
An egg case or egg capsule is the casing that surrounds the eggs of oviparous sharks, skates, and chimaeras. Egg cases typically contain one embryo, except for big skate and mottled skate egg cases, which contain up to 7 embryos. Oviparity is completely absent in the superorder Squalomorphii.

The chain catshark or chain dogfish is a small, reticulated catshark that is biofluorescent. The species is common in the Northwest Atlantic, Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean. It is harmless and rarely encountered by humans. It has very similar reproductive traits to the small-spotted catshark.

The horn shark is a species of bullhead shark, in the family Heterodontidae. It is endemic to the coastal waters off the western coast of North America, from California to the Gulf of California. Young sharks are segregated spatially from the adults, with the former preferring deeper sandy flats and the latter preferring shallower rocky reefs or algal beds. A small species typically measuring 1 m (3.3 ft) in length, the horn shark can be recognized by a short, blunt head with ridges over its eyes, two high dorsal fins with large spines, and a brown or gray coloration with many small dark spots.

Cephaloscyllium is a genus of catsharks, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, commonly known as swellsharks because of their ability to inflate their bodies with water or air as a defense against predators. These sluggish, bottom-dwelling sharks are found widely in the tropical and temperate coastal waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. They have stocky, spindle-shaped bodies and short, broad, and flattened heads. The mouth is capacious, containing many small teeth and lacking furrows at the corners. The two dorsal fins are placed far back on the body, with the first much larger than the second. Different species have various color patterns of saddles, blotches, reticulations, and/or spots. The largest members of the genus can grow over 1 m (3.3 ft) in length. Swellsharks prey on a variety of fishes and invertebrates, and are oviparous, with females producing egg capsules in pairs. They are harmless and have been deemed of having no commercial value.

The tawny nurse shark is a species of carpet shark in the family Ginglymostomatidae, and the only extant member of the genus Nebrius.
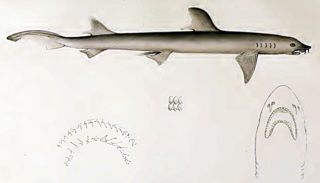
The barbeled houndshark is a species of ground shark and the only member of the family Leptochariidae. This demersal species is found in the coastal waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean from Mauritania to Angola, at depths of 10–75 m (33–246 ft). It favors muddy habitats, particularly around river mouths. The barbeled houndshark is characterized by a very slender body, nasal barbels, long furrows at the corners of the mouth, and sexually dimorphic teeth. Its maximum known length is 82 cm (32 in).

The draughtsboard shark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, so named for its "checkerboard" color pattern of dark blotches. It is endemic to New Zealand, where it is also known as the carpet shark. This shark typically reaches 1 m (3.3 ft) in length and has a thick body with a broad, flattened head and a capacious mouth. Its two dorsal fins are placed far back on the body, with the first much larger than the second.

The Australian swellshark or draughtboard shark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to southern Australia. This bottom-dwelling species can be found on the continental shelf down to a depth of 220 m (720 ft). Usually measuring 1 m (3 ft) long, it is a stout-bodied, broad-headed shark with a short tail and a first dorsal fin much larger than the second. It can be identified by its variegated dorsal coloration of brown or gray patches and numerous spots.

The blotchy swellshark, or Japanese swellshark, is a common species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. The Blotchy swellshark is found at depths of 90–200 m (300–660 ft) in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, from Japan to Taiwan. It is benthic in nature and favors rocky reefs. Reaching 1.4 m (4.6 ft) in length, this thick-bodied shark has a broad head, large mouth, and two unequally-sized dorsal fins positioned far back past the pelvic fins. It can be identified by its dorsal coloration, consisting of seven brown "saddles" and extensive darker mottling on a light tan background. This species has often been confounded with the draughtsboard shark and the Sarawak pygmy swellshark in scientific literature.

The pyjama shark or striped catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the coastal waters of South Africa. This abundant, bottom-dwelling species can be found from the intertidal zone to a depth of around 100 m (330 ft), particularly over rocky reefs and kelp beds. With a series of thick, parallel, dark stripes running along its stout body, the pyjama shark has an unmistakable appearance. It is additionally characterized by a short head and snout with a pair of slender barbels that do not reach the mouth, and two dorsal fins that are placed far back on the body. It can grow up to a length of 1.1 m (3.6 ft) long.

