A sawshark or saw shark is a member of a shark order bearing a unique long, saw-like rostrum edged with sharp teeth, which they use to slash and disable their prey. There are eight species within the Pristiophoriformes, including the longnose or common sawshark, shortnose sawshark, Japanese sawshark, Bahamas sawshark, sixgill sawshark, African dwarf sawshark, Lana's sawshark and the tropical sawshark.

The brown catshark is commonly found in the Pacific Ocean, ranging from the northern Pacific waters off the coast of British Columbia and south to the Baja California peninsula in Mexico. They may live as far south as Ecuador and Peru. Brown catsharks are deep-water sharks that live on the outer continental shelf and the upper slope. They have been known to live at depths ranging from 30 to 650 m and live on the bottom, usually in muddy or sandy areas. The brown catshark, when originally described, was called Catulus brunneus.

The African ribbontail catshark, Eridacnis sinuans, is a finback catshark of the family Proscylliidae, found in the western Indian Ocean, from Tanzania, South Africa, and Mozambique, at depths between 180 and 480 m. It can grow up to a length of 37 cm.

Holohalaelurus is a genus of deepwater catshark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, commonly known as Izak catsharks or hallelujah sharks.
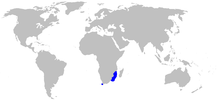
The balloon shark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the southwestern Indian Ocean off South Africa and Mozambique. Benthic in nature, it is found over sandy and muddy flats at depths of 40–600 m (130–1,970 ft). This thick-bodied species has a broad, flattened head and a short tail; its distinguishing traits include narrow, lobe-like skin flaps in front of the nostrils, and a dorsal color pattern of faint darker saddles on a light grayish background.

The pyjama shark or striped catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the coastal waters of South Africa. This abundant, bottom-dwelling species can be found from the intertidal zone to a depth of around 100 m (330 ft), particularly over rocky reefs and kelp beds. With a series of thick, parallel, dark stripes running along its stout body, the pyjama shark has an unmistakable appearance. It is additionally characterized by a short head and snout with a pair of slender barbels that do not reach the mouth, and two dorsal fins that are placed far back on the body. It can grow up to a length of 1.1 m (3.6 ft) long.

The Izak catshark or simply Izak is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This species is common off the coasts of South Africa and southern Namibia. It typically inhabits the outer continental shelf at depths of 100–300 m (330–980 ft), with the males found deeper than the females and juveniles. The Izak catshark has a short, wide, flattened head and a robust body tapering to a long, slender tail. It can be identified by its ornate color pattern of dark brown spots or reticulations and blotches on a light yellowish background, as well as by the enlarged dermal denticles over its pectoral fins and along its dorsal midline from the snout to the second dorsal fin. This species reaches 69 cm (27 in) in length, with the males larger than females.

The smooth lanternshark or slender lanternshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae, found widely in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It inhabits benthic environments at a depth of 274–1,000 m (899–3,281 ft), and pelagic environments at a depth of 0–708 m (0–2,323 ft). The smooth lanternshark forms a species group with the larger blurred lanternshark, both of which are distinguished from other members of their family by small, irregularly arranged dermal denticles with a truncated shape. This species has a slender, dark brown body with an indistinct black band on the sides over the pelvic fins, and reaches 50 cm (20 in) in length. This slow-growing, ovoviviparous shark feeds on smaller squid, fishes, and fish eggs. Smooth lanternsharks are often caught as bycatch in eastern Atlantic and Japanese commercial fisheries. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has evaluated this species as of Least Concern because of its wide distribution and limited threats.

The quagga catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. A small, slim-bodied shark reaching 37 cm (15 in) in length, it has a distinctive color pattern of narrow, dark brown vertical bars, which resemble those of the quagga. Its head is short and flattened, with a pointed snout tip that is not upturned.

The bristly catshark iis a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This shark is found from southeastern India and the Andaman Islands, between latitudes 15° N and 5° N, at depths between 200 and 300 m. Its length usually ranges from around 20–26 cm (7.9–10.2 in), and it is regarded as the smallest catshark of Bythaelurus.

The speckled catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. It is found in the Gulf of Aden and off the coast of Somalia. It occurs at depths of between 37 and 250 m. Its length is up to 48 cm.

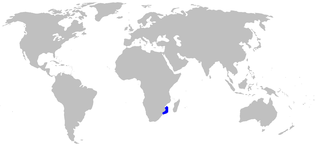
The yellowspotted catshark is a rare catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found in the southeast Atlantic, from Lüderitz, Namibia to central Natal, South Africa, between latitudes 0° and 37° S. It can grow up to a length of about 1.22 metres. The reproduction of this catshark is oviparous.

The African sawtail catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. Demersal in nature, it is found at depths of 160–720 m (520–2,360 ft) off the western African coast from Morocco to South Africa. This slender species has a rather long, pointed snout, a series of dark saddles along the back and tail, and a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the upper edge of the caudal fin. Its maximum known length is 46 cm (18 in).
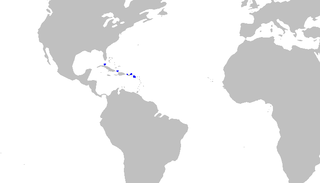
Springer's sawtail catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This shark is found in waters 457–699 m (1,499–2,293 ft) deep off the islands of the Antilles, from Cuba to the Leewards. A small, slim-bodied species reaching a length of 48 cm (19 in), the Springer's sawtail catshark can be identified by its color pattern of horizontal dark stripes in front of the first dorsal fin, and dark dorsal saddles behind. It is additionally characterized by the presence of saw-toothed crests, made of enlarged dermal denticles along both the dorsal and the ventral edges of the caudal fin. The Springer's sawtail catshark is oviparous.
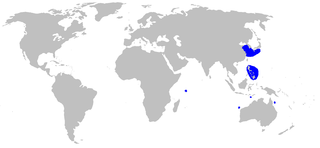
The longhead catshark or smoothbelly catshark is a species of shark, family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This shark has a patchy distribution in the Indo-Pacific from Mozambique to southern Japan to northern Australia. It is found in water between 500 and 1,140 m deep. This species grows to 59 cm (23 in) long and is characterized by its extremely long and narrow snout, short abdomen, and long anal and caudal fins. In addition, a large area of the anterior ventral portion of its body lacks dermal denticles. The longhead catshark is oviparous and the only known cartilaginous fish that is normally hermaphroditic, with the majority of individuals having both the functional reproductive organs of one sex and the undeveloped reproductive organs of the opposite sex.
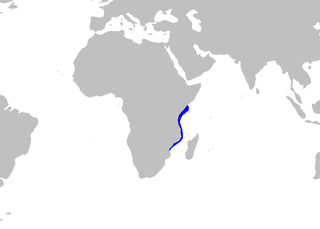
The crying Izak is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. It is found in the western Indian Ocean off Mozambique and Tanzania, at depths of between 600 and 660 m. It can grow up to 38 cm (15 in)m in length.
The grinning Izak or East African spotted Izak is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This species is found in the waters of the Western Indian Ocean, near Kenya.
The honeycomb Izak or Natal Izak is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. This species is found in the Western Indian Ocean, near South Africa. It reaches a maximum length of around 50 cm. Since the mid-1970s, no specimens have been collected, even with recent biodiversity research cruises.
The jaguar catshark, also known as the Galápagos catshark, is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks, endemic to the Galápagos Islands. The species was first described in 2012. This catshark is about 30 cm (12 in) long when mature, and it is colored blackish-brown with an asymmetrical pattern of light spots.