
Acquire is a board game published by 3M in 1964 that involves multi-player mergers and acquisitions. It was one of the most popular games in the 3M Bookshelf games series published in the 1960s, and the only one still published in the United States.

Checkers, also known as draughts, is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve forward movements of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Checkers is developed from alquerque. The term "checkers" derives from the checkered board which the game is played on, whereas "draughts" derives from the verb "to draw" or "to move".
Sid Sackson was an American board game designer and collector, best known as the creator of the business game Acquire.
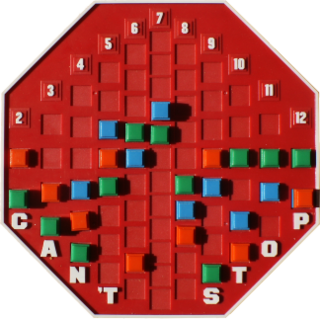
Can't Stop is a board game designed by Sid Sackson originally published by Parker Brothers in 1980; however, that edition has been long out of print in the United States. It was reprinted by Face 2 Face Games in 2007. An iOS version was developed by Playdek and released in 2012. The goal of the game is to "claim" three of the columns before any of the other players can. But the more that the player risks rolling the dice during a turn, the greater the risk of losing the advances made during that turn.

Epaminondas is a strategy board game invented by Robert Abbott in 1975. The game is named after the Theban general Epaminondas, known for the use of phalanx strategy in combat. The concept of the phalanx is integral to the game.
A Gamut of Games is an innovative book of games written by Sid Sackson and first published in 1969. It contains rules for a large number of paper and pencil, card, and board games. Many of the games in the book had never before been published. It is considered by many hobbyist gamers to be an essential text for anyone interested in abstract strategy games, and a number of the rules were later expanded into full-fledged published board games.
Three Musketeers is an abstract strategy board game by Haar Hoolim. It was published in Sid Sackson's A Gamut of Games (2011). Like the traditional game fox and geese, it uses the principle of unequal forces; the two players neither use the same types of pieces nor the same rules, and their victory conditions are different.

TwixT is a two-player strategy board game, an early entrant in the 1960s 3M bookshelf game series. It became one of the most popular and enduring games in the series. It is a connection game where players alternate turns placing pegs and links on a pegboard in an attempt to link their opposite sides. While TwixT itself is simple, the game also requires strategy, so young children can play it, but it also appeals to adults. The game has been discontinued except in Germany and Japan.
Crossings is a two-player abstract strategy board game invented by Robert Abbott. The rules were published in Sid Sackson's A Gamut of Games. Crossings was the precursor to Epaminondas, which uses a larger board and expanded rules.

Fields of Action is an abstract strategy board game for two players.

Surakarta is an Indonesian abstract strategy board game for two players, named after Surakarta, Central Java. The game features an unusual method of capture which is "possibly unique" and "not known to exist in any other recorded board game". Little is known about its history.
Cups is a contemporary American two-ranked single-lap member of the ancient game family of Mancala.

The Game of the Generals, also called GG or GOG or simply The Generals, is an educational war game invented in the Philippines by Sofronio H. Pasola Jr. in 1970. Its Filipino name is "Salpakan." It can be played within twenty to thirty minutes. It is designed for two players, each controlling an army, and a neutral arbiter to decide the results of "challenges" between opposing playing pieces that have their identities hidden from the opponent.

Blue and Gray is a strategy board game for two players invented by Henry Busch and Arthur Jaeger in 1903. They obtained a patent for the game, but may never have published it. The name Blue and Gray "refers to the uniforms of the South and the North in the Civil War and in the original game the playing pieces of the contestants were of those colors." Blue and Gray is a variant of checkers.
Brax is a two-player abstract strategy board game. It was invented in 1889 in America by Frederic B. Denham of New York City. The board design is unique. The players move their pieces along paths on the square board; each path is one of two colors. A piece can move one or two spaces in a turn depending upon whether it matches the color of the path. Players attempt to capture each other's pieces.

Lines of Action is an abstract strategy board game for two players invented by Claude Soucie. The objective is to connect all of one's pieces into a single group. The game was recommended by the Spiel des Jahres in 1988.
Bowling Solitaire is a patience or solitaire card game that uses a single deck standard playing cards to simulate a round of ten-pin bowling.
Tri-nim is a mathematical abstract strategy game developed by brothers Bruce L. Hicks and Hervey C. Hicks and published by WFF 'N PROOF Games from 1970 to 1975. Players move pieces around a triangular board, attempting to score points by being the last to enter each of the corners. It is a variation on the strategy game Nim.
The Generals, or The Generals Electronic Strategy Game, is an electronic abstract strategy game published in 1980 by Ideal Toy Company. It implements the gameplay of the 1970 game Game of the Generals, in which two players contest control of spaces on a game board by moving game pieces with ranks hidden to their opponent and challenging opposing pieces; the results of challenges are determined by the hierarchy of ranks of those pieces, in a manner similar to Stratego, and decided by an electronic arbiter.
Domain is a tile-based abstract strategy game first published throughout Europe in 1982. Players place multicoloured polymino tiles on a game board and flip any of their opponent's pieces adjacent to them in order to have the most squares covered by their colour at the end of the game.












