
Algebraic notation is the standard method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is based on a system of coordinates to uniquely identify each square on the board. It is now almost universally used by books, magazines, newspapers and software, and is the only form of notation recognized by FIDE, the international chess governing body.

Bughouse chess is a popular chess variant played on two chessboards by four players in teams of two. Normal chess rules apply, except that captured pieces on one board are passed on to the teammate on the other board, who then has the option of putting these pieces on their board.
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some unorthodox chess problems, known as fairy chess. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts.

TwixT is a two-player strategy board game, an early entrant in the 1960s 3M bookshelf game series. It became one of the most popular and enduring games in the series. It is a connection game where players alternate turns placing pegs and links on a pegboard in an attempt to link their opposite sides. While TwixT itself is simple, the game also requires strategy, so young children can play it, but it also appeals to adults. The game has been discontinued except in Germany and Japan.
Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a standard plain text format for recording chess games, which can be read by humans and is also supported by most chess software.
Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN) is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position.

Quoridor is a two- or four-player intuitive strategy game designed by Mirko Marchesi and published by Gigamic Games. Quoridor received the Mensa Mind Game award in 1997 and the Game Of The Year in the United States, France, Canada and Belgium.
Chess notation systems are used to record either the moves made or the position of the pieces in a game of chess. Chess notation is used in chess literature, and by players keeping a record of an ongoing game. The earliest systems of notation used lengthy narratives to describe each move; these gradually evolved into more compact notation systems. Algebraic notation is now the accepted international standard, with several variants. Descriptive chess notation was used in English- and Spanish-language literature until the late 20th century, but is now obsolescent. Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a text file format based on English algebraic notation which can be processed by most chess software. Other notation systems include ICCF numeric notation, used for international correspondence chess, and systems for transmission using Morse code over telegraph or radio. The standard system for recording chess positions is Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN).

Crazyhouse is a chess variant in which captured enemy pieces can be reintroduced, or dropped, into the game as one's own. It was derived as a two-player, single-board variant of bughouse chess.
A Go game record is an archival record for a game of Go.
Maharajah and the Sepoys, originally called Shatranj Diwana Shah and also known as the Mad King's Game, Maharajah chess, or Sarvatobhadra "auspicious on all sides", is a popular chess variant with different armies for White and Black. It was first played in the 19th century in India. It is a solved game with a forced win for Black.
Portable Draughts Notation (.PDN) is the standard computer-processable format for recording draughts games. This format is derived from Portable Game Notation, which is the standard chess format.
PlayOK, also known as kurnik, is a website of classic board and card games to play online against live opponents in real-time. It was created in 2001 by Marek Futrega, and was initially a Polish-only website. As of early 2005 it supported over 30 board and card games, and the site is available in 33 languages so far.
Sensei's Library is an Internet website and wiki, dedicated to articles about, and discussion of, the game of Go. It was started in September 2000, by the Go players Morten Pahle and Arno Hollosi. Hollosi is also known for designing version 4 of Anders Kierulf's popular SGF file format and for his work with the Austrian Citizen Card project.

The 3M bookshelf game series is a set of strategy and economic games published in the 1960s and early 1970s by 3M Corporation. The games were packaged in leatherette-look large hardback book size boxes in contrast to the prevalent wide, flat game boxes. The series grew to encompass over three dozen games. Most were multi-player board games or card games; a few were trivia games or two-handed board games. Acquire and TwixT were among the best-selling titles. The series later became part of the Avalon Hill Bookcase games. Very few of these games are still being published.

There is an abundance of go software available to support players of the game of Go. This includes software programs that play Go themselves, programs that can be used to view and/or edit game records and diagrams, programs that allow the user to search for patterns in the games of strong players and programs that allow users to play against each other over the Internet.
A connection game is a type of abstract strategy game in which players attempt to complete a specific type of connection with their pieces. This could involve forming a path between two or more endpoints, completing a closed loop, or connecting all of one's pieces so they are adjacent to each other. Connection games typically have simple rules, but complex strategies. They have minimal components and may be played as board games, computer games, or even paper-and-pencil games.
This glossary of board games explains commonly used terms in board games, in alphabetical order. For a list of board games, see List of board games; for terms specific to chess, see Glossary of chess; for terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems.
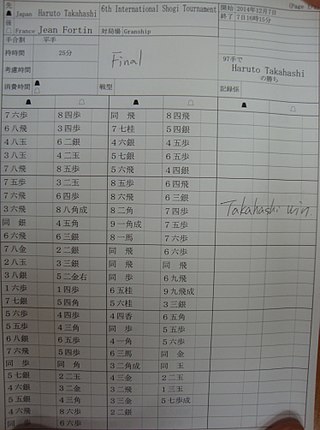
Shogi notation is the set of various abbreviatory notational systems used to describe the piece movements of a shogi game record or the positions of pieces on a shogi board.
Octi is an abstract strategy game designed by Donald Green for 2 or 4 players. The game was first published in 1999 by The Great American Trading Company.








