorption at 596–605 nm and melting point 120–124 °C. It stains blue-black.

Sudan II (C18H16N2O) is a lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) azo dye used for staining of triglycerides in frozen sections, and some protein bound lipids and lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of red powder with melting point 156–158 °C and maximum absorption at 493(420) nm.

Allura Red AC is a red azo dye that goes by several names, including FD&C Red 40. It is used as a food dye and has the E number E129.

Sudan Red G is a yellowish red lysochrome azo dye. It has the appearance of an odorless reddish-orange powder with melting point 225 °C. It is soluble in fats and used for coloring of fats, oils, and waxes, including the waxes used in turpentine-based polishes. It is also used in polystyrene, cellulose, and synthetic lacquers. It is insoluble in water. It is stable to temperatures of about 100–110 °C. It was formerly used as a food dye. It is used in some temporary tattoos, where it can cause contact dermatitis. It is also used in hair dyes. It is a component of some newer formulas for red smoke signals and smoke-screens, together with Disperse Red 11.

Aniline Yellow is a yellow azo dye and an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder. Aniline Yellow was the first azo dye. it was first produced in 1861 by C. Mene. The second azo dye was Bismarck Brown in 1863. Aniline Yellow was commercialized in 1864 as the first commercial azo dye, a year after Aniline Black. It is manufactured from aniline.
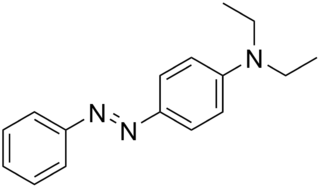
Solvent Yellow 56 is the organic compound N,N-diethyl-p-(phenylazo)aniline. It is an azo dye, which has the appearance of a reddish yellow powder. Its EINECS number is 219-616-8. Its structure is similar to Solvent Yellow 124, which used as a fuel dye in European Union, and to Aniline Yellow.
A solvent dye is a dye soluble in organic solvents. It is usually used as a solution in an organic solvent.
Sudan yellow may refer to:
3G is a generation of standards for mobile telecommunication.

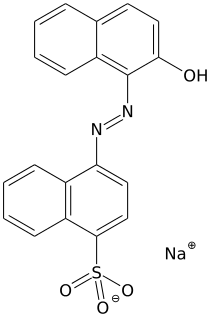
Acid red 88 is an azo dye. Due to its intense colour, solid samples appear almost black. It is used to dye cotton textiles red. A closely related acid dye is Acid Red 13.
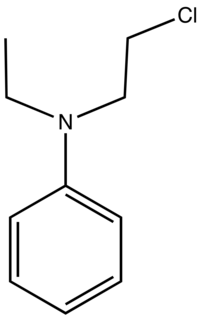
N-Ethyl-N-(2-chloroethyl)aniline is the organic compound with the formula C6H5N(Et)(CH2CH2Cl) (Et = ethyl). It is a low-melting colorless solid that is an alkylating agent. The compound is a precursor to several cationic azo dyes via reaction of the chloroethyl group with tertiary amines or pyridine followed by azo coupling. Examples of derived dyes include C. I. Basic Red 18, Maxilon Red 2GL, and Yoracryl Red 2G.
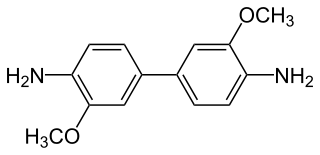
o-Dianisidine is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3O)(H2N)C6H3]2. A colorless or white solid, it is a bifunctional compound derived via the benzidine rearrangement from o-anisidine.