The sharptooth houndshark, or spotted gully shark is a species of houndshark in the family Triakidae found in shallow inshore waters from southern Angola to South Africa. Favoring sandy areas near rocky reefs and gullies, it is an active-swimming species that usually stays close to the bottom. This robust shark reaches 1.7 m (5.6 ft) in length and has characteristically large, rounded fins; the pectoral fins in particular are broad and sickle-shaped in adults. It also has a short, blunt snout and long furrows around its mouth. This species is gray or bronze in color above, with variable amounts of black spotting.

The dark shyshark or pretty Happy is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the temperate waters off southern Namibia and western South Africa. It is benthic in nature and inhabits shallow, inshore waters and favors rocky reefs and kelp forests. Growing to 60 cm (24 in) long, this small, stocky shark has a wide, flattened head with a rounded snout and a large flap of skin extending from before the nostrils to the mouth. Its dorsal coloration is extremely variable and may feature black-edged orange to blackish saddles and/or white spots on a light brown to nearly black background.

The tiger catshark is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found over sandy areas and near reef peripheries off South Africa and perhaps Mozambique, from close to shore to usually no deeper than 100 m (330 ft). Reaching a length of 50 cm (20 in), this small, slim shark has a broad, flattened head with an upturned snout tip. It can additionally be identified by its dorsal colour pattern of ten dark brown saddles on a yellowish brown background.

The cloudy catshark is a common species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. It is a bottom-dweller that inhabits rocky reefs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, from the shore to a depth of 320 m (1,050 ft). Growing up to 50 cm (20 in) long, this small, slim shark has a narrow head with a short blunt snout, no grooves between the nostrils and mouth, and furrows on the lower but not the upper jaw. It is also characterized by extremely rough skin and coloration consisting of a series of dark brown saddles along its back and tail, along with various darker and lighter spots in larger individuals.
The saddled swellshark is a rare species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to Eastern Australia. This bottom-dwelling species is found on the outer continental shelf and upper continental slope at a depth of 115–605 m (377–1,985 ft). It is a robustly built shark with a short, broad, flattened head and a capacious mouth. Adults are patterned with saddles on a brownish or grayish background, which varies between tropical and temperate sharks; juveniles are light-colored with many spots. This shark reaches 74 cm (29 in) in length. Like other swellsharks, it can inflate itself as a defensive measure. Reproduction is oviparous.
The Cook’s swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. This shark is found in the Arafura Sea at a depth of 223–300 m (732–984 ft). It is a stocky-bodied shark with a short, broad head and a large mouth, and can be identified by the eight dark, pale-edged saddles along its grayish brown body and tail. The maximum known length of this species is 30 cm (12 in). Like other swellsharks, it can inflate itself with water or air when threatened.

The Australian reticulate swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found off the coast of northwestern Australia at depths of 290–420 m (950–1,380 ft). This shark has a stocky body and a short, wide head with a capacious mouth. It is characterized by a striking dorsal color pattern of dark brown lines that trace a series of hollow saddles and narrow rings, on a light background. Like other swellsharks, this species can inflate itself when threatened. Its reproduction is oviparous.
The painted swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found in eastern Indonesia. This species reaches a maximum known length of 72 cm (28 in), and has a thick body with a short, broad and flattened head. It is dark gray with a variegated pattern of irregular darker and lighter blotches above, and lighter below with gray blotches and speckling on the snout. Like other swellsharks, it can inflate itself as a defensive measure.
The flagtail swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found at a depth of 480–700 m (1,570–2,300 ft) off northeastern Queensland, and possibly also nearby islands. This stout-bodied shark has a short, broad, and flattened head with a capacious mouth. Adults have a variegated brown coloration with 9–10 darker dorsal saddles and "V"-shaped blotch at the tip of the upper caudal fin lobe. Juveniles are yellow with narrow brown bars instead of saddles, and a distinctive marking between the spiracles shaped like two loops connected by a line. Like other swellsharks, this species can inflate its body when threatened.




































