
Pristimantis nebulosus, also known as the Huanuco robber frog, is a species of frog in the family Strabomantidae. It is endemic to Peru and only known from its type locality in the southern Cordillera Azul, Huánuco Region.
Choerophryne valkuriarum is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the eastern New Guinea in Papua New Guinea and is known from near Wau in the Ekuti Dividing Range south to Myola in the Owen Stanley Range. The nominal species might consist of more than one distinct species.

Barygenys atra is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to eastern New Guinea and is known from the Morobe and Northern Provinces, Papua New Guinea. Common name Gunther's Papua frog has been proposed for it.
Barygenys cheesmanae is a species of frogs in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to eastern New Guinea and is only known from Mount Tafa in Central Province, Papua New Guinea. The specific name cheesmanae honors Lucy Evelyn Cheesman, an English entomologist, explorer, curator at London Zoo, and collector of the holotype. Common name Cheesman's Papua frog has been coined for this species.
Barygenys exsul is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea. It is known from Rossel and Sudest Islands in the Louisiade Archipelago, east of New Guinea. It is uncertain whether the specimens from Sudest really are conspecific with this species. Barygenys apodasta and Barygenys resima were mixed with this species prior to their description in 2013.
Barygenys nana is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and is known from the mountains of Eastern Highlands and Western Highlands Provinces, Papua New Guinea. The specific name nana refers to the small size of this species. Common name highland Papua frog has been proposed for it.
Callulops boettgeri, also known as Boettger's Callulops frog, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Halmahera in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. It is only known from the holotype collected from Galela in 1894. The genus-level placement of this little known frog has changed many times, and it is still unclear whether it should be placed in some other genus.

Callulops personatus is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the northern lowlands of central New Guinea and occurs in both Western New Guinea (Indonesia) and Papua New Guinea. The specific name personatus is Latin adjective meaning "masked", in reference to the head coloration. Common name Maprik callulops frog has been proposed for it.

Callulops stictogaster is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and occurs in the central mountain ranges of Papua New Guinea in the Western Highlands, Eastern Highlands, Chimbu, and Morobe Provinces. The specific name stictogaster is derived from the Greek stictos (="spotted") and gaster (="belly"). Common name Irumbofoie callulops frog has been proposed for it.

Cophixalus pipilans is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to northern mainland Papua New Guinea and occurs between Lae and the Adelbert Mountains. The specific name pipilans is derived from the Latin verb pipilio and means "peeping". Common name Sempi rainforest frog has been coined for this species.
Cophixalus riparius is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the New Guinea Highlands in Madang, Southern Highlands, and Western Highlands provinces southeastward to the Morobe Province. The specific name riparius refers to the creek-side habitat from which many specimens in the type series were collected. Common name Wilhelm rainforest frog has been coined for this species.

Cophixalus zweifeli is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to northern Queensland, Australia, and only known from the area of its type locality in the Cape Melville National Park. The species was named to honour American herpetologist Richard G. Zweifel. Common name Zweifel's frog has been coined for it. It is one of the five northeast Australian Cophixalus species that are specialized in boulder field habitats.
Ctenophryne minor is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Colombia and only known from its type locality in the upper Río Saija drainage, Cauca Department. Common name Colombian egg frog has been coined for it.
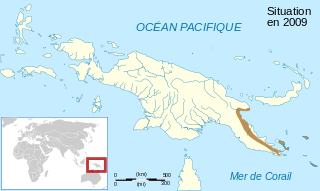
Sphenophryne thomsoni, sometimes known as Thomson's toothless frog, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the southeastern peninsular New Guinea, Louisiade Archipelago, d'Entrecasteaux Islands, and Woodlark Island. It was formerly in its own monotypic genus Genyophryne. The specific name thomsoni honours Basil Thomson, a British intelligence officer, police officer, prison governor, colonial administrator, and writer.
Oreophryne minuta is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua, Western New Guinea, and only known from its type locality in the Derewo River basin, in the mountains to the southeast of Cenderawasih Bay. It is a very small frog, and at the time of species description, the smallest Oreophryne species.
Oreophryne notata is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from two localities, Ialibu, its type locality in the Southern Highlands Province, and Tabubil in the Western Province. It might occur more widely. The specific name notata is from Latin nota meaning a "mark" or "letter" and refers to the diagnostic U-like pattern on the lores.
Aphantophryne parkeri is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the north coast of New Guinea and only known from Matapan and the Bewani Mountains in the West Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea, and from Sentani in the Papua Province, Western New Guinea (Indonesia). This species was formerly included in the genus Oreophryne, but was in 2017 moved to Aphantophryne based on molecular data. The specific name parkeri honours Hampton Wildman Parker, an English zoologist and herpetologist. Common name Parker's cross frog has been coined for it.
Xenorhina zweifeli is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and is only known from the Bewani and Hunstein Mountains in northern Papua New Guinea. The species is named for American herpetologist Richard G. Zweifel, a specialist in New Guinean herpetology and microhylid frogs; he is also said to share "characteristically terse vocalizations" with this frog.
Xenorhina parkerorum is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea Highlands and occurs in both eastern Western New Guinea (Indonesia) and western Papua New Guinea. Common name Imigabip snouted frog has been proposed for it. The specific name parkerorum honours herpetologists Fred Parker and Hampton Wildman Parker.
Synapturanus zombie is a South American species of frog in the family Microhylidae.







