
Gomoku, also called Five in a Row, is an abstract strategy board game. It is traditionally played with Go pieces on a Go board. It is played using a 15×15 board while in the past a 19×19 board was standard. Because pieces are typically not moved or removed from the board, gomoku may also be played as a paper-and-pencil game. The game is known in several countries under different names.

Fanorona is a strategy board game for two players. The game is indigenous to Madagascar.

The game of go has simple rules that can be learned very quickly but, as with chess and similar board games, complex strategies may be employed by experienced players.

Checkers, also known as draughts, is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Checkers is developed from alquerque. The term "checkers" derives from the checkered board which the game is played on, whereas "draughts" derives from the verb "to draw" or "to move".

Go is an abstract strategy board game for two players in which the aim is to surround more territory than the opponent. The game was invented in China more than 2,500 years ago and is believed to be the oldest board game continuously played to the present day. A 2016 survey by the International Go Federation's 75 member nations found that there are over 46 million people worldwide who know how to play Go and over 20 million current players, the majority of whom live in East Asia.

The rules of Go have seen some variation over time and from place to place. This article discusses those sets of rules broadly similar to the ones currently in use in East Asia. Even among these, there is a degree of variation.
Grand Chess is a large-board chess variant invented by Dutch games designer Christian Freeling in 1984. It is played on a 10×10 board, with each side having two additional pawns and two new pieces: the marshal and the cardinal.

Havannah is a two-player abstract strategy board game invented by Christian Freeling. It belongs to the family of games commonly called connection games; its relatives include Hex and TwixT. Havannah has "a sophisticated and varied strategy" and is best played on a base-10 hexagonal board, 10 hex cells to a side.

Christian Freeling is a Dutch game designer and inventor of abstract strategy games, notably Dameo, Grand Chess, Havannah, and Hexdame.

There are many variations of the simple rules of Go. Some are ancient digressions, while other are modern deviations. They are often side events at tournaments, for example, the U.S. Go Congress holds a "Crazy Go" event every year.

Turkish draughts (Armenian: շաշկի)(Arabic: دامە)(Kurmanji: دامە) is a variant of draughts (checkers) played in Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Kuwait, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and several other locations around the Mediterranean Sea and Middle East.
Ming Mang is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Tibet. Ming Mang is also a general term for the word "boardgame" in Tibet. The correct name and spelling of the game may actually be Mig Mang(s), but pronounced Ming Mang or Mi Mang. The term Mig Mang is also applied to Tibetan Go with both games using exactly the same board which is a 17 x 17 square board, and black and white pieces. Mig is in reference to the chart of the board, and Mangs refers to the notion that the more charts are used on the board, the more pieces are needed to play the game, but some state that it means "many eyes". The game may also be known as Gundru. The game was popular among some Tibetan monks before the Chinese invasion of Tibet in 1950, and the uprising in 1959, and among aristocratic families.

Armenian draughts, or Tama, is a variant of draughts played in Armenia. The rules are similar to Dama. Armenian draughts, however, allows for diagonal movement.
Tiger and buffaloes is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Myanmar. It belongs to the hunt game family. The board is a 4x4 square grid, where pieces are placed on the intersection points and move along the lines. It is one of the smallest hunt games. Three tigers are going up against eleven buffaloes. The tigers attempt to capture as many of the buffaloes by the short leap as in draughts or Alquerque. The buffaloes attempt to hem in the tigers.

Emergo is an abstract strategy game created by Christian Freeling and Ed van Zon in 1986. It belongs to the "stacking" category of games, or column checkers, along with Bashni and Lasca. The name comes from the motto of the Dutch province of Zeeland: Luctor et emergo meaning: "I wrestle and emerge". The goal of the game is to capture all of the opponents pieces similar to checkers/draughts. Emergo, and all column checkers, differ from most draughts variants because of their unique method of capture. A opponent's piece is added to the capturing player's column rather than being removed. Men can be recaptured from an opponent later on in the game.
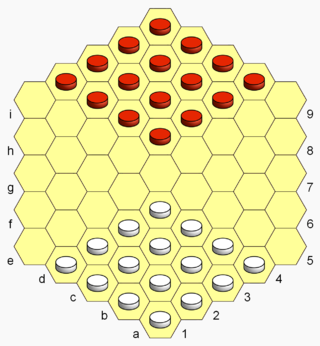
Hexdame is a strategy board game for two players invented by Christian Freeling in 1979. The game is a literal adaptation of the game international draughts to a hexagonal gameboard.

Dameo is an abstract strategy board game for two players invented by Christian Freeling in 2000. It is a variant of the game draughts and is played on an 8×8 checkered gameboard.

Congo is a chess variant invented by Demian Freeling in 1982 when he was nearly 8 years old. His father encouraged him to design a variant using a 7×7 gameboard. Demian was already familiar with chess and xiangqi, and the result blends some features from both. Congo became the second-most popular chess variant at the Fanaat games club in Enschede, the Netherlands.

Symple is a two-player abstract strategy game created in 2010 by Christian Freeling and Benedikt Rosenau. The goal of Symple is to end the game with the highest score, with score being determined via points for controlling territory on the board less a penalty for each separate group of stones. Like Go, Symple is played on a 19x19 grid of lines; unlike Go, there are no mechanics allowing capture of stones once placed. Symple is a drawless finite perfect information game.













